Databases contain some of the most critical data in enterprises, so vulnerabilities in them are serious issues.
Researchers at Singapore-based cybersecurity company Group-IB recently discovered thousands of databases exposed to the internet that could have been exploited when they were left unprotected. The Attack Surface Management team at Group-IB said it constantly scans the IPv4 landscape for exposed databases, potentially unwanted programs, and other risks. From Q1 2021 to Q1 2022, the team discovered 399,200 exposed databases due to those efforts.
Also read: Database Security: 7 Best Practices & Tips
Redis DBMS Tops the List
The open source Redis database management system (DBMS) was used by the majority of the exposed databases, followed by MongoDB and Elastic. Hackers could use the same methods as Group-IB to exploit the databases.
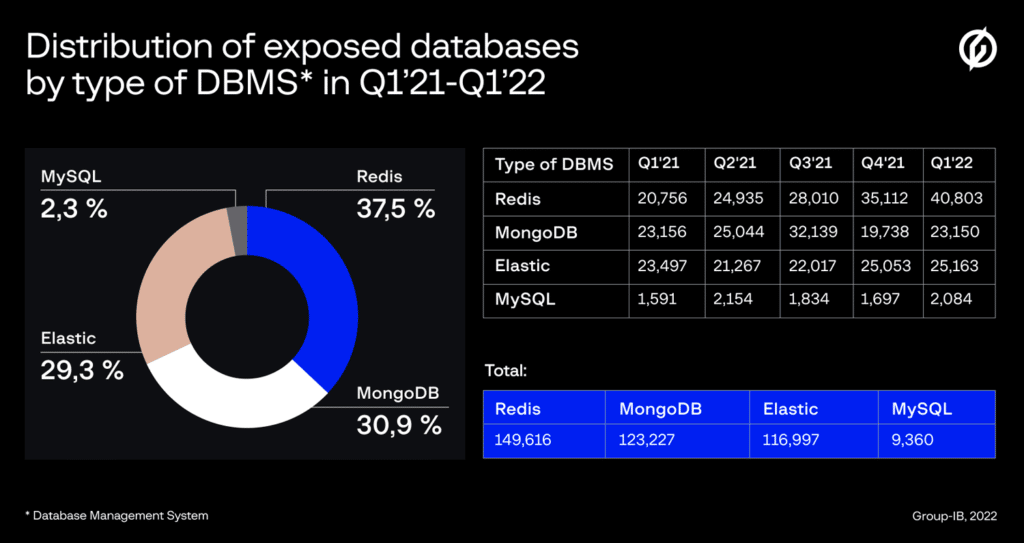
According to Group-IB, the likelihood of the database systems being used in cybercrime and security breaches is high. A data breach, a follow-up strike on clients whose data was exposed, and other risks may result from an exposed database.
When it comes to managing high-risk digital content, prompt discovery of vulnerabilities is critical because threat actors are good at recognizing an opportunity to steal sensitive data, escalate privileges or move laterally in the system.
Time to Resolve Issues is High
According to the Attack Surface Management team, an average of 170.2 days was required for an exposed database owner to resolve a security issue in the first quarter of 2021. The average time decreased gradually throughout 2021, but it returned to the original count of 170 at the start of 2022.
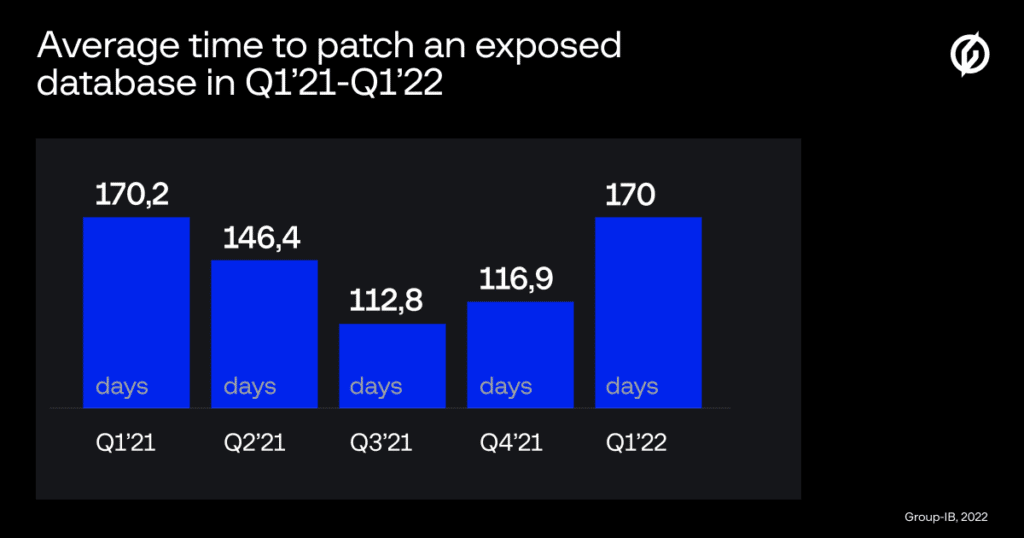
The pandemic was one of the primary reasons for the exposed databases. Remote work compelled organizations to connect their databases to the internet to allow employees access. Changes were frequently made hastily. The policies were incorrectly configured.
U.S. Organizations Most Exposed
Group-IB noted that malware does not infect all internet-facing databases, they just have a chance of being impaired. The U.S. had the highest number of exposed databases, followed by China and Germany.
According to Group-IB, 37.5% of exposed databases used the Redis database management system. MongoDB was the second most vulnerable database management system, used by 31% of the exposed databases. The third most susceptible database management system was Elastic, used by 29% of the exposed databases.
Approximately 93,700 exposed databases were found on servers in the United States, followed by China, with 54,700 exposed databases. German servers hosted 11,100, and France hosted 9,723 of the exposed databases.
“A lot of the security incidents can be prevented with very little effort and a good toolset,” stated Tim Bobak, Attack Surface Management Product Lead at Group-IB.
“Last year, over 50% of our incident response engagements stemmed from a preventable, perimeter-based security error. A public facing database, an open port, or a cloud instance running vulnerable software are all critical but ultimately avoidable risks. As the complexity of corporate networks keeps growing, all the companies need to have complete visibility over their attack surface.”
See our picks for the Top Database Security Solutions
Expectations for Security Breaches Run High
As per Trend Micro’s recent international Cyber Risk Index (CRI) findings for the second quarter of 2021, 76% of those surveyed anticipate a breach within the next 12 months. While this represents a 10% decline, it still indicates critical security holes. Over one-third of organizations experienced seven or more impactful cyberattacks in the preceding 12 months, a 10% rise from the previous year.
The semi-annual report’s findings quantify the gap between respondents’ readiness for attacks and their probability of being breached. The CRI report surveyed over 3,500 chief information security officers (CISOs), IT professionals and managers from Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, and South America in the latter part of 2021.
The CRI study noted five major cyber threats:
- Social engineering and phishing attacks that gain entrance to networks via scam emails with malicious attachments or links
- Botnets that infiltrate and take control of a company’s network
- Fileless attacks that take over legitimate system tools
- Ransomware
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks that target victims’ operational processes
Cyber attacks can lead to stolen or broken tools, costly outside advisors and specialists, regulatory issues and court cases, prestige or reputational damage, and customer turnover, security researchers note.
When it comes to IT infrastructure threats, companies are most concerned about mobile or remote employees, third-party apps, and smartphones. As a result, companies are spending on information security tools to enable secure remote work and increase business efficiency.
Read next: Top Vulnerability Management Tools








