When originally conceived, secure web gateways (SWGs) filtered and managed web traffic, and firewalls filtered and managed all network traffic of which web traffic was a subset. However, as the technologies matured, vendors continually added features and capabilities so that the most robust solutions now have more in common than distinct differences. A remaining distinction is that SWGs provide data loss protection and more detailed user website access reports.
To truly understand the differences, get to know each solution at a basic level and then examine key differences. This information can inform how and when firewalls and SWGs can be used separately or even together.
Table of Contents
SWG vs Firewall Overview
This table provides a quick overview of major capabilities and deployment options:
| Secure Web Gateways | Firewalls | |
|---|---|---|
| Web Traffic Inspection | Robust inspection and reporting; core feature | Effective inspection of web traffic; secondary feature |
| Network Traffic Inspection | Generally no network traffic inspection | Robust inspection and reporting; core feature |
| URL & Website Filtering | Robust filtering and reporting; core features | Effective filtering and blocking; secondary feature |
| Malware Detection | Performs antivirus signature detection and blocking, acts as a web proxy to scan encrypted web traffic | Some can perform antivirus scans based on signatures and indicators of behavior; acts as network proxy to scan encrypted traffic |
| Data Loss Protection | Monitors web traffic for potential data exfiltration | Only available in select advanced firewalls; secondary feature |
| Email Security | Examines emails for attack or data loss protection | Email security scanning isn’t usually available |
| Bandwidth Control | Manages web traffic bandwidth through the SWG | Some firewalls can manage network traffic bandwidth |
| Deployment & Architecture | Primarily cloud-based, can be a local deployment | Depends on the type of firewall, most deploy locally, others on the cloud. |
| Installation & Integration | Simple, one-tool installation, configuration and integration are more complex due to many features and granular web traffic rules | Depends on the type of firewall, some come included on devices, others enjoy simple installation; integration depends upon the number of features and connections |
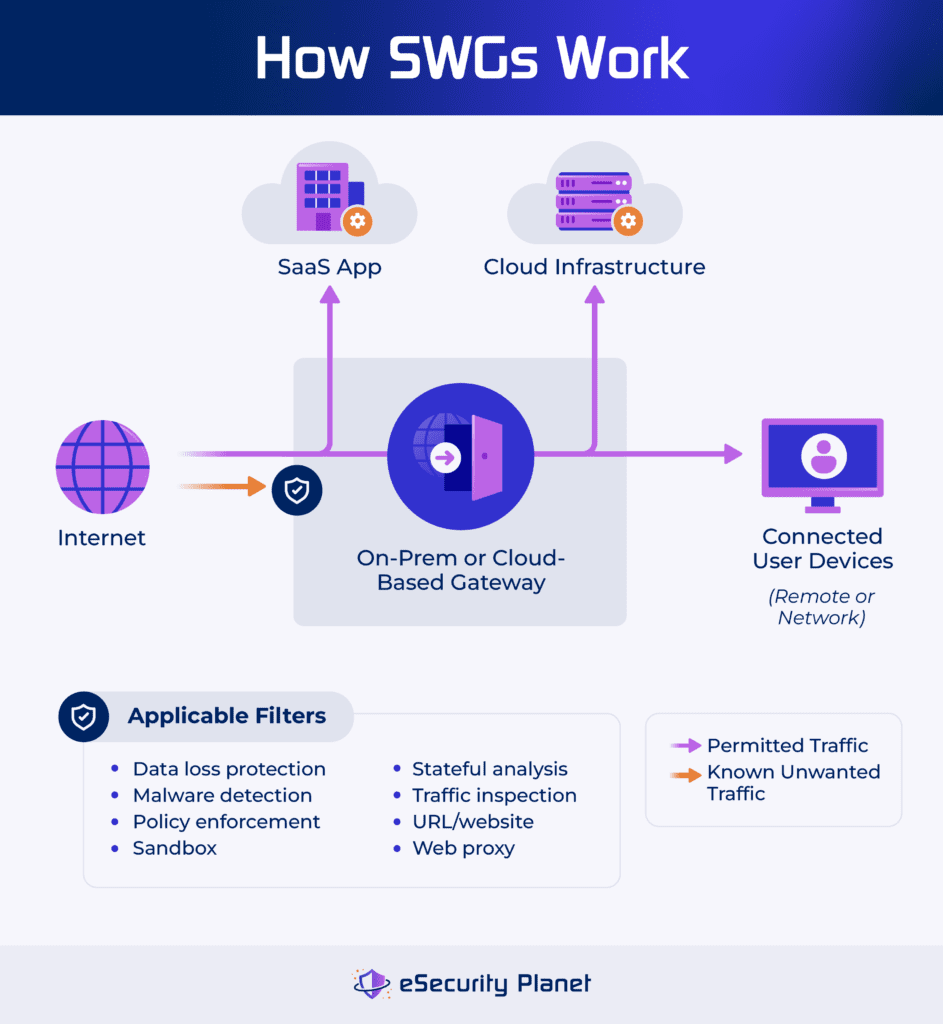
What Is a Secure Web Gateway?
A secure web gateway is a security tool that controls traffic to and from the internet to a network or to remote devices that connect to the internet through the SWG. SWGs can be deployed locally to protect specific networks, but many choose cloud-based deployments to take advantage of scale and to protect remote users and branch networks with a consolidated solution.
To enforce control over traffic, a SWG will:
- Block malicious traffic: Uses lists of known-malicious URLs and websites to block traffic to and from these IP addresses to cut off possible infection vectors.
- Deny undesired content: Applies administrator-defined blacklists (aka denylists) to block user access to undesired websites and applications (gambling, pornography, etc.).
- Manage network bandwidth: Limits the amount of bandwidth to less critical functions, such as streaming media, to ensure sufficient bandwidth for critical business functions.
- Monitor employee behavior: Enforces policies, simple rules, and even artificial intelligence (AI) anomaly detection to detect and block unwanted user behavior.
- Prevent discovery: Obscures IP addresses and assets protected by the SWG by inserting a web proxy in between the assets and the internet sources.
Advanced SWG tools often incorporate threat intelligence feeds and data loss prevention (DLP) inspection for sensitive data.
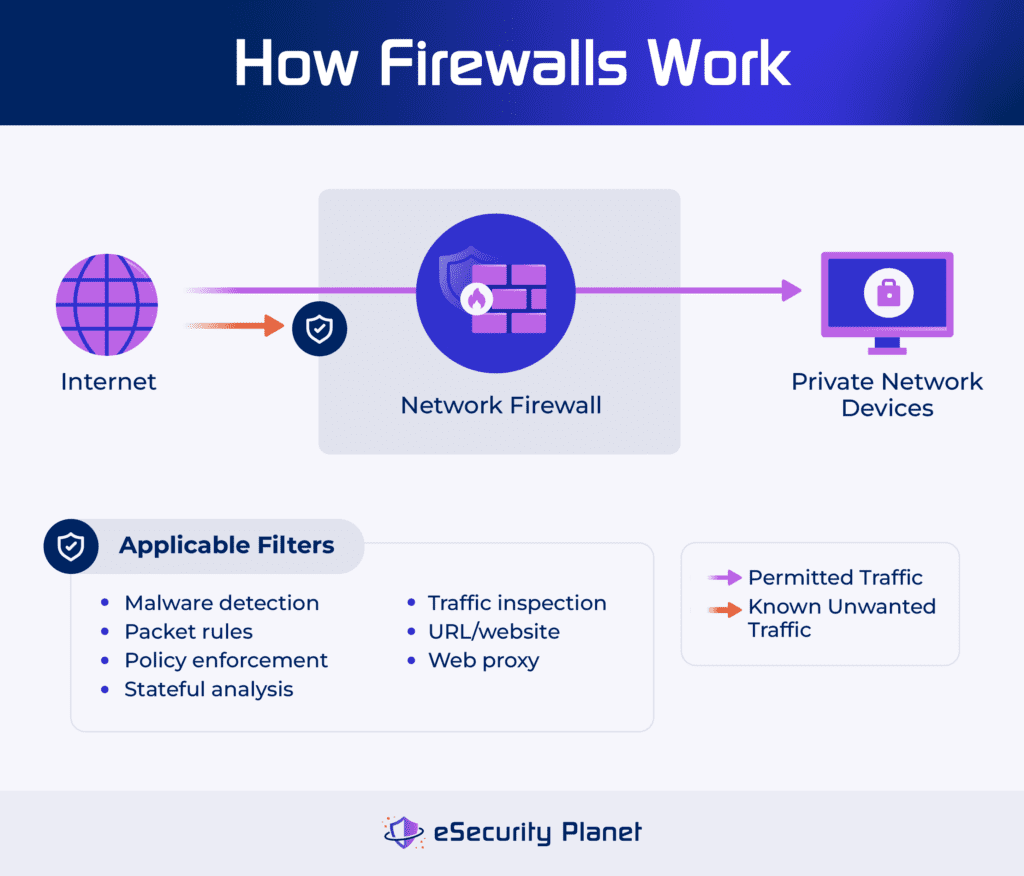
What Is a Firewall?
Firewalls are security controls that control traffic at the border of a network, a host-based or device-specific protection (server, router, PC), an application, a database, or even between two network segments. The most common type of firewall focuses on controlling traffic entering and exiting a network, but more advanced firewalls add features for email security, URL filtering, and malware detection.
When enforcing traffic control, firewalls will:
- Apply policies: Examines packets and drops them based on packet filtering rules, blocked ports, and even complex access rules such as port knocking.
- Block bad traffic: Uses stateful inspection, session filtering, and circuit-level gateway proxy capabilities to drop traffic unrelated to existing communication requests.
- Detect attacks: Inspects network traffic for signs of malware and even, for next generation firewalls (NGFW), decrypts traffic to analyze malicious behavior.
More complex firewall solutions, such as NGFW and unified threat management (UTM) will incorporate features associated with other types of security solutions. For example, they can screen data with an antivirus inspection, block malicious URLs like a SWG or domain name service (DNS), or inspect email like an email gateway.
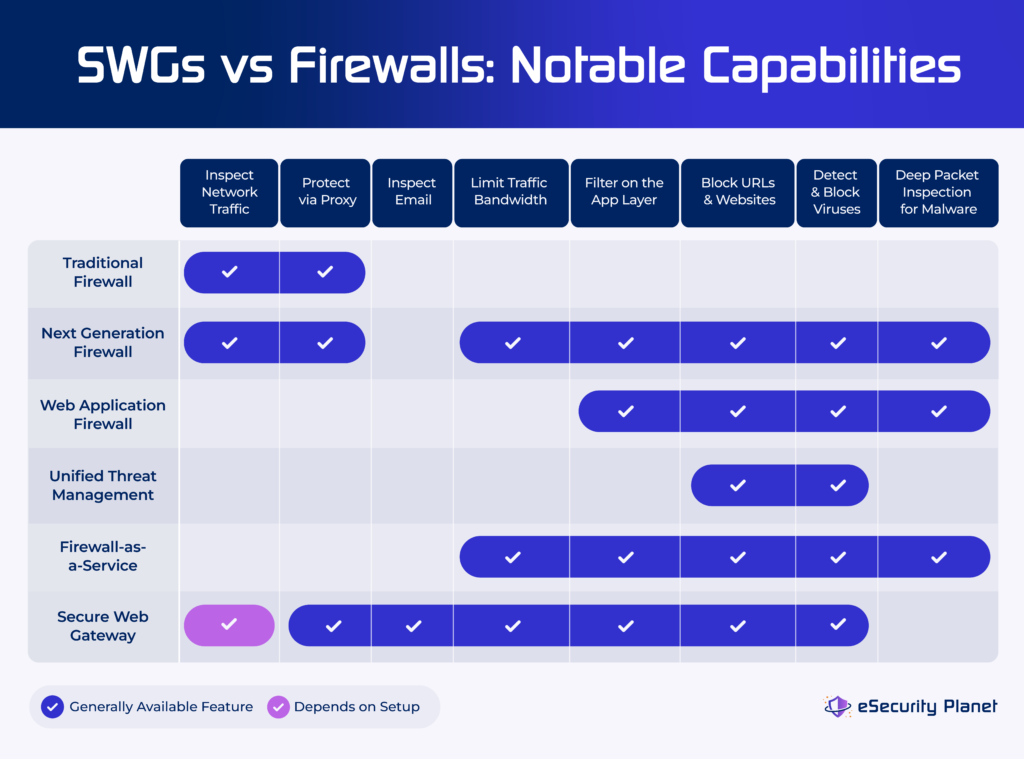
Key Similarities & Differences of SWGs vs Firewalls
Secure web gateways and firewalls, once distinct, now share features that deliver similar benefits, advantages, and disadvantages. To find the remaining distinguishing aspects, we dig deeper into the benefits, pros, and cons of these technologies.
Notable Benefits Comparison
As security solutions, firewalls and secure web gateways enjoy nearly identical benefits because they perform very similar roles to protect data flows at the edge of the network. Comparisons also become challenging because different types of firewalls offer different capabilities, with simple, traditional firewalls providing limited overlap with SWGs and NGFW providing strong overlap with SWG features.
Both SWGs and firewalls offer the following primary benefits:
- Protect against data loss: Enforce policies, detect anomalous behavior, and inspect data flows for regulated, sensitive, or secret information.
- Screen attacks: Filter known-malicious domains, enable sandbox file inspection, and detect malicious packets using signatures, indicators, AI, or machine learning (ML).
- Simplify management: Manages the consolidated features that might otherwise require separate, non-integrated tools through a single installation and management dashboard.
- Throttle unproductive content: Block, limit access, or limit bandwidth to streaming media, gambling sites, pornographic sites, and other defined sites and applications.
The primary differences are primarily device, model, and implementation specific. Some vendors will focus SWG benefits on controlling website traffic and firewall benefits on the internal network data. In part, this is because the SWG focuses on analyzing data at the application layer and most firewalls focus on the network layer information of packets.
However, they often fail to note the types of firewalls that also scan packets at the application layer such as NGFW or web application firewalls (WAF). While it can be academically useful to draw distinct lines, in reality, the best SWGs and firewalls have heavy overlap of capabilities.
Primary Pros Comparison
The strongest pro for both SWGs and firewalls is good security protection against attacks. The distinct and shared advantages to their use reveal the specific ways in which each technology provides protection. SWGs provide strong security for email and HTTPS-encrypted traffic. Firewalls block internal network threats, apply quick policy-based filtering, and some firewalls can also inspect HTTPS-encrypted traffic.
Both SWGs and Firewalls can be installed in the cloud for high scalability and performance. SWGs and certain types of firewalls can also save significant money compared to buying the component tools separately, such as mail security, proxy gateways, data loss protection, and antivirus software.
| Firewall | SWG | |
|---|---|---|
| Email protection | ❌ | ✔️ |
| Monitor for network threats (intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS)) | Some firewall models (NGFW, UTM, etc.) | ❌ |
| Rapid policy-based threat filtering | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Cloud-enabled scalability | Depends on installation | Depends on installation |
| HTTPS encrypted traffic malware inspection | Some firewall models (NGFW, WAF, FWaaS, etc.) | ✔️ |
| Save money and time compared to buying separate solutions for equivalent protection | Some firewall models (NGFW, UTM, FWaaS, etc.) | ✔️ |
Significant Cons In Common
The benefits and pros make a strong argument that every organization needs both SWG and firewalls to add defense in depth security. Both technologies share the exact same drawbacks, which can introduce some hesitation to purchase, yet they don’t significantly undermine either solution.
- Complex configuration: While more simple to manage and maintain than a suite of tools, the consolidated features of advanced SWGs and firewalls create much more complex and time-consuming tools to initially setup and configure.
- High costs: Although cost effective in comparison to many individually purchased solutions, if you don’t need all of the features, advanced SWGs and firewalls are quite expensive to purchase, install, and configure.
- Variable capabilities: The same feature won’t perform the same or provide similar capabilities for all products; most SWG and firewalls offer ‘reports’ but the type of reports and the detailed contents will vary extremely from product to product.
The primary cons can be summarized as product confusion. An inexpensive, simple firewall won’t provide the same protection as an expensive NGFW, but some of the features will be labeled similarly. Likewise, while implementing three to five separate solutions takes much more time than setting up a robust SWG, most companies set up the separate solutions over time and can become overwhelmed by options setting up a complex tool.
Should You Use SWGs & Firewalls Together or Separately?
Most large organizations use both secure web gateways and a variety of firewalls. However, many small and medium businesses (SMBs) start with a firewall for basic security and incorporate a SWG as their security needs mature.
Firewall and SWG capabilities will also be incorporated into other modern security solutions to protect remote users and remote assets. For example, Enterprise virtual public networks (VPNs) enable safer access for remote users by adding basic firewall and SWG URL or malware filtering to cloud-based VPN infrastructure.
Secure service edge (SSE) incorporates FWaaS and SWG capabilities with other security technologies to protect remote users, application data, and cloud resources. Similarly, secure access service edge (SASE) builds off of SSE remote security to add software defined wide area network (SD-WAN) networks for location independent segmentation.
All of these solutions play important roles in securing businesses, non-profits, and government agencies, but buyers need to fully understand their own needs to understand which product provides the best fit. Additionally, given the wide range of capabilities within any product category, or even the products from a specific vendor, buyers also need to fully test tools to ensure that the theoretical capabilities match needs and expectations.
Use Case Comparisons
To best illustrate when and how to use SWG and firewall technologies, it helps to consider a variety of specific use cases. When exploring the needs to secure a headquarters, remote contractors, an international office architecture, or a cloud-based application, the benefits of and need for SWG and firewall solutions will vary considerably.
Headquarters Protection
A municipal government maintains a central headquarters building (city hall) with a data center. Previously established firewall protection is sufficient but they want additional protection against rising internet threats. They might add an on-prem SWG appliance to improve the layers of security between users and potential threats.
Remote Contractor Protection
A medical transcription company employs thousands of international and domestic contractors that use bring-your-own-device (BYOD) laptops and phones to access web-based applications (Google Docs, Office 365, Box, etc.). To protect against malware uploaded to company repositories, require all contractors to access resources through a secure web gateway that monitors up and down traffic for signs of trouble.
Multi-Office Global Infrastructure
A growing restaurant chain continues to rapidly expand overseas and needs to protect a wide number of restaurant networks, branch headquarters, and even monitor remote users. Without the sunk cost of existing infrastructure, they can deploy FWaaS and SWG in tandem to protect a wide variety of network and user data connections with reduced deployment and configuration requirements.
High Performance Web App
A streaming site builds cloud-based infrastructure to host and run the back-end applications to deliver video and audio content. Without users, much of the SWG features won’t be useful for this environment, and even a powerful NGFW would cause too many delays with packet inspections. Instead, deploy simple packet-screening firewalls, WAFs, and database firewalls to protect specific components of the architecture with minimal operational delay.
SWG & Firewall Considerations
To determine which solution or combination of solutions might be the best fit, a buyer needs to answer specific questions about how the technology will fit into the existing security stack and the resources available to use it. Honest answers to these questions filter out unrealistic hopes and deliver practical, functional solutions.
Replace Existing Technology or Add-on More Technology?
An organization with extensive and older legacy solutions might be ready to rip and replace all solutions with a multi-purpose solution. However, a handful of expensive, recently purchased solutions make it more attractive to add on a separate solution to add specific features. Pick a full-featured SWG or firewall solution when performing rip-and-replace, or select a tool with the specific security features required when adding on to the security stack.
What Architecture Is Required: Full-Control, Cloud, or SaaS?
Organizations with heavy compliance or secrecy needs require full control of all security controls in a local data center, but those prioritizing scalability requirements might prefer cloud-based solutions. SaaS solutions remove direct control and often reduce customization options, but organizations of all sizes enjoy the reduced maintenance and management demands of SaaS solutions. Select the correct SWG or firewall configuration to match the required architecture.
How Much Delay Is Tolerable?
High speed applications and communications systems can’t tolerate extensive packet and connection inspections. Data, connections, and security controls need to be streamlined to balance security with high speed data transmission. Different combinations of SWGs and firewall types can be used to perform specific security screens for different data flows within the network architecture for effective and rapid information transmission.
Is There a Resource Match?
Each tool will require different financial and technical resources to install, configure, maintain, and operate the solution. When comparing solutions, factor in all expected expenses and labor requirements to ensure sufficient resources to effectively reach the tool’s potential capabilities. This analysis will prevent the wasteful acquisition of expensive shelf-ware or a tool that can’t be used effectively with the current resources.
Does the Security Solution Fit the Existing Security Stack?
All security tools must fit into an existing security stack and processes without too many traumatic overhauls. Verify integration capabilities of the SWG or firewall under consideration with other related security tools such as IDS/IDP, privilege access management (PAM), security information and event management (SIEM), and network monitoring. This will ensure smooth transitions and compatibility with existing processes.
Bottom Line: Deploy Both SWG & Firewall Capabilities
As SWGs and firewalls continue to add features, advanced versions may reach the point where only one solution might provide effective security. Of course, that single solution will be quite expensive and complicated to implement, so expect more simple solutions to continue to satisfy needs for years to come. Once you figure out which solution(s) might be a good fit, contact the company for a demo and come armed with a list of features to explore in depth.
SWGs and firewalls help to secure the network perimeter, to consider other solutions might be required for a full security stack, read more about network security architecture.