Cloud security management is the process of safeguarding cloud data and operations from attacks and vulnerabilities through a set of cloud strategies, tools, and practices. The cloud security manager and the IT team are generally responsible for managing cloud security. This empowers enterprises to effectively use their cloud technology capabilities while maintaining a safe and efficient infrastructure — a crucial practice as cloud adoption expands.
Table of Contents
How Cloud Security Management Works
Led by the cloud security manager and the IT team, cloud security management starts with the assessment and identification of security requirements and tools. Next, the IT team sets up access controls and data encryption methods, followed by network security configuration and cloud activities monitoring. Then, the IT team develops and applies incident response plans, while the manager maintains compliance.
An effective cloud security management fully works through a combination of the technical controls, rules, and procedures that specify how to use and safeguard your cloud resources. This is a shared responsibility between the user, the security team, and the provider. Cloud security management covers the following key processes meant to protect your organization’s cloud environment:
- Risk assessment: Begin by identifying the cloud services you use and assessing security and potential risks.
- Access control: Set user rights to restrict access to sensitive information and update them as needed.
- Data encryption: Ensure that your data is safe in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Network security: Manage and protect connections to allow genuine traffic while restricting suspicious activity.
- Security monitoring: Constantly monitor cloud activity to detect and respond to any threats in real time.
- Incident response: Create and enforce plans to respond rapidly to any security breaches, limit any damage, and restore normal operations.
- Compliance: Verify that you satisfy every regulatory and legal standard for cloud security.
Your cloud security team must evaluate and update native security settings within each application. Manage all users and devices to make sure that only authorized devices and individuals have access to data and services. Then, get an overview of cloud activity through reporting and monitoring for improved risk management and operational control.
Cloud security management covers three types, each focusing on securing different cloud functions. To maximize the benefits of cloud security management and counteract its challenges, apply effective strategies and tailored cloud security tools.
3 Types of Cloud Security Management
There are three categories of cloud security management: cloud database security, cloud migration security, and cloud database management. Cloud database security focuses on protecting data stored in cloud databases. Cloud migration security protects data and applications as they transfer to cloud environments. Finally, cloud database administration entails supervising the storage, organization, and accessibility of data in cloud databases for maximized performance.
Cloud Database Security
Cloud database security protects data from breaches, DDoS assaults, viruses, and unauthorized access in cloud environments. To protect data, it uses encryption, access controls, monitoring, and audits. Access controls restrict user access, encryption protects confidentiality, and monitoring detects unusual activities. To improve security and resilience, additional approaches include data masking, patch management, disaster recovery, and backup.
Cloud database security mainly focuses on these cloud security functions:
- Encryption: Maintains confidentiality and protection of data stored in cloud databases.
- Access control: Regulates cloud data access to minimize unauthorized users’ entry.
- Audits and monitoring: Detects suspicious database activities for timely intervention.
To properly apply cloud database security best practices, learn the shared responsibility model. Understand the scope of you and your provider’s security responsibilities. Then, ask your cloud provider about their security procedures and practices to check that they meet your needs. Write policies outlining cloud service usage and security procedures, and use automated enforcement methods when possible.
Cloud Migration Security
Cloud migration security is the process of moving traditional programs, IT resources, and digital assets to the cloud, either completely or partially. This can include transitioning from one cloud to another or implementing a multi-cloud architecture. Cloud migration security protects data and applications during the move, protecting their confidentiality and integrity.
It targets the secure handling of these cloud operations:
- Data migration: Develops solid outlines of the migration process, timelines, roles, and responsibilities.
- Data transfer: Checks and uses secure protocols to validate that all data in transit and at rest are encrypted.
- Identity and access management (IAM): Establishes policies to control data access and authenticate user identities.
As a best practice, consider applying additional security measures to prevent data corruption and unwanted access. Configure the control plane to manage baselines and maintain constant synchronization with the data plane. You may also take advantage of the cloud’s pay-as-you-go model to reduce costs as you migrate your on-premises data to the cloud.
Cloud Data Management
Cloud data management entails storing company data in remote data centers maintained by cloud providers such as AWS or Microsoft Azure. This technique provides automated backups, professional support, and remote access from anywhere. Benefits include automated backups, expert assistance, and remote access, all of which streamline data administration and improve corporate accessibility and reliability.
The goal of cloud data management focuses on the following aspects:
- Data backup and recovery: Assists in creating a copy of your data and recovery plans in case of data corruption or loss.
- Data integration: Manages the synchronization of data across different cloud and on-premises systems.
- Data governance: Supports the enforcement of data governance policies and cloud-specific regulatory requirements.
To ensure effective cloud data management, develop a plan first. Include defining the scope and deployment model, establishing access restrictions, and comparing different approaches to data processing. Monitor data by validating, cleansing, and ensuring its quality for accurate analytics and decision-making. Make it a habit to save copies of your data on a regular basis to prevent loss, ensure availability, and verify automated copies of data.
Benefits of Cloud Security Management
Cloud security management includes more effective monitoring, user and device management, improved data protection, easier policy enforcement, and dynamic scalability. These enable you to effectively monitor your infrastructure, securely manage people, protect data thoroughly, strictly enforce policies, and seamlessly change security measures as your organization evolves.
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities
With extensive monitoring capabilities, your IT staff may remotely access a dashboard to assess the security of your entire cloud infrastructure. This lets them monitor potential threats and weaknesses in real time from any location. Increased accessibility allows for rapid responses to security incidents, improving overall security posture and reducing the chance of data breaches or system compromises.
Convenient User & Device Management
The proper application of cloud security management safely manages devices and users from any location. This resolves concerns about malware on user-owned devices in remote work environments. By efficiently managing access and security policies, you reduce the risks associated with illegal access or compromised devices, delivering a strong and secure cloud environment.
Enhanced Data Protection
Increased data protection secures your data from threats by installing strong measures like access restriction and threat detection. These safeguards guarantee that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data while actively monitoring for potential breaches. Cloud security management reduces the risk of data breaches while ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of your organization’s digital assets.
Improved Enforcement of Internal & External Security Policies
By improving the implementation of internal and external security policies and standards, you also improve your capacity to detect and resolve policy infractions quickly. This proactive approach to cloud security management protects your organization by identifying and fixing security vulnerabilities before they become more serious. With this, you maintain strong security standards and ensure compliance with industry requirements.
Dynamic Scalability & Flexibility
Cloud security management allows you to readily modify your security measures as your business develops. This lets you respond to emerging threats and changing requirements without the need for major infrastructure changes. By smoothly expanding your security processes, you ensure that your organization stays resilient and adaptable in dealing with threats, and promotes ongoing growth and innovation.
Challenges of Cloud Security Management
Complex data tracking, multi-tenant security concerns, access restriction complications, and potential asset misconfigurations all pose challenges that cloud security management must address. To effectively protect data integrity and prevent threats, these challenges need regular monitoring, strong security measures, and proactive management.
Complex Data Tracking
An intricate data tracking presents issues since third-party providers host cloud services, complicating monitoring and mandating audit trail log retrieval. This has an influence on data governance and compliance initiatives, increasing the risk of data breaches and regulatory noncompliance. To counteract this, develop clear data tracking processes, check audit logs on a regular basis, and maintain vendor engagement in delivering critical data usage insights.
Security Risks in Multi-Tenant Environments
Multi-tenant setups pose security threats from potential malicious attacks, endangering data integrity and system stability. Collateral damage is an issue since an attack on one tenant can affect others. To avoid wide consequences, install strong security measures such as encryption and access controls, as well as routinely monitor for unusual activity.
Access Restriction Complexity
Access restriction complexity issues emerge when managing access between on-premises and cloud environments, requiring seamless transitions and BYOD policy compliance. This intricacy might result in unwanted access and security breaches. To prevent this, develop clear access protocols, strictly enforce BYOD policies, and employ identity and access management solutions to achieve unified access control across many environments.
Potential for Asset Misconfiguration
Without paying close attention to management and swift remediation by dedicated teams, asset misconfigurations might lead to exploitable vulnerabilities. To ensure network security, employ strict configuration management processes, conduct frequent audits, and resolve any flaws as soon as possible.
5 Strategies for Cloud Security Management
With cloud security management strategies like performing audits, setting protection, managing and monitoring users, and using cloud security tools, you can maximize the benefits of cloud technology while minimizing risks. Implementing these procedures will allow you to protect sensitive data, ensure compliance, and keep your operations running smoothly. Consider some of these basic strategies for managing cloud security effectively.
Perform Security Audits
Security audits protect the integrity of your cloud infrastructure. It entails regularly scanning your cloud-based products and services for potential security flaws. By following these actions on a regular basis, you can discover and remedy any security vulnerabilities:
- Define objectives: Determine the audit scope and objectives in accordance with regulatory standards and business goals.
- Assess controls: Examine your organization’s current security controls and configurations for cloud assets.
- Scan for vulnerabilities: Use scanning software to find potential security flaws and vulnerabilities.
- Examine logs: Analyze access records for illegal access attempts and identify questionable activities.
- Monitor changes and fixes: Create a remediation strategy, implement security measures, and constantly monitor for changes and vulnerabilities.
Here’s an overview of performing security audits using SolarWinds’ auditing tool:
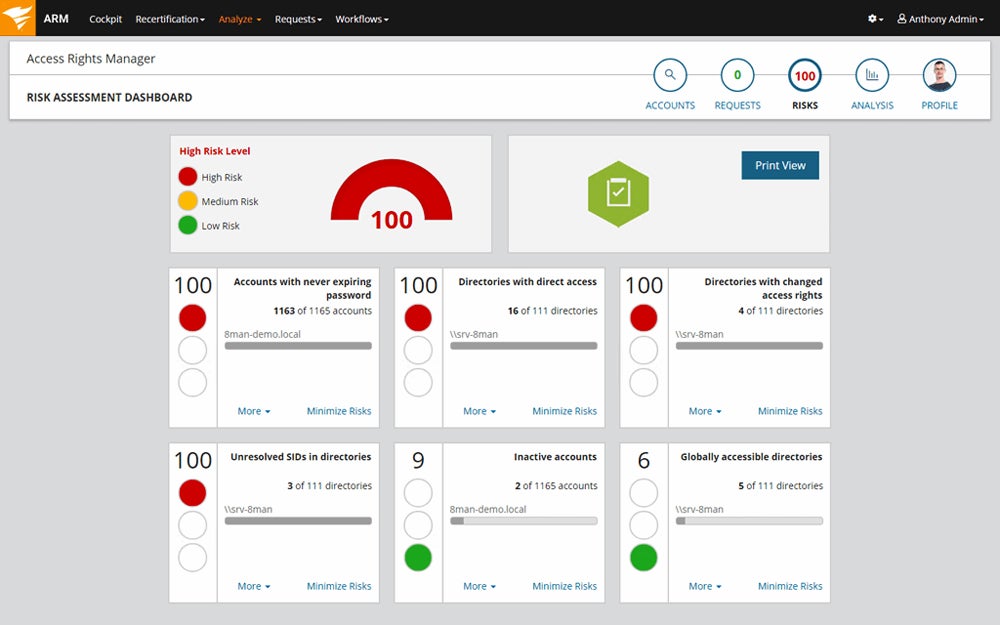
Set Proper Levels of Protection
Implementing appropriate levels of protection entails giving your IT security staff complete control over the security settings for cloud-based applications and configuring them to the highest security level. This provides protection against cyber attacks, unlawful access, and data breaches. Deploy these security measures to protect sensitive data, ensure regulatory compliance, and strengthen your overall cloud cybersecurity resilience:
- Define security policies: Create comprehensive security rules that specify the required security levels and requirements for cloud-based applications.
- Assign access controls: Grant suitable access permissions to users and roles while limiting access to necessary resources according to the concept of least privilege.
- Implement encryption: Secure sensitive data in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access or interception.
- Implement threat detection tools: Use threat detection and monitoring technologies to discover and respond to potential security risks in real time.
- Conduct regular security check-ups: Evaluate the efficacy of security measures, discover vulnerabilities, and ensure adherence to security rules and regulations.
Use tools to easily configure your security settings. Take a look at this example from CrowdStrike:
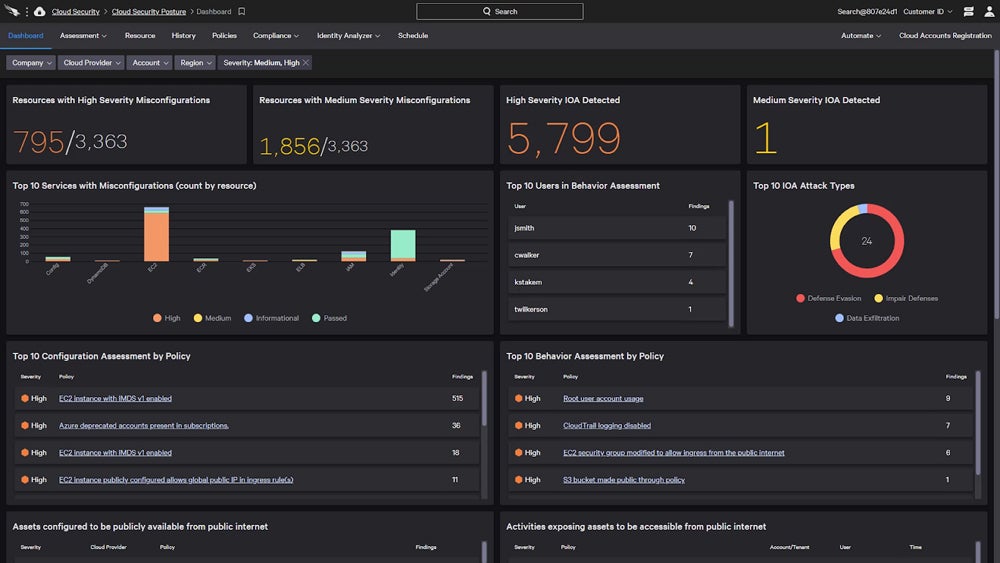
Manage Users & Devices
Ensure only authorized devices access your network and data, setting user-level controls to limit data access appropriately. By aligning access permissions with role requirements, you optimize operational efficiency while safeguarding data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance in your cloud environment. Here are a few ways to manage users and end-user devices:
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC): Assign access permissions based on users’ roles and responsibilities to ensure they only access data necessary for their tasks.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA): Require additional authentication factors, such as passwords and biometrics, to enhance security and prevent unauthorized user access.
- Utilize mobile device management (MDM) solutions: Employ MDM solutions to manage and secure mobile devices accessing cloud resources. Enforce security policies and encryption.
- Regularly update access controls: Review and update access controls periodically to reflect changes in user roles. This ensures continued alignment with security requirements.
- Track device activities using tools: Use monitoring tools to track user and device activity in real-time. Detect and respond to any suspicious behavior or security incidents promptly.
Here’s what user and device management looks like using a monitoring tool from ManageEngine:
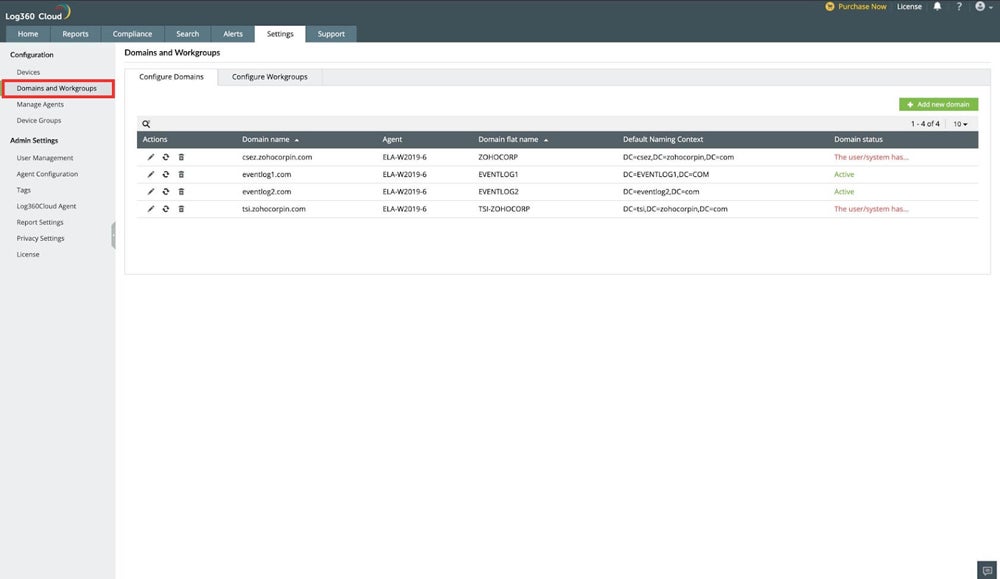
Monitor User Activities
This strategy involves going through reports to track user interactions in your cloud environment, which can provide insights into security concerns and compliance violations. By getting visibility into user activity, companies may detect and mitigate possible security threats in real time, improving overall security posture. Follow these steps to perform immediate responses to security incidents while assuring data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance:
- Define monitoring objectives: Determine the precise user actions and behaviors to monitor in accordance with security and compliance standards.
- Select monitoring tools: Choose tools and software that can track user actions and generate detailed results.
- Configure monitoring parameters: Set monitoring parameters and thresholds to record relevant user logs and detect odd patterns that may indicate a security threat.
- Analyze monitored data: Review and analyze monitoring reports on a regular basis to detect patterns, abnormalities, and potential security threats in user activity.
- Take preventive security measures: Address identified security concerns, such as modifying access controls or initiating incident response procedures when necessary.
This is the typical activity monitoring scenario using Microsoft Azure:
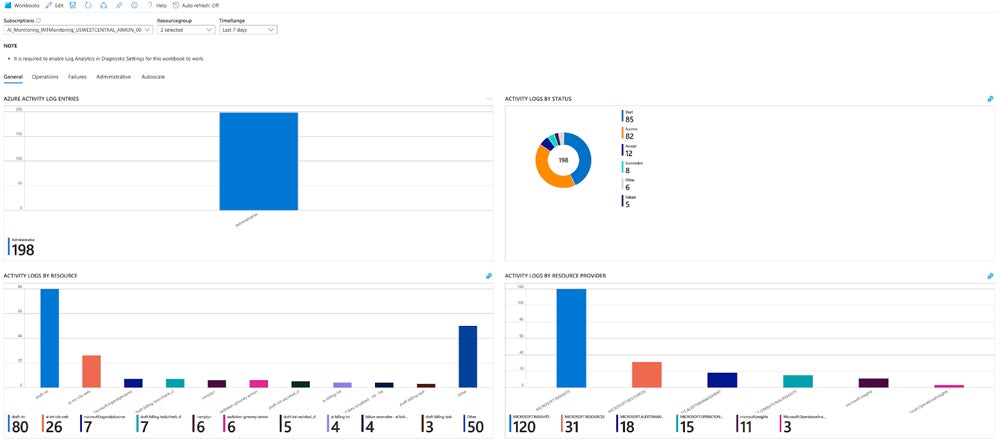
Use Cloud Security Tools
Use cloud security solutions to strengthen your cloud security management strategy. These tools include threat detection and encryption solutions, as well as identity and access management systems. Integrating these solutions into your cloud environment allows you to improve threat detection, impose access rules, and protect data confidentiality. Assess the cloud security solutions by employing these steps:
- Assess security needs: Evaluate your organization’s security needs and identify areas where cloud security products can help address weaknesses and threats.
- Research available options: Look for cloud security solutions that meet your security requirements, taking into account features, compatibility, and reputation.
- Implement selected tools: Deploy and configure your cloud security products in accordance with manufacturer specifications and best practices.
- Integrate with current systems: Combine new cloud security technologies with existing security infrastructure and processes to ensure smooth operation.
- Monitor and optimize tools: Continuously monitor the performance and efficacy of cloud security tools, modifying configurations and processes as needed.
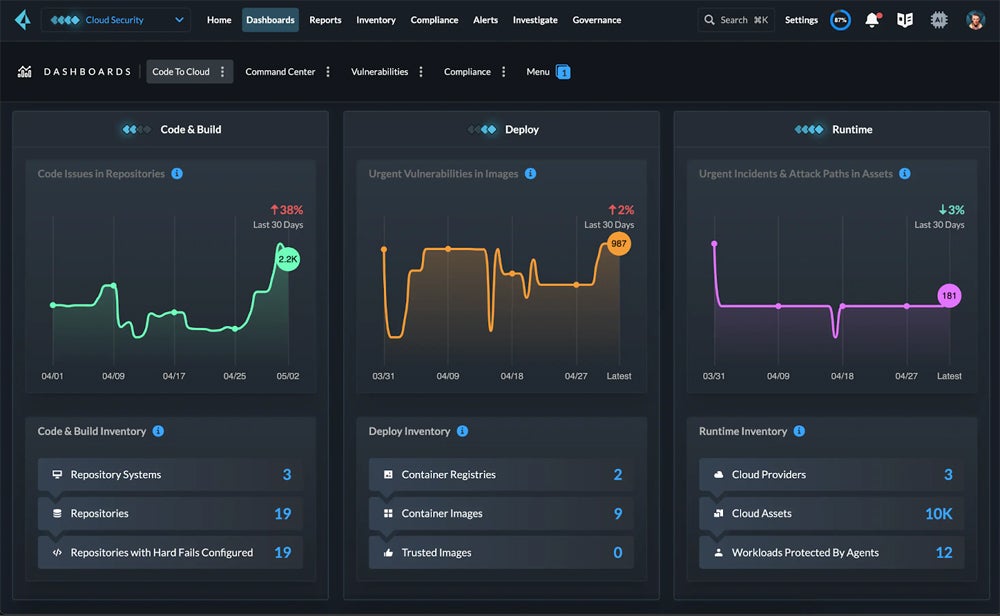
Most cloud security tools commonly open to their dashboard view, like this one from Prisma Cloud:
Check out our guide on the fundamentals of cloud security to understand and develop more robust cloud security management strategies.
3 Top Tools for Cloud Security Management
Choosing the right cloud security management provider is essential for complete protection, cost effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. When selecting a cloud service provider, carefully review their security policies and processes to verify that your sensitive data is adequately protected. For easier management, use common cloud security tools like CWPP, CSPM, or CNAPP. Check out our recommended provider for each solution below.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
CWPP defends against a variety of threats, including malware and data breaches. It provides unified visibility and administration of physical computers, virtual machines (VMs), containers, and serverless applications, hence improving cloud security. CWPP adoption improves security posture by limiting risks and reducing the impact of security incidents.
Our recommended solution: Illumio Core excels in advanced micro-segmentation by providing granular cloud security control and real-time threat detection. It offers significant workload visibility and adapts to fluctuating workloads, making it suitable for organizations looking to improve cloud workload safety. Illumio Core starts at $7,080 per year for 50 protected workloads and 25 ports.
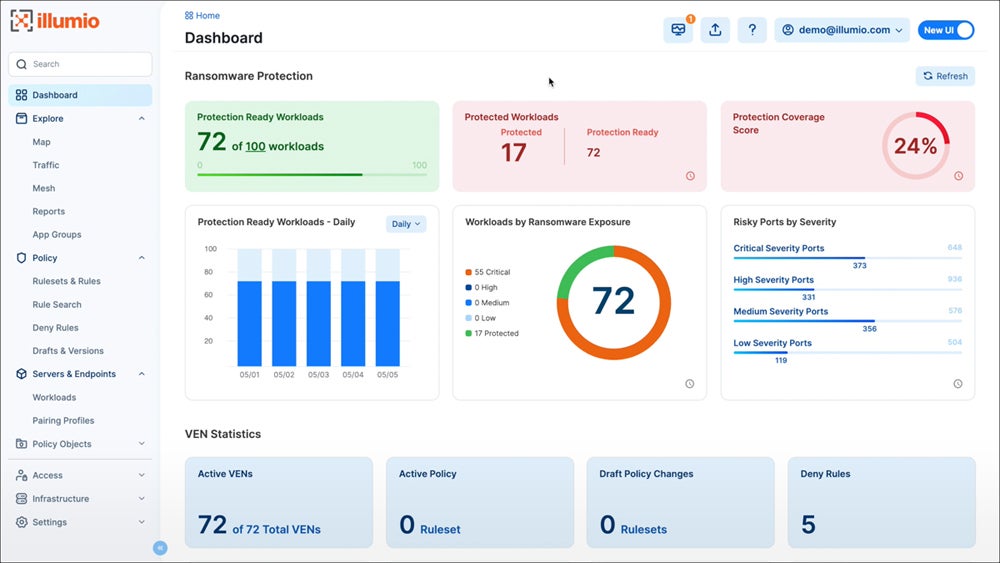
Explore other alternative cloud workload protection platforms and compare each solution’s advantages, key features, pricing, and more.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM tools monitor, evaluate, and resolve security and compliance issues in cloud systems in real time. These tools, along with CWPP and CIEM, are essential components of comprehensive CNAPPs. The ability to quickly detect and correct cloud misconfigurations makes standalone CSPM solutions useful tools for enterprises of all sizes.
Our recommended solution: Cyscale specializes in cloud security mapping, with support for AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and Alibaba setups. Cyscale’s mapping features let firms visualize and manage security and compliance risks more efficiently. The Pro plan costs $10,000 for a 12-month subscription that includes up to 1,000 assets via Azure Marketplace.
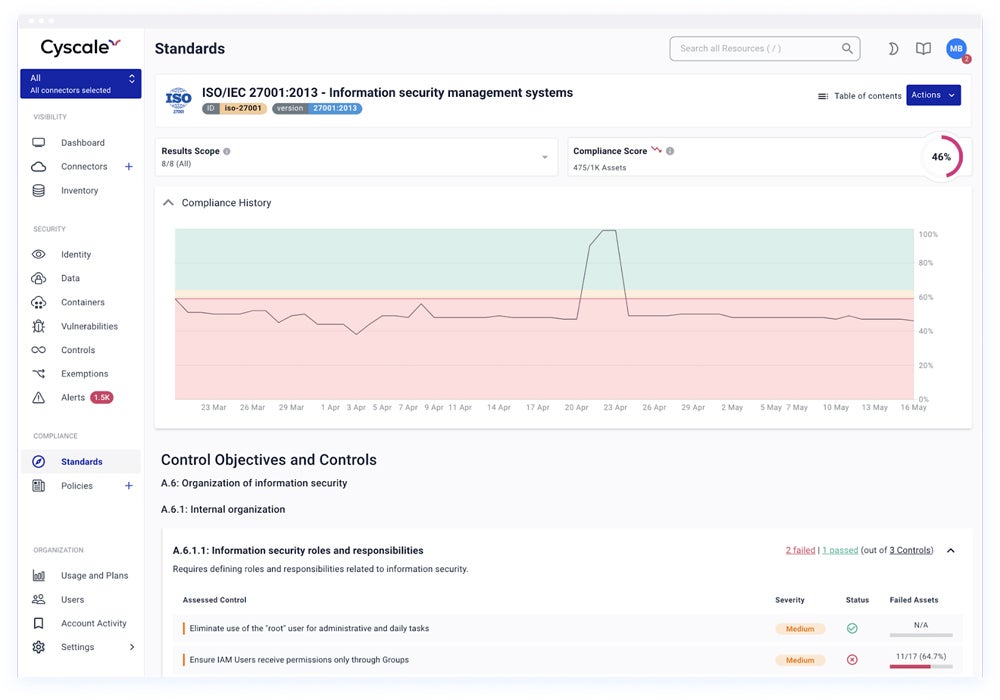
Read our comprehensive review on the different cloud security posture management tools to assess their features, benefits, and cost.
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP)
CNAPP is an all-in-one solution for protecting cloud applications and workloads from various security threats. Combining various cloud security functionalities such as CWPP, CSPM, and CIEM, CNAPP ensures protection across several levels. This includes workloads, applications, identity management, and development environments, handling a wide range of threats and vulnerabilities in cloud-native environments.
Our recommended solution: Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Networks offers full cloud-native application security features. Its CNAPP solution provides full-stack protection for cloud settings and encourages collaboration between security and DevOps teams. Prisma Cloud CNAPP is suited for businesses requiring proactive cloud-native application security. Prices begin at $9,000 per year for 100 Business Edition credits.
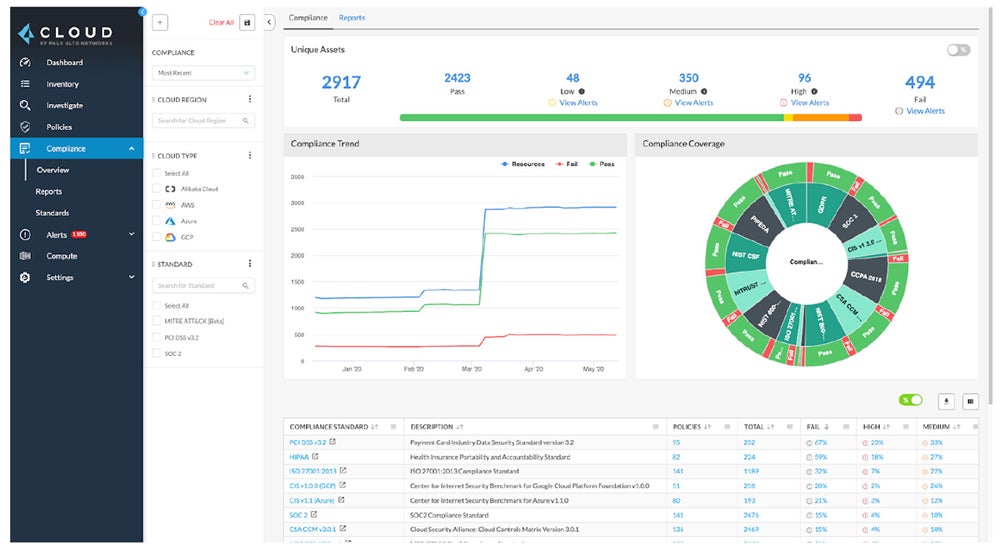
Compare the top cloud native application protection platforms available in the market by checking out our full buyer’s guide covering their distinct features, cost, pros, and cons.
Bottom Line: Enhance Your Strategies with Cloud Security Management
In-house cloud security management guided by a dedicated manager gives firms complete control over their cloud security strategies. You may protect sensitive data and assure continuous cloud operations by leveraging the appropriate knowledge, techniques, and technologies. Combine these strategies with the general cloud security best practices to create a safer, more secure cloud ecosystem.
Take a look at our guide for the cloud security best practices and tips to further improve your cloud security management strategies.








