Cloud security fundamentals are the core requirements that ensure data protection, regulatory compliance, and access management in a cloud environment. These standards assist businesses in establishing trust with their consumers, avoiding financial losses due to breaches, and ensuring business continuity. Understanding cloud security challenges and knowing the cloud security tools available in the market significantly contribute to enhanced cloud security.
Table of Contents
Featured Partners: Cloud Backup & Storage Software
How Secure Is the Cloud?
Generally, when you adhere to the cloud security best practices, such as strong authentication, data encryption, and continuous monitoring, the cloud can be extremely safe. However, vulnerabilities can occur from misconfigurations, insider threats, or sophisticated cyberattacks. This is why you need continuous vigilance and risk management.
Cloud security is determined by various factors, including the kind of cloud deployment (public, private, or hybrid). It’s also set by the security measures provided by the cloud service provider, and user adherence to best practices. While cloud providers often deploy strong security features such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits, the shared responsibility model requires users to also implement appropriate standards to ensure the security of the cloud.
Read our guide to learn the strategies for enhancing the security across the different cloud environment types.
10 Fundamentals of Cloud Security
The NIST cybersecurity framework‘s core functions — identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover — combined with the key components of the NIST cloud security model, such as security controls, risk assessments, incident response plans, and more, form a comprehensive cloud security approach. Aligned with the NIST standards, we’ve listed 10 fundamentals of cloud security below to provide you with a solid foundation for protecting cloud systems.

Identify the Assets to Protect
The first step in the NIST cybersecurity framework’s core function is to “identify.” To accomplish this, recognize and prioritize crucial components such as data, apps, and resources that must be protected in the cloud. Understanding the important components enables firms to effectively spend resources to adopt suitable security measures and eliminate potential risks. You can determine the assets to protect through the following steps:
- Create an asset inventory: Make a detailed list of the data, apps, and resources stored in the cloud.
- Classify data: Categorize data according to its sensitivity, importance, and regulatory needs. Determine the importance of each item and the probable impact if compromised.
- Assess risks: Consider potential threats to each asset, such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Seek stakeholder input: Consult with relevant parties to identify important assets for business operations.
- Document the findings: Keep track of the discovered assets, their classification, and the rationale for priority.
Implement Security Controls
Following NIST’s cloud security model, develop policies, methods, and technology for protecting cloud assets, such as access control, encryption, and network security. Evaluate cloud providers’ security features. Take into account physical data center security, network attack protection, data encryption, and strong access restrictions to prevent unwanted access to data and applications. Consider applying these methods for checking your security controls:
- Ensure physical security: Verify the data center’s security measures, such as surveillance, access controls, and the presence of security officers, to prevent unwanted access.
- Apply strong network security: Use firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures to prevent malware, DDoS attacks, and unauthorized network access.
- Encrypt data: Ensure that data is encrypted at rest and in transit. Convert data into unreadable ciphertext that can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key.
- Manage access controls: Implement strong user authentication measures. Employ thorough permissions management so only authorized users can access important system data and apps.
- Check compliance: Regularly assess and enforce compliance with security processes, including physical and network security, data encryption, and access controls.
Conduct Risk Assessments
Find, assess, and evaluate potential risks and vulnerabilities that could jeopardize the security and integrity of data and applications in the cloud environment. NIST recommends comprehensive risk assessments that enable businesses to gain insights into their entire risk exposure, prioritize mitigation activities, and implement suitable security measures to limit the chance and impact of possible security incidents. Follow these measures:
- Define goals and scope: Outline the risk assessment’s goals and bounds, including the assets, processes, and cloud environments that will be examined.
- Identify threats and vulnerabilities: Conduct a study to identify cloud-specific threats and vulnerabilities. Take into account aspects like exposure, misconfiguration, and insider threats.
- Assess impact and plausibility: Determine the possible impact and likelihood of identified risks to the organization’s operations, data integrity, and regulatory compliance.
- Prioritize risks: Sort detected risks by severity, chance of occurrence, and potential impact, focusing on high-risk areas first to reduce the most serious threats.
- Implement mitigation measures: Establish methods such as security patches, access controls, and data encryption. Regularly monitor risks to ensure effective mitigation strategies.
Manage User Access Rights
Managing user access rights means regulating and restricting user identities and permissions so that only authorized users can access sensitive cloud resources. To improve security and prevent unwanted access, best practices include limiting access to authorized users, enforcing strong password restrictions, and utilizing multi-factor authentication (MFA). Employ these strategies that anchor on NIST’s access control guidelines:
- Implement access controls: Create systems for managing user access, such as authentication techniques and permissions management, to guarantee that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive cloud resources.
- Regularly monitor activities: Continuously monitor user actions and system activity inside the cloud environment to detect suspicious behaviors or unauthorized access attempts in real time, enabling rapid reaction to and mitigation of security issues.
- Enforce data encryption: Use encryption techniques to secure data at rest and in transit in the cloud to make sure you’re preventing unauthorized system access and preserving data confidentiality and integrity.
- Update security policies: Review and update security policies and procedures regularly to keep up with new threats and regulatory requirements. Ensure that security measures stay effective and compliant.
- Train staff on securing access: Provide thorough security awareness training to staff. Educate them on best practices for safeguarding data and systems in the cloud and schedule regular training programs.
To help you manage the burden of access management, discover the best IAM tools in our comprehensive buyer’s guide.
Develop Incident Response Plans
Create plans for swiftly responding to and managing security breaches or cyberattacks, minimizing damage and assuring quick recovery. Incident response plans describe how to discover occurrences, assess their severity, contain threats, and resume regular operations. Here’s how you can create an effective incident response strategy:
- Identify an incident response team: Form a dedicated team responsible for organizing and carrying out incident response actions. Include persons with necessary technical skills and decision-making authority.
- Create response processes: Document the steps to be done in response to different types of security incidents, such as your strategies for detection, containment, eradication, and recovery plans in case of an attack.
- Conduct regular exercises: Use simulated drills and tabletop drills to assess the effectiveness of incident response plans. Highlight areas for improvement and familiarize team members with their roles and duties.
- Establish communication channels: Create communication channels and protocols for reporting issues. Share information among team members, coordinate response activities, and inform stakeholders.
- Review and update plans: Incorporate lessons learned from previous incidents, address emerging risks and vulnerabilities. Collaborate with your team to update any organizational structure changes. Keep up with new tools that you may use in the future.
Read our guide to learn more about the function, components, and tips on how to create an incident response plan.
Protect Your Data
To avoid unauthorized access and data loss, NIST encourages data protection measures, including encryption, backups, and secure storage methods. This key idea in cloud security ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data stored in the cloud to reduce the risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, and data loss incidents. Try these approaches for data protection:
- Secure cloud storage practices: Use secure storage solutions that include access restrictions, auditing capabilities, and data integrity checks.
- Utilize encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit with strong encryption techniques to make it unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Implement regular backups: Set up automated backup systems to produce or recover copies of cloud-stored data on a regular basis in the case of data loss or corruption.
- Enforce access controls: Employ strong access controls and authentication to limit access to sensitive data. Allow only authorized people to gain access or edit it.
- Monitor data access: Deploy logging and monitoring tools to track user activity and data access in real time and enable prompt identification of suspicious activities.
Secure Credentials
Secure credentials is the technique of preventing sensitive access keys, passwords, and other authentication information from being publicly exposed on websites, repositories, or Kubernetes dashboards. To maintain the integrity and security of user authentication data in cloud environments, create strong password policies, employ secure storage mechanisms, rotate credentials on a regular basis, and enforce access constraints.
- Implement strong password policies: Avoid password guessing or brute-force attacks by enforcing complex password criteria such as minimum length and character variety.
- Secure your storage methods: Encrypt and hash passwords and other authentication data to ensure their security.
- Perform credential rotations: Update passwords and access keys on a regular basis to ensure that compromised credentials don’t pose a long-term security risk.
- Enforce access controls: Design and enforce granular access permissions that limit user rights based on roles and responsibilities using IAM tools.
- Require MFA: Implement additional verification methods in addition to passwords to provide an extra layer of protection and reduce the chance of credential theft or misuse.
If you’re looking for a tool with features that can best help you verify the access for each device and user, read our review of the top network access control (NAC) solutions.
Monitor Cloud Systems Continuously
Continuous monitoring involves regularly surveilling cloud systems to detect suspicious activity or anomalies, enabling fast reactions to any security threats. Organizations that maintain attentive monitoring can quickly detect and address security incidents, minimizing their impact. Here are several ways to perform and easily maintain monitoring:
- Apply automated monitoring tools: Set up automated monitoring solutions to continuously examine cloud systems for deviations from typical behavior.
- Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS): Set up IDS tools to monitor network traffic. Detect potential security breaches or unauthorized access in real time.
- Enable log management and analysis: Gather and analyze log data from cloud services, apps, and infrastructure components to detect security incidents, abnormalities, and potential threats.
- Use security information and event management (SIEM) systems: Gather, correlate, and analyze security event data from multiple sources through SIEM.
- Establish alerts and notifications: Set up automated alerts and notifications to notify security teams of any anomalies or suspicious activity.
Follow Industry Compliance Standards
Adhering to industry compliance standards ensures that your firm is in line with regulatory regulations specific to its sector and data sensitivity. Healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA, while banking institutions must adhere to PCI DSS. Be aware of these standards to guarantee that your cloud provider satisfies your collaborative deployment needs, testing procedures, and frequent compliance assessments.
- Identify applicable standards: Determine whether compliance requirements are applicable to your industry and geographical area, such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI DSS.
- Assess compliance status: Evaluate your organization’s present compliance posture, noting any gaps or flaws that must be corrected.
- Implement necessary controls: Meet the requirements indicated in applicable compliance standards by using appropriate security controls and procedures.
- Monitor and audit on a regular basis: Verify continuous compliance with applicable regulations. Keep track of any changes in requirements to adjust your methods.
- Document compliance activities: Keep detailed records of compliance activities, including policies, procedures, audit reports, and evidence of applied security controls.
Adopt a Shift-Left Approach
The shift-left approach to cloud security entails incorporating security practices and considerations earlier in the software development lifecycle, rather than addressing security concerns later on or after deployment. This method incorporates security at every stage of the development process. Through this, companies can discover and mitigate security issues earlier, minimize vulnerabilities, and improve the overall cloud security posture.
- Implement cloud security training: Provide comprehensive cloud security training to developers and stakeholders. Focus on awareness of cloud-specific hazards and best practices to foster a security-conscious culture from project creation.
- Define cloud security needs: Include cloud security needs in the project planning and design phases. Ensure that cloud security is considered early in the software specifications stage and maintained throughout.
- Automate cloud security testing: Detect vulnerabilities early in the development cycle through automated cloud security testing tools. Assess your cloud environment, apps, and infrastructure posture using tools and scripts.
- Integrate cloud security into DevOps processes: Promote collaboration among development, operations, and security teams. Automate cloud security policies and ensure continuous security throughout the cloud application development lifecycle.
- Use cloud-native security tools and services: Leverage cloud-native tools from your cloud service provider to improve your security posture, such as AWS GuardDuty, Azure Security Center, or Google Cloud Security Command Center.
To balance data accessibility with security and ensure agility, proper implementation of the cloud security fundamentals requires tailored solutions across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Seek services that manage public, hybrid, and private cloud platforms while also providing operational insights and security controls to efficiently support corporate scaling and your evolving needs.
Read our extensive guide on the top active directory security tools for auditing, monitoring, and protection throughout your network.
5 Common Cloud Security Challenges
While the cloud provides security benefits, challenges remain. Some of these challenges are AI-powered assaults, technical resource constraints, adjusting to new technologies, complexity in cloud settings, and compliance adherence. Overcoming these demands strong security rules and regular monitoring to properly manage threats and secure cloud assets and services.
AI-Powered Attacks
AI-powered attacks exploit vulnerabilities with powerful algorithms, creating a worldwide danger. Palo Alto’s 2024 State of Cloud-Native Security survey says that 61% of enterprises are concerned about these assaults. The research, which includes views from 2,800 cybersecurity experts, focuses on critical decisions that shape cloud-native security.
How to overcome this challenge: Implement enhanced detection systems, invest in AI-powered cybersecurity solutions, and cultivate a cybersecurity-aware culture. Keep up with evolving attack strategies to protect sensitive data and preserve confidence in the cloud.
Technical & Resource Limitations
Due to the diverse cloud environments, organizations confront challenges in providing consistent security across numerous cloud platforms. According to Fortinet and Cybersecurity Insiders’ 2024 Cloud Security Report, technological constraints (52%) and resource limits (49%) are significant barriers to cloud adoption.
How to overcome this challenge: Invest in tailored cloud-native security solutions and use automation tools to improve security management. Collaboration with managed security service providers (MSSPs) to supplement internal skills.
Difficulty in Adapting to Rapid Technological Changes
The rapid emergence of new cloud computing technologies demands constant upgrades and developments. This makes it difficult for enterprises to keep up with changing risks and security measures. These changes might pose new security concerns, requiring businesses to constantly alter their security systems to successfully meet emerging threats.
How to overcome this challenge: Focus on continual staff training, and employ automation technologies to expedite security operations. Establish active partnerships with cloud service providers and security suppliers to stay updated on developing trends and best practices.
Complexity & Fragmentation in Cloud Environments
Modern cloud infrastructures are complex and fragmented, with several services, platforms, and configurations. This complexity makes it difficult to maintain uniform security and governance across numerous cloud environments.
How to overcome this challenge: Apply centralized management solutions that provide visibility and control over diverse cloud resources. Standardizing security rules and configurations across cloud platforms and conducting frequent audits and automation can simplify management and guarantee the efficient implementation of security measures.
Compliance Concerns
The Cybersecurity Insiders’ 2024 Cloud Security Report states that 59% of respondents hesitate to employ multi-cloud due to security and compliance concerns. Evolving rules, disparities in international and industry-specific standards, technology improvements, and the decentralized nature of cloud environments all contribute to these problems.
How to overcome this challenge: Check cloud security technologies and solutions that manage compliance automatically. These solutions can improve compliance procedures by constantly monitoring cloud environments, finding gaps, and automatically performing corrective actions.
5 Common Cloud Security Solutions
As cloud computing evolves, so does cloud security, with relatively new solutions such as CSPM, CWPP, CIEM, CNAPP, and CASB signifying distinct security domains. Understanding what these tools do could help you properly protect your cloud environments against emerging threats through a suitable solution. Each solution addresses a distinct aspect of cloud security, designed to meet specific cloud security concerns and requirements.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Solution
CSPM tools constantly monitor, identify, score, and address security and compliance vulnerabilities across cloud infrastructures in real time. CSPM, which frequently works in tandem with other cloud security technologies, aids in the rapid detection and resolution of misconfigurations. Standalone CSPM solutions provide effective detection and remediation of cloud misconfigurations for both small and large corporations.
Recommended solution: Palo Alto’s Prisma Cloud CSPM offers several distinct CSPM advantages, including flexible deployment, wide third-party integrations, ML-driven threat detection, and code scanning capabilities. It offers full security and compliance solutions, starting at $18,000 for a 12-month subscription in AWS Marketplace. You can take advantage of Prisma Cloud’s demo and 30-day free trial to evaluate its capabilities firsthand.
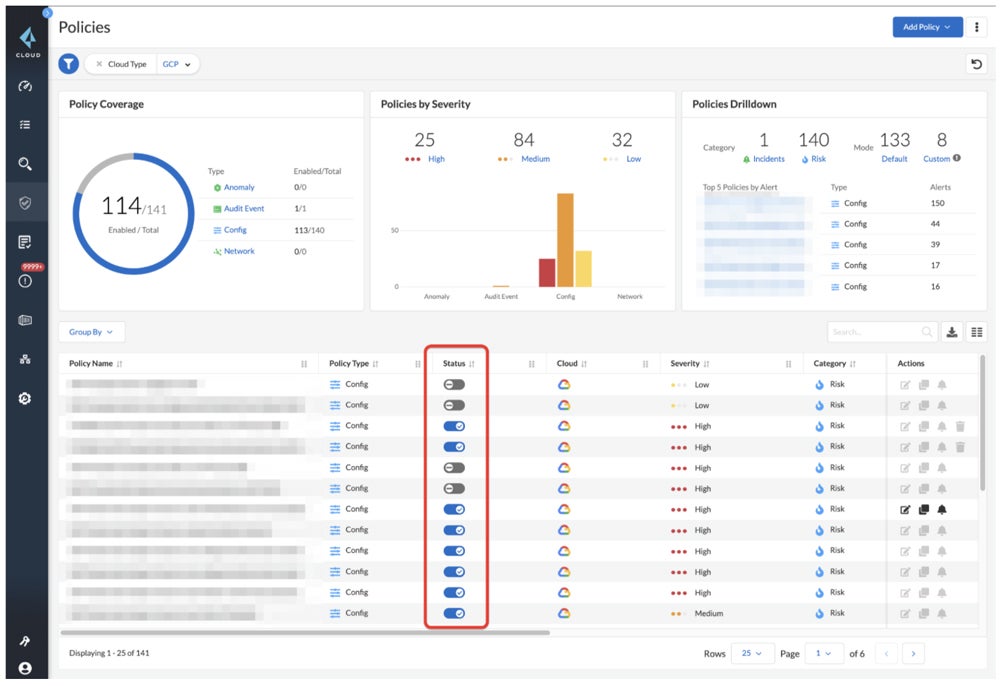
Discover more alternative solutions in our extensive guide on the top CSPM tools, which also covers their best features, benefits, and more.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
CWPP protects cloud workloads against a number of threats, including malware, ransomware, DDoS assaults, misconfigurations, insider threats, and data breaches. Offering unified visibility and administration for physical systems, virtual machines, containers, and serverless applications, CWPP solutions improve security posture and reduce the risk of security incidents, making them critical for cloud-based applications.
Recommended solution: Sophos Cloud Workload Protection is an easy-to-use solution, which uses Intercept X Advanced for Server to efficiently integrate CSPM and Sophos Cloud Optix Standard capabilities. It provides increased security by protecting essential cloud services and effortlessly integrating with Sophos server agents in AWS, Azure, and GCP. Contact Sophos Sales for custom quotes and free trial requests.
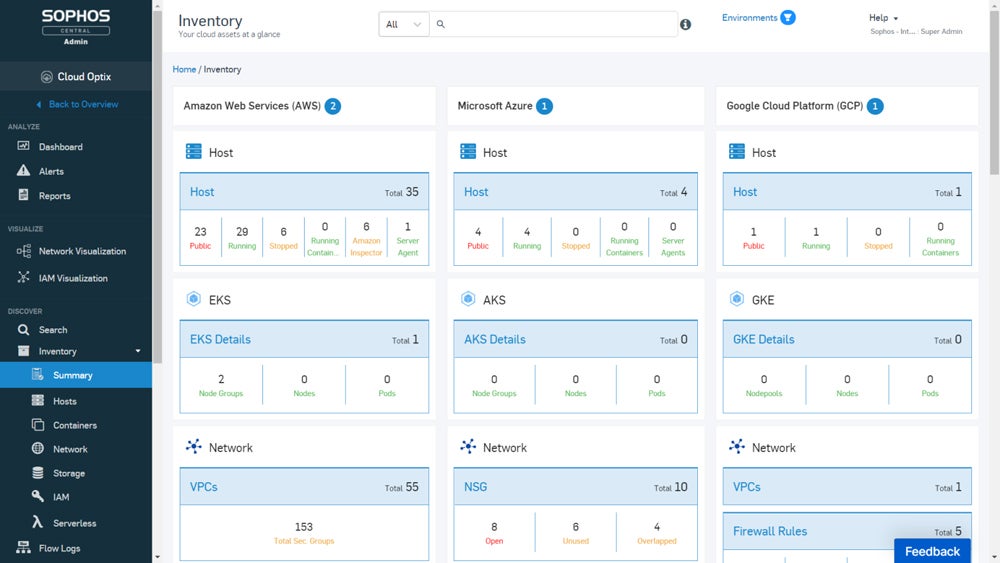
See the full list of our top cloud workload protection platforms to evaluate the most suitable solution for you.
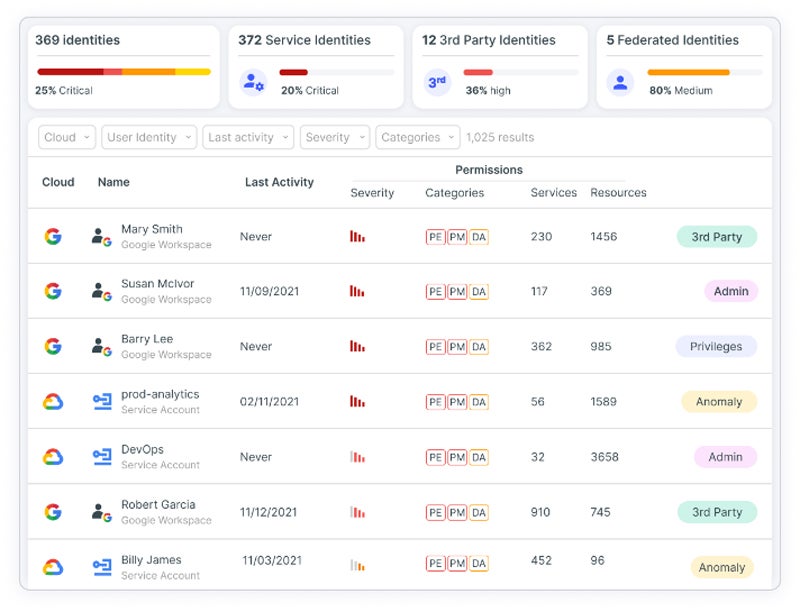
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) Solution
CIEM security solutions leverage data analytics and machine learning to detect abnormalities, manage user entitlements, and enforce data governance. This enables enterprises to systematically implement tight access controls and zero-trust rules across cloud environments. It solves issues such as entitlement tracking, limited cloud capacity, continuous assessment, automated remediation, scalability, and multi-cloud support.
Recommended solution: Tenable CIEM provides a comprehensive solution for securely maintaining human and service identities in cloud environments. It visually represents all identities and entitlements, utilizing automated analysis to precisely and contextually reveal and prioritize dangers such as excessive permissions and hazardous combinations. You may contact Tenable sales to request a free demo and a custom quote.
Cloud Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP)
CNAPP provides complete capabilities for organizations to defend their cloud apps and workloads from security threats. CNAPPs provide comprehensive threat and vulnerability protection for cloud workloads, apps, identity management, development environments, and more by combining multiple cloud security technologies such as CWPP, CSPM, CIEM, and IAC scanning.
Recommended solution: Check Point CloudGuard stands out for its strong container security and runtime protection, making it an appealing option for businesses looking to improve cloud-native application security. As a single platform, CloudGuard CNAPP enables consistent enforcement across cloud providers while prioritizing prevention. On AWS Marketplace, pricing for 25 assets starts at $625 per month.
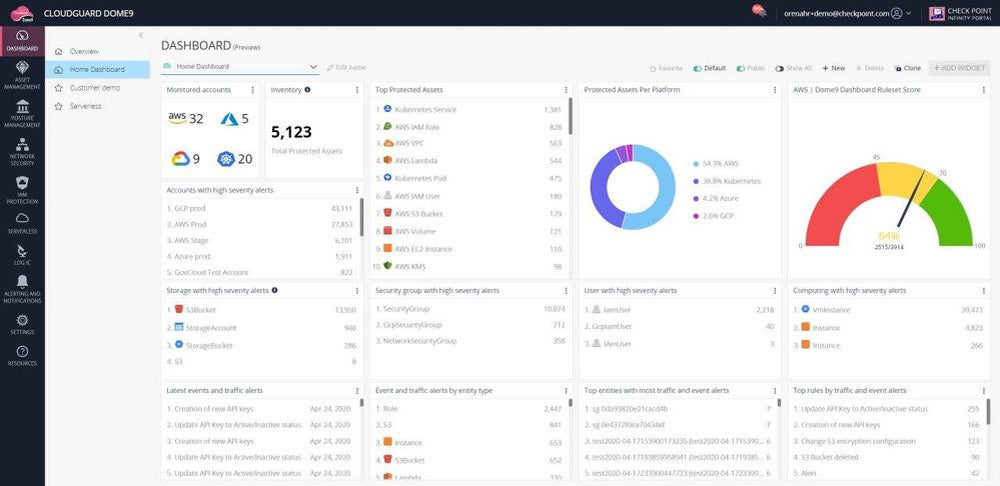
Explore our complete guide on the best cloud native application protection platforms on the market and assess the most ideal platform for your business.
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) Tools
A CASB solution connects users to cloud services, protecting data and enforcing security regulations. CASBs are evolving into secure access service edge (SASE) technology. They address vulnerabilities beyond the network perimeter such as edge computing, IoT, mobile, cloud, and more. For enterprises that prioritize SaaS application and shadow IT risk mitigation, standalone CASBs provide essential protection.
Recommended solution: Skyhigh Security CASB excels at access restrictions, providing data loss protection rules, and preventing unwanted downloads to personal devices. It connects effortlessly with a wide range of corporate applications and identity management systems, using both forward and reverse proxy for inline deployment. Skyhigh offers three plans: Essential, Advanced, and Complete, with demos and custom pricing available upon request.
Read our comprehensive guide to the top cloud access security broker solutions to know their differences and what each solution offers.
Bottom Line: Develop a Strong Cloud Security Fundamental Strategy
As more businesses implement advanced multi-cloud architectures, persisting cloud security issues highlight the importance of implementing the cloud security fundamentals. To secure a cloud environment’s security, focus on critical areas such as data security, compliance, infrastructure security, IAM, and security monitoring with disaster recovery. Assess your current security measures, identify weaknesses, and develop effective remediation plans.
Aside from the solutions mentioned above, you may also add an extra layer of security to your network infrastructure by employing a secure remote access solution.









