Cloud migration security refers to the safe execution of standard security procedures when transitioning data and apps to the cloud. It includes pre-migration preparation, cloud migration security strategies, and security management and maintenance post-migration. Effective cloud migration security preserves data confidentiality, integrity, and continuous application performance, shielding businesses from potential breaches and operational disruptions.
Table of Contents
How Cloud Migration Security Works
A complete cloud migration security strategy consists of three main stages: pre-migration, migration, and post-migration.
Pre-migration security focuses on evaluating the current infrastructure, identifying weaknesses, and establishing security objectives. This stage entails completing a detailed risk assessment, reviewing present systems, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure a secure move.
Cloud migration security involves securing data in transit and facilitating access control. It includes encrypting data to prevent unwanted access, adopting strong identity and access management (IAM) protocols to manage user rights, and continuously monitoring activity to detect and mitigate any threats in real time.
Post-migration security requires enhancing cloud resources for increased security, regularly monitoring performance, and verifying compliance with the applicable regulations. In this stage, you perform frequent security audits, fine-tune resource allocation to prevent vulnerabilities, ensure compliance standards are met, and apply your incident response strategy to address any security breaches as soon as possible.
2 Types of Cloud Migration
The two types of cloud migration are on-premise to cloud and cloud to cloud. An on-premise to cloud migration (lift and shift) works well for rapid conversions with minimum adjustments. Cloud to cloud migration allows greater flexibility and optimization when moving cloud providers. Choosing an appropriate type of cloud migration depends on your specific demands and goals. Regardless of the method used, properly plan and execute secure ways for a safe migration.
On-Premise to Cloud
On-premise to cloud migration is also known as “Lift and Shift,” a fundamental cloud migration type. The process includes moving data and applications from an on-premise data center to a cloud environment. This can be done manually or using migration software.
This method is often faster and less difficult, requiring just minor adaptations for applications and data. It enables fast deployment and lowers infrastructure expenses by eliminating the need to maintain on-premise hardware. However, it may not completely optimize programs for cloud performance and may encounter compatibility concerns.
Cloud to Cloud
Cloud to cloud migration is the process of migrating data, workloads, and applications from one cloud environment to another. This type of migration is expected when firms change cloud providers or combine different cloud services. Applications and data may need to be reconfigured to fit into the new cloud environment.
It allows businesses greater flexibility in leveraging better pricing, features, or performance from a new cloud provider. It also enables enterprises to use more advanced cloud services while reducing reliance on a single cloud provider. Still, data movement across clouds can be complex and time-consuming, with the possibility of outages and security issues.
Benefits of Cloud Migration Security
Cloud migration security benefits businesses by improving security, scalability, flexibility, productivity, and compliance. It lays a solid basis for you to safeguard their data, manage resources efficiently, and quickly respond to new opportunities.
- Strengthens security: Applies advanced security technologies to safeguard data from breaches, unauthorized access, and cyber threats.
- Improves scalability: Easily adjusts scales up or down based on demand, resulting in more efficient management and lower costs.
- Increases flexibility: Rapidly launches new applications and services, allowing for quick responses to market changes and client needs.
- Improves productivity: Enables remote work and collaboration by granting secure access to data and applications from anywhere.
- Maintains compliance: Uses strong security methods and controls to meet industry requirements and standards while protecting data integrity and privacy.
According to Gartner’s cloud predictions, by 2026, three out of four businesses will undergo a digital transformation based on cloud computing. This implies that businesses should start investing in cloud to gain the benefits above.
Risks & Challenges of Secure Cloud Migration
Despite the benefits, migrating to the cloud involves risks and challenges that businesses should be aware of. Cloud migration risks are direct threats to data and systems, potentially resulting in breaches or data loss. Challenges, on the other hand, such as regulatory difficulties and skill shortages, impede successful security implementation. Managing risks and challenges reduces vulnerabilities and enables a seamless transition to the cloud.
Cloud Migration Security Risks
Cloud migration security risks are potential threats to data integrity, confidentiality, and availability during and after transfer to the cloud. Address data breaches, IAM lapses, API flaws, key management issues, and insider threats through implementing different mitigation methods.
| Risk | Causes | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Data compromise | • Misconfigured cloud resources. • Inadequate security measures during data transmission. | • Implement effective security setups. • Use robust encryption for data in transit and at rest. • Conduct frequent security audits. • Utilize DLP tools. |
| Identity and access management (IAM) lapses | • Oversight in access privileges. • Poorly configured IAM controls. | • Implement strict IAM policies. • Enable multi-factor authentication. • Review and update the access controls. • Use IAM tools. • Enforce the least privilege principles. • Check access records for any unusual activity. |
| API vulnerabilities | • Inadequate application protection measures. | • Create and enforce a robust API gateway implementation. • Security testing occurs on a regular basis. • Keep track of any unexpected API activity. • Ensure that APIs use proper authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms. |
| Weak encryption and inadequate key management | • Using outdated encryption algorithms. • Poor management of encryption keys. • Using default or shared keys. | • Use strong encryption techniques. • Adopt strict key management practices. • Rotate encryption keys using dedicated key management services (KMS). |
| Insider threats | • Malicious actions by disgruntled employees. • Negligent behaviors | • Conduct a comprehensive background check upon hiring. • Implement stringent access controls. • Regularly audit user activity. • Offer comprehensive security training. • Develop clear offboarding procedures for departing staff. |
Cloud Migration Security Challenges
Cloud migration challenges — such as proliferating environments, monitoring issues, skills shortage, new compliance requirements, and misunderstanding the shared responsibility — affect business continuity. Fortunately, there are several ways to manage these challenges.
| Challenge | Impact to Businesses | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Uncontrolled environments proliferation | • Security blind spots in threat detection. | • Implement cloud management and governance frameworks. • Maintain control of cloud resources. • Use cloud security posture management tools. |
| Monitoring issues | • Difficulty in maintaining visibility for potential security incidents. | • Deploy security information and event management systems. • Monitor cloud activity. • Adjust the monitoring configurations. |
| Cloud security skills shortage | • Hampers effective incident handling and security management. | • Invest in training programs for your existing personnel. • Engage with managed security service providers (MSSPs). • Use automation and AI-powered security tools. |
| New compliance requirements | • Compliance gaps | • Stay updated on applicable rules. • Work with compliance specialists. • Implement cloud governance frameworks. • Conduct internal and external audits regularly. |
| Misunderstanding the shared responsibility | • Security gaps • Compliance issues | • Define and document the shared responsibility model with your CSP. • Evaluate and modify security policies. • Ensure that all parties understand their roles and obligations. |
Cloud issues exist not just in cloud migration, but also while implementing your overall cloud security. Explore our guide to learn more about the top cloud security issues and the different methods to mitigate them.
How to Implement Cloud Migration Security (+ Checklist)
To integrate security into the whole cloud migration process, begin with extensive pre-migration evaluations and planning. Then, assure application readiness, securely migrate data and infrastructure, rigorously test and verify, and execute a smooth go-live process. Finally, maintain post-migration optimization by managing your cloud environment.
We’ve created a sample checklist for implementing secure cloud migration processes. Click the image below to download the file and customize your own cloud migration security checklist. Then, continue reading below to see our step-by-step explanation on how to perform each task on the checklist.
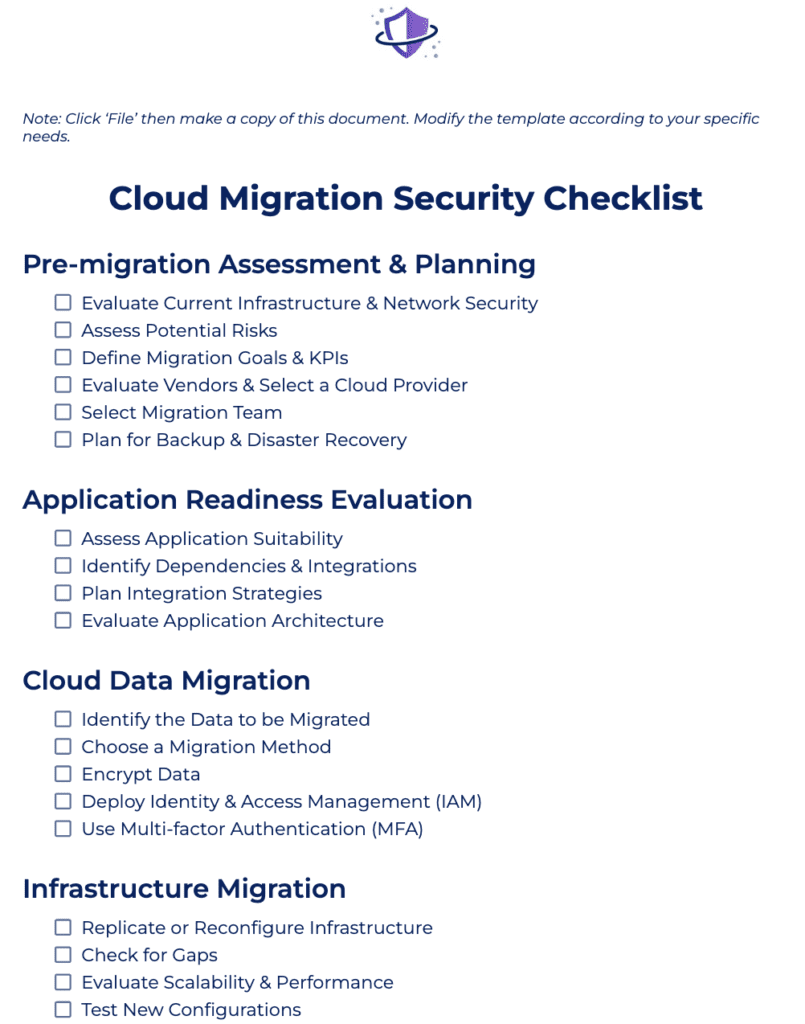
1. Conduct Pre-Migration Assessment & Planning
Before you begin your cloud migration, do the following steps to assess your readiness:
- Evaluate your current IT infrastructure and network security: Create a complete inventory of all your data center’s hardware, software, network infrastructure, firewalls, and security measures.
- Assess potential risks: Identify and plan for any security risks and problems during the relocation process. Then, conduct a risk assessment to identify weaknesses and potential threats.
- Define migration goals and KPIs: Establish specific objectives and success indicators to drive the migration process. Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals and KPIs.
- Assess vendors and choose a cloud provider: Choose a cloud provider that fulfills your requirements and provides dependable services. Compare providers based on reliability, scalability, pricing, support, and compliance capabilities.
- Select migration team: Put together a professional team to oversee the migration process successfully. Determine essential positions (e.g., project managers, cloud architects, security specialists) and delegate duties.
- Prepare backup and disaster recovery plans: Ensure your data integrity and availability in the event of an unforeseen issue. Create a robust backup and disaster recovery plan to prevent data loss.
2. Evaluate Your Application Readiness
Prepare for the cloud migration process by assessing your apps through these actions:
- Assess application suitability: Determine whether apps are compatible with your cloud environment.
- Identify dependencies and integrations: Map out interdependencies and necessary integrations.
- Plan integration strategies: Create detailed plans to integrate different applications with new cloud systems.
- Examine application architecture: Ensure that your app architecture supports scalability, dependability, and performance.
3. Perform a Secure Cloud Data Migration
Conduct a secure data migration and check if you’ve performed the following:
- Identify the data to be migrated: Ensure that all necessary data is included in the migration. Collaborate with teams to identify key data sources and eliminate data silos.
- Choose a migration method: Determine the best way for migrating data to the cloud. Choose based on data volume, complexity, and downtime tolerance.
- Encrypt data: Preserve data privacy policies and integrity during transmission. Use encryption tools to secure data in transit and at rest.
- Control access to cloud resources: Use identity and access management protocols that govern user rights and responsibilities.
- Use multi-factor authentication: Require multiple verifications. Enable MFA to ensure that only authorized users can access the cloud environment.
4. Secure Your Infrastructure Migration
Do these methods to safely conduct infrastructure migration:
- Replicate or reconfigure infrastructure: Create a cloud architecture that mirrors or improves on your current configuration.
- Double check your infrastructure: Identify gaps, check for scalability and performance, and test new configurations.
5. Test & Validate Your Environments & Apps
Perform testing and validate your environments by doing the processes below:
- Apply functional testing: Verify that apps work as intended in the new environment. Create test cases and scenarios to validate all important features.
- Conduct performance testing: Determine how apps function under various scenarios. To evaluate system performance, test it under load, stress, and endurance.
- Validate security and compliance: Ensure that the migrated environment fulfills security and regulatory standards. Perform scans, vulnerability assessments, and audits.
6. Go Live
Take these steps to ensure security while going live:
- Verify data accuracy: Ensure that all data has been sent correctly and consistently. Perform data validation checks after migration.
- Perform final data synchronization: Record any changes made during migration. Synchronize the final data to maintain uniformity across systems.
7. Manage & Maintain Secure Cloud Environment Post-Migration
Monitor and analyze the post-migration performance of your cloud environment using these methods:
- Update DNS and network parameters: Reroute traffic to the new cloud environment. Validate DNS and network setups.
- Validate connectivity: Confirm that all users can connect seamlessly. Check and confirm network connectivity.
- Optimize resource allocation with cloud tools: Maximize the use of cloud resources. Use cloud provider tools for dynamic scaling and cost optimization.
- Performance monitoring and fine-tuning: Ensure that the system is performing optimally and securely. Set up monitoring systems and modify resources.
- Verify and update new compliance and regulation adherence: Maintain continuing compliance with applicable rules. Conduct regular audits and updates to policies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Do I Protect Data During Cloud Migration?
To maintain cloud data security during transfer, categorize it according to its criticality. Encrypt data in transit and at rest to protect its security. Use strong identity and access management and multi-factor authentication to govern and safeguard access to critical data.
What Are the 4 Phases of Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration consists of four phases: assessment, planning, execution, and post-migration.
- Assessment: Determines whether workloads are eligible for migration by examining current infrastructure and gathering data.
- Planning: Includes designing the cloud environment, mapping migration stages, and selecting the appropriate cloud service provider.
- Execution: Completes the migration, configures the new environment, and tests apps to ensure correct functionality.
- Post-migration: Monitors performance, backs up data, and handles any issues or dangers that arise.
What Are the 7 Cloud Migration Strategies?
AWS’s 7 Rs migration model for cloud migration includes rehost, relocate, replatform, refactor, repurchase, retire, and retain.
- Rehost: Transfers existing IT assets to the cloud with little adjustments, also known as “Lift and Shift.”
- Relocate: Moves your whole virtualized environment to the cloud with no changes to the hypervisor, resulting in increased efficiency and performance.
- Replatforming: Involves migrating apps to the cloud with some adjustments to take use of cloud-native features, also known as “Lift and Reshape.”
- Refactor: Redesigns apps to fully leverage cloud capabilities, including secure coding principles and cloud platform features.
- Repurchase: Replaces current apps with cloud-based SaaS products that take advantage of the SaaS provider’s security controls.
- Retire: During migration, decommission any old or non-essential programs to reduce your threat surface and simplify security administration.
- Retain: Keep certain programs on-premises due to security concerns or technical restrictions, carefully weighing the risks and advantages.
Bottom Line: Apply Cloud Migration Security Practices for Enhanced Data Protection
Security in cloud migration should be performed across all integral phases, from initial planning to execution and post-migration. Different cloud tools are easily accessible now, so utilize these to enhance your cloud protection methods. Integrate cloud migration security with the broader cloud security strategies so your business can establish a cohesive defense architecture that successfully protects data, apps, and infrastructure from both common and new threats.
After a successful cloud migration, a post-migration practice requires maintaining and managing your cloud data. Read our review of the top cloud data management solutions and compare their key features, strengths, weaknesses to evaluate which is best for you.








