Vulnerability management tools discover security flaws in network and cloud environments and prioritize and apply fixes. They go beyond vulnerability scanning tools, creating an overall vulnerability map for businesses with features like risk scores, asset discovery, and reports. I scored industry-leading vulnerability management tools and selected six of the best, analyzing their features, pros, and cons to help you find the right product for your team.
Here are the top six vulnerability management systems:
- Tenable Nessus and Tenable Vulnerability Management: Best overall
- Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management: Best for Microsoft environments
- Rapid7 InsightVM: Best solution for enterprise needs
- Qualys VMDR: Best for organizations with complex infrastructures
- Holm Security: Best tool for improving employee security posture
- Digital Defense Fortra VM: Best for SMB vulnerability testing
Table of Contents
Top Vulnerability Management Software Compared
The following table briefly compares our top picks, including features like asset categorization and risk scores as well as pricing details.
| Asset Grouping | Risk Scoring | IoT Asset Identification | Pricing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenable Nessus & Tenable Vulnerability Management | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | • Nessus Professional plan: $3,990/year • Nessus Expert plan: $5,990/year • Tenable VM: $3,500 for 100 assets • Tenable VM: $7,000 for 200 assets |
| Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management | ✔️ | ❌ | ❌ | • Standalone product: $3/user/month • Defender for Endpoint add-on: $2/user/month |
| Rapid7 InsightVM | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | • $1.93/asset/month for 500 assets |
| Qualys VMDR | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | • Priced per asset; requires quote request |
| Holm Security | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | • Requires quote request |
| Digital Defense Frontline VM | ✔️ | ✔️ | ❌ | • Requires quote request |
While all these products are strong vulnerability management solutions, I found Tenable to be the best based on its features, pricing, and overall capabilities. Read more about our picks for the top vulnerability management products, or jump down to see how I evaluated them across six different categories.
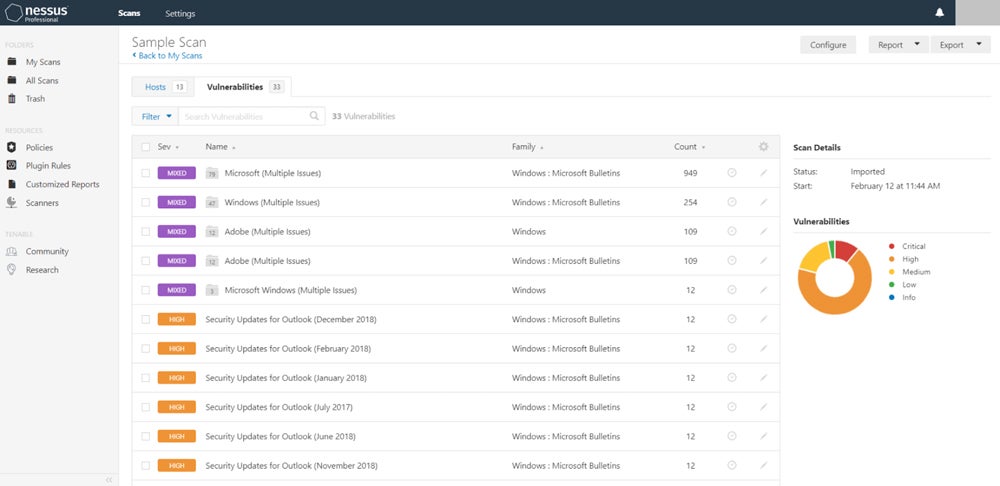
Tenable Nessus & Tenable Vulnerability Management – Best Overall Vulnerability Management Solution
Overall Rating: 4.2/5
- Pricing: 3.5/5
- Core features: 4.7/5
- Additional features: 3.5/5
- Ease of use and admin: 4/5
- Customer support: 4.2/5
- Integrations and customization: 5/5
Tenable Vulnerability Management is a vulnerability assessment solution for both businesses and security contractors. It’s built on Nessus, Tenable’s scanning solution, and offers features like role-based access controls, as well as asset grouping to simplify threat remediation for similar issues. SMBs, developers, pen testers, and consultants will find Nessus Expert useful, and features like external attack surface scanning have broad appeal.
Pros
Cons
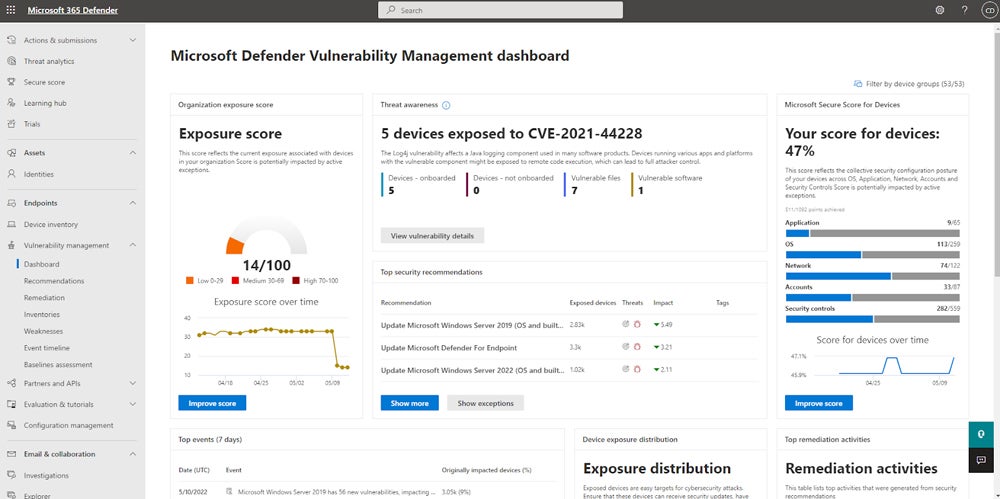
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management – Best Tool for Extensive Microsoft Ecosystems
Overall Rating: 4.1/5
- Pricing: 5/5
- Core features: 3.6/5
- Additional features: 4/5
- Ease of use and admin: 4.2/5
- Customer support: 4.3/5
- Integrations and customization: 4.3/5
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management is a VM product that makes sense for existing Microsoft customers, but it can stand on its own, too. Microsoft’s security business is impressive, if its recent MITRE scores are any indication, and it offers features like app blocking. Defender VM also integrates with plenty of other Microsoft products, including Microsoft Sentinel. Consider Defender if you want to build out your Windows security infrastructure.
Pros
Cons
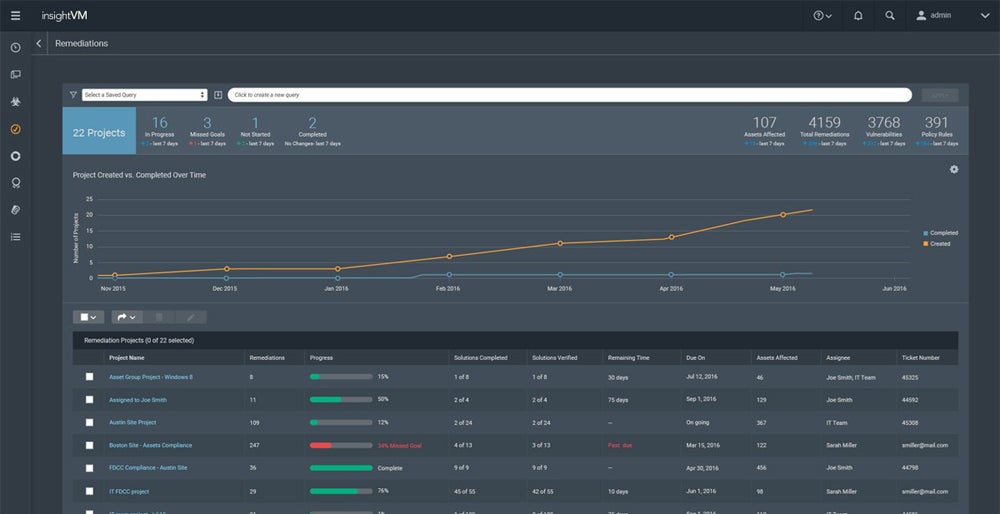
Rapid7 InsightVM – Best Solution for Enterprise Needs
Overall Rating: 4.1/5
- Pricing: 5/5
- Core features: 4.4/5
- Additional features: 3.3/5
- Ease of use and admin: 3.9/5
- Customer support: 3.4/5
- Integrations and customization: 3.9/5
Rapid7 InsightVM is a scalable vulnerability management solution for enterprises of all sizes. One of its most sought-after features is risk prioritization, with step-by-step instructions for effective remediation. Good value and automation make InsightVM particularly useful for SMBs, but organizations with greater expertise can benefit from its risk prioritization capabilities. For those lacking sophisticated security teams, InsightVM is also available as a managed service.

Pros
Cons
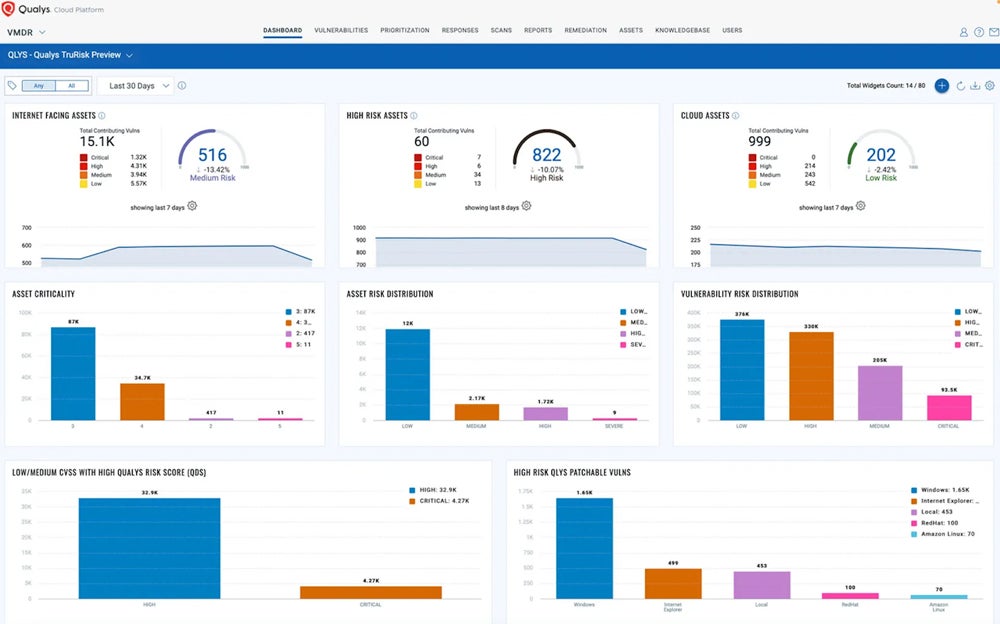
Qualys VMDR – Best for Organizations with Complex Infrastructures
Overall Rating: 3.9/5
- Pricing: 3/5
- Core features: 4.7/5
- Additional features: 3.5/5
- Ease of use and admin: 3.9/5
- Customer support: 3.2/5
- Integrations and customization: 4.3/5
Qualys VMDR is an enterprise-grade cyber risk management solution for complex security environments. VMDR uses Center for Internet Security (CIS) benchmarks to find misconfigurations and vulnerabilities in your business’s assets. Consider Qualys if you’re a medium-to-large organization with a security infrastructure that’s already built out. It’s a good solution for complex environments because it can scan IoT devices and operational tech.

Pros
Cons
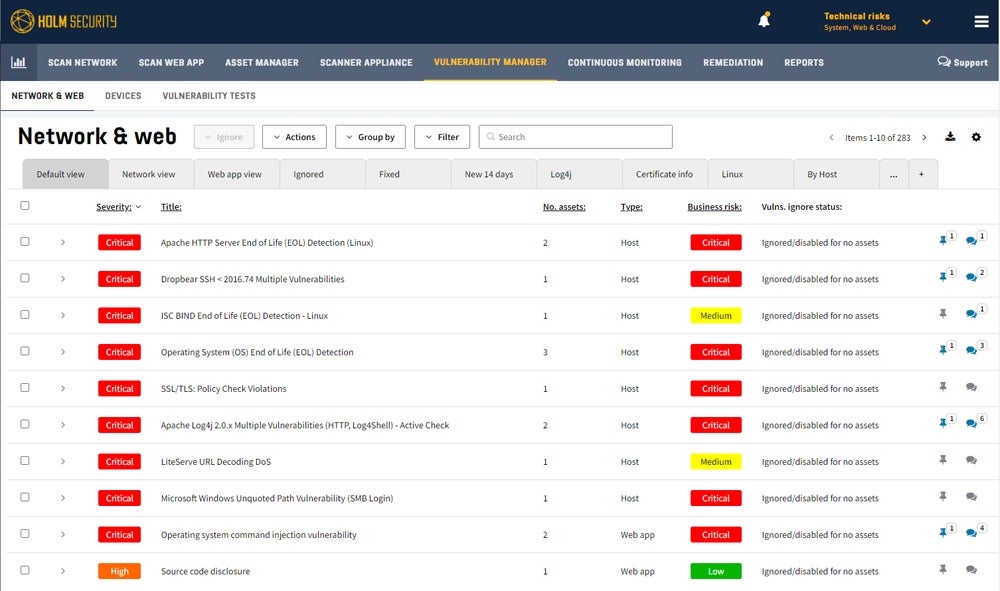
Holm Security – Best Tool for Improving Employee Security Posture
Overall Rating: 3.5/5
- Pricing: 1.5/5
- Core features: 4.5/5
- Additional features: 4.5/5
- Ease of use and administration: 2.5/5
- Customer support: 3.2/5
- Integrations and customization: 4.3/5
Holm Security VMP is a next-gen vulnerability management platform that helps detect weaknesses across your network and human assets on a single platform. Among the platform’s standout features is its phishing module, which simulates phishing attacks on employees to identify weaknesses and train teams in security. Holm Security is preferred by SMBs thanks to its value and features like phishing awareness, but its capabilities also apply to large teams.

Pros
Cons
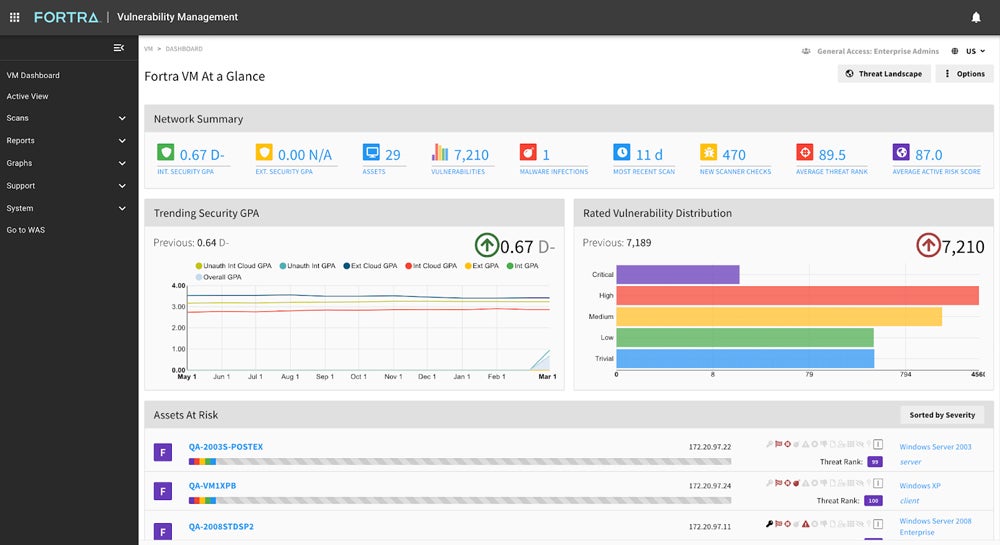
Digital Defense Fortra VM – Best for SMB Vulnerability Testing
Overall Rating: 3.4/5
- Pricing: 2/5
- Core features: 3.5/5
- Additional features: 3.5/5
- Ease of use and admin: 3.8/5
- Customer support: 4.3/5
- Integrations and customization: 3.5/5
Digital Defense Frontline Vulnerability Manager (Frontline VM) is a comprehensive SaaS VM tool that covers all network assets. Frontline VM is among the most user-friendly tools on this list. It’s well suited to the vulnerability and penetration testing demands of SMBs. That said, Digital Defense’s on-demand service can also meet the needs of a large-scale organization — just keep in mind that you’ll need to source your patch management functionality elsewhere.

Pros
Cons
5 Key Features of Vulnerability Management Software
Shortlist the top features your business needs, including monitoring, risk scores, attack surface visualization, automation, and reports, when you’re selecting any cybersecurity solution.
Continuous Monitoring & Scanning
Vulnerability management systems should be a consistently-active line of defense, scanning for new and old threats and monitoring your business networks and applications. Your vulnerability management software should continuously look for potential problems when you aren’t able to. Zero-day vulnerability management, in particular, needs to rapidly identify issues so your business can mitigate threats before they cost you money.
Risk Scoring
Cataloging and remediating risks can easily become overwhelming if your security team doesn’t know exactly what steps to take. Scoring risks based on their severity helps personnel prioritize remediation tasks. For example, an unpatched zero day is probably a more urgent fix than an employee’s outdated version of Microsoft Word. Risk scoring plays a critical role in ensuring that vulnerability management is successful over time because it helps employees avoid overwhelm.
Attack Surface Visualization
Attack surface visualization is intended to simplify the process of identifying all the places your business could be attacked. It should cover internet-facing and internal assets to give your team a complete picture of its vulnerabilities and the areas that the team needs to protect. A strong attack surface visualization solution needs to be comprehensive so you aren’t missing key pieces of the security puzzle.
Automated Remediation
Security teams don’t always have time to fix every vulnerability. This is where automation comes in: Remediation strategies should ideally have automatic fixes for at least some vulnerability management tasks. For example, a predesigned patch management workflow might be triggered when a vulnerability scanner detects an unpatched asset. Then your security team knows exactly what to patch.
Customizable Reporting
Often, other teams in your organization need to know what’s going on in the IT department. Reports help security teams provide the most relevant information to company stakeholders, including the executive team.
Policy-driven compliance reports are also important, not just current vulnerability stats. Ideally, the reporting feature in a vulnerability management tool should offer both premade templates and customization options so your security team can tailor reports to your business’s needs.
How I Evaluated the Best Vulnerability Management Software
We evaluated a broad selection of vulnerability management products using a product scoring rubric. I looked at available information, including vendor product pages, data sheets, and independent user reviews, to determine which products are best for our audience. I divided the rubric into six major categories. Each of the categories had subcriteria with its own weighting, which factored into the total score. Each product received an overall score out of five.
Evaluation Criteria
To create the scoring rubric, I first considered the most important vulnerability management features that businesses need. Then I looked at ease of use and administrative features, like documentation and managed services. I then evaluated nice-to-have features, like asset groups, and pricing, including per-asset pricing and free trials. Lastly, I scored the solutions based on their customer support offerings, relevant integrations, and customization features.
- Core features (30%): I looked at the most important features of vulnerability management tools, including asset discovery, risk scoring, patching, and reporting capabilities.
- Criterion winner: Multiple winners
- Ease of use and administration (20%): I considered availability of knowledge bases, documentation, training videos, and whether the product is available as a managed service.
- Criterion winner: Microsoft
- Pricing (15%): This category evaluated the vendor’s pricing availability, its relative value, and any free product trials.
- Criterion winner: Multiple winners
- Additional features (15%): I scored less common features like RBAC and risk exceptions.
- Criterion winner: Holm Security
- Customer support (10%): I evaluated chat, email, and phone technical support as well as hours of availability.
- Criterion winner: Multiple winners
- Integrations and customization (10%): This category included capabilities like integrations with continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) tools and custom reports.
- Criterion winner: Tenable
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is the Difference Between Vulnerability Scanning & Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is broader than vulnerability scanning. It’s not just scanning assets and networks but also helping security teams remediate vulnerabilities and improve their overall security posture. Vulnerability management should help your business create a map of sorts to locate common weaknesses in your security infrastructure and make lasting improvements.
What Is the Difference Between Risk Management & Vulnerability Management?
Risk management is a broader enterprise category because it covers all aspects of business risk, including security vulnerabilities but also financial risks and events like natural disasters. A risk management plan should include planning for cybersecurity risks, which may include a vulnerability management strategy.
What Is an Example of a Vulnerability Management KPI?
Vulnerability management key performance indicators (KPI) should be easily measurable metrics that your team aims to hit, such as a specific length of time between a vulnerability being observed and being remediated. The more detailed your KPIs are, the more easily your security team can decide whether your vulnerability management strategy is working and whether it needs to be changed.
Read about creating a vulnerability management policy, including policy best practices, required sections for a policy, and a free policy template.
Bottom Line: Vulnerability Management Is Critical for Security
There are roughly 20,000 new vulnerabilities discovered each year — and many of them are zero-day vulnerabilities that aren’t discovered until they’ve been used in a cyberattack. Plugging those holes takes a lot of time and dedication, even for the most secure companies and networks. For everyone else, they need all the help they can get from vulnerability management tools and services.
To find the right vulnerability management tool for your organization, take advantage of any demos or free trials that vendors offer and choose a product that suits your security and IT teams’ expertise. The right VM tool’s ability to prioritize fixes should help your team focus on the vulnerabilities that are most likely to impact your organization.
If your business is considering a managed VM service, read Vulnerability Management as a Service: Ultimate Guide next. This guide covers the top managed VM providers and major steps of the VMaaS process.