SaaS security checklists are frameworks for protecting data and applications in cloud-based environments. They serve as benchmarks for upholding strong security requirements, evaluating existing tools, and assessing potential solutions. These checklists include security standards and best practices for SaaS and cloud applications, and B2B SaaS providers use them to guarantee that their solutions match customer security standards.
Table of Contents
Free SaaS Security Checklist Template
Each organization’s SaaS security checklist varies — some are customizable to meet specific demands, while others are industry or use-case specific. To begin, you can use a sample checklist to review your SaaS tools or explore new alternatives, then adjust it to your organization’s needs. We’ve designed a customizable template to help you develop your own SaaS security checklist. Click the image below to download the full template.
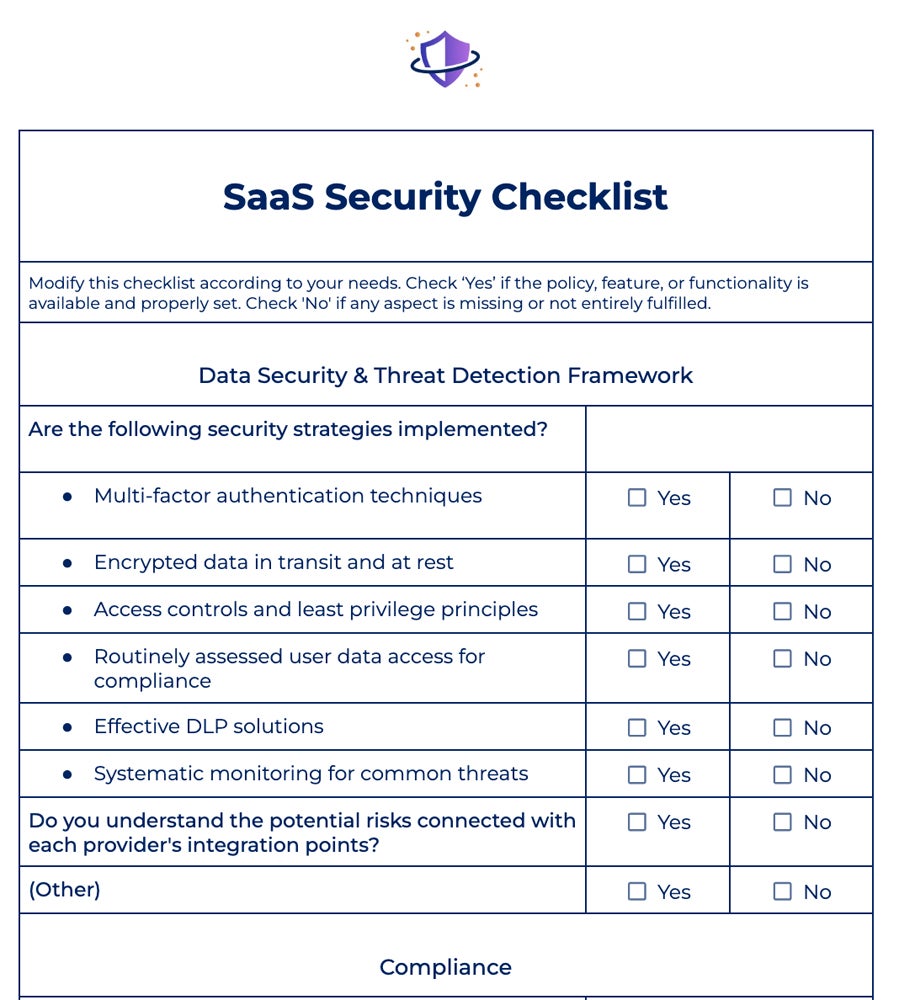
Once you’ve finalized your checklist, respond ‘Yes’ to each checklist item if the listed policy, feature, or functionality is available and properly set. Otherwise, check ‘No’ if any aspect is missing or not entirely fulfilled.
Data Security & Threat Detection Framework
The data security and threat detection framework serves as the foundation for data protection plans, protecting intellectual property, customer data, and employee information. This framework guarantees that appropriate authentication measures, encryption techniques, data retention policies, and backup procedures are in place.
Determine which threats and vulnerabilities affect your firm and its SaaS apps. Common threats include misconfigurations, cross-site scripting attacks, and data breaches. This step reduces the risks of illegal access, data loss, and regulatory noncompliance, as well as protects the integrity and security of sensitive information within SaaS applications.
Questions to Answer
Consider these questions to verify your organization’s data security and threat detection strategies:
- Are multi-factor authentication techniques required for user access?
- Is data encrypted in transit and at rest?
- Are access controls and least privilege principles successfully implemented?
- Is user access to data routinely checked and assessed for compliance?
- Are your data loss prevention (DLP) solutions effective at preventing illegal sharing?
- Do you understand the potential risks connected with each provider’s integration points?
- Is there systematic monitoring in place for common threats?
How to Ensure Data Security & Threat Prevention
To test the efficiency of your SaaS platform’s data security and threat prevention strategy, perform these recommended protocols:
- Encrypt data: Make sure that any data saved in your SaaS application’s databases is encrypted at rest. Data transferred between users’ devices and your servers should be secured during transit using protocols such as transport layer security.
- Implement strong access controls: Employ strategies for verifying user identities. To reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data, users should only be provided with the level of access required to perform their tasks within the program.
- Conduct frequent security audits and penetration testing: Detect and resolve any vulnerabilities before they are exploited by fraudulent actors to minimize the likelihood of data breaches.
- Implement strong monitoring mechanisms: Continuous monitoring and incident response tactics detect suspicious activity or illegal access attempts in real time. Security breaches have a lower impact when they are detected and responded to on time.
- Stay updated with security best practices: Keep up with the latest security best practices and update your security processes and policies on a regular basis to align with emerging threats and regulatory requirements.
Here’s the data security and threat prevention section of our template:

Compliance
Understanding regulatory compliance standards helps organizations meet legal and regulatory requirements. Failure to comply with these standards risks organizations of legal problems, fines, or reputational damage. SaaS systems frequently handle sensitive client information, and compliance covers this by protecting data security, reduces risks, and fosters trust among stakeholders.
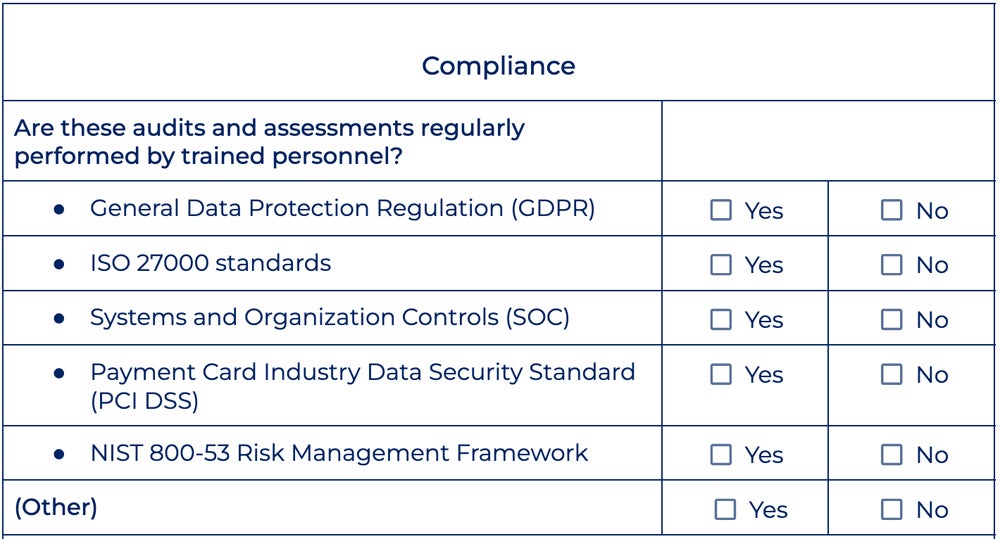
Common compliance standards include GDPR, which governs data processing for EU members; PCI DSS, which guarantees safe credit card transactions; and NIST 800-53 for IT risk management. ISO 27000 is a standard for information security and SOC is for maintaining consumer data integrity and security across several dimensions.
Questions to Answer
Check if you adhere to these common compliance standards:
- Do you conduct frequent audits and evaluations to guarantee continuous compliance with applicable regulatory standards and frameworks?
- Are you in compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for the collection and processing of EU member data?
- Is your firm in compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) to protect cardholder data during transactions?
- Do you use the NIST 800-53 Risk Management Framework to examine IT risks?
- Are you in compliance with ISO 27000 information security management standards for securing third-party data, financial information, intellectual property, and employee data?
- Have you implemented Systems and Organization Controls (SOC) to ensure customer data integrity, confidentiality, and availability in accordance with SOC framework criteria?
How to Verify Compliance Standards Adherence
Here are some guidelines to help you decide whether your business needs to comply with certain standards:
- Check the applicability: Establish whether your company handles sensitive data or conducts transactions subject to regulatory standards such as GDPR or PCI DSS. Research whether a specific compliance is required in your sector.
- Identify the client requirements: If your clients or partners demand compliance, make sure your organization fulfills their criteria in order to continue business partnerships.
- Review your legal obligations: Determine whether your organization is subject to any legal mandates based on its location or jurisdiction, and consider the potential legal implications of noncompliance.
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis: Do a thorough study of the costs and benefits of compliance in order to make informed decisions consistent with your organization’s strategic goals and objectives.
- Consider voluntary compliance: Consider implementing industry best practices to improve data security and establish trust with stakeholders even if compliance is not required. Then, examine the risks connected with data security and privacy.
- Maintain transparency and communication: Explain your organization’s approach to data security and privacy to customers, partners, and stakeholders. Transparency about your security policies can help build confidence and credibility.
Below is the compliance section of our checklist:
SaaS Vendor Evaluation
When assessing SaaS vendors, consider a variety of aspects, including service metrics such as uptime, response time, and customer assistance availability. Examine cost factors like license terms, price, and professional service fees. Furthermore, assess features including integrations, single sign-on (SSO) support, reporting capabilities, contract conditions, and the vendor’s ability to supply actionable insights and recommendations.
Questions to Answer
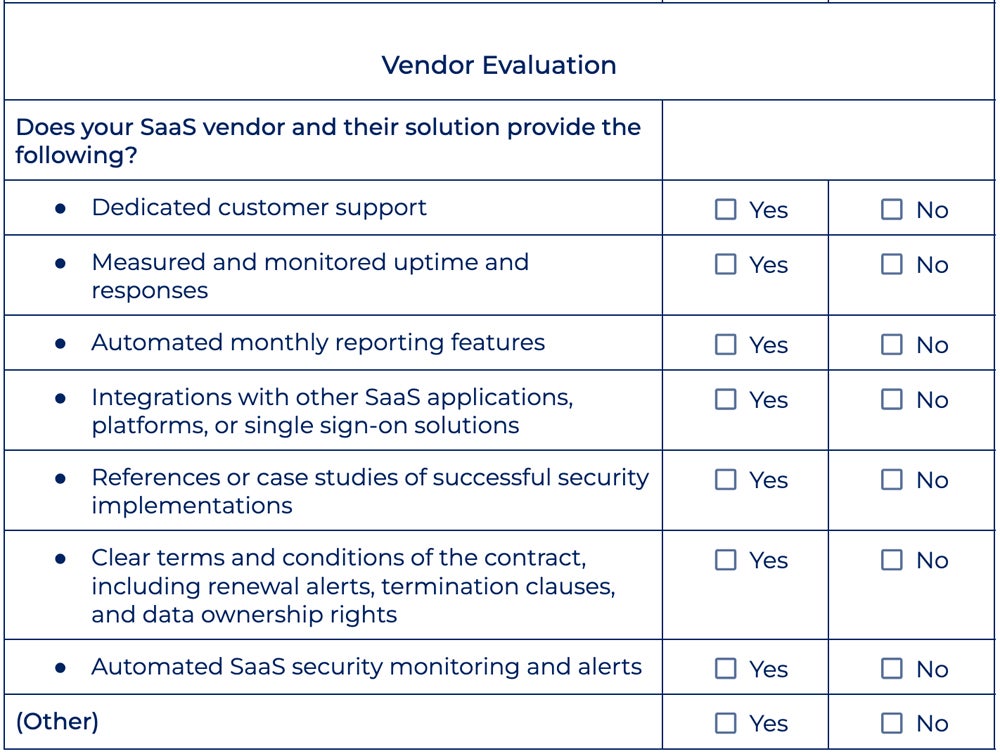
To evaluate your SaaS vendor, ask yourself these questions:
- Does the vendor offer dedicated customer support and what is their availability?
- What are the SaaS service’s uptime and response time assurances, and how are they determined and monitored?
- Are there automated monthly reporting features that provide insight into security performance and compliance?
- What integrations does the vendor provide with other SaaS apps, platforms, and single sign-on solutions?
- Can the vendor give references or case studies that show effective security deployments in similar organizations?
- What are the contract’s terms and conditions, including renewal notices, termination provisions, and data ownership rights?
- Do your cloud providers provide automated SaaS security monitoring and alerts?
How to Evaluate Your SaaS Vendor
Every vendor solution your organization uses should fit with your needs. Do the following to test its suitability:
- Check the vendor’s privacy policies: Inquire about the vendor’s data encryption processes, both at rest and during transit. Review the vendor’s privacy policies to see how they handle and secure consumer data, such as data retention and sharing.
- Assess vendor solution’s security features: Evaluate the vendor’s security controls and access management features to see how they prevent unwanted access to your data. Look for features such as RBAC, MFA, SSO, and audit logs.
- Consider security certifications in evaluation: Look for SaaS vendors who have received necessary security certifications, follow industry standards and regulations, and provide solutions to manage compliance.
- Explore incident response and data breach policies: Inquire about the vendor’s solutions for detecting, reporting, and responding to security issues, as well as their communication protocols for alerting customers about any breaches or vulnerabilities.
- Security infrastructure and redundancy: Check the vendor’s data centers, network architecture, backup and disaster recovery plans, and uptime assurances. Confirm that the vendor uses industry-standard security technologies and processes.
Take a closer look at the SaaS vendor evaluation checklist below:
IT Infrastructure Analysis
This phase underscores the value of investing in IT infrastructure security. This includes protecting diverse technological assets, such as software, hardware, devices, and cloud resources, from potential security flaws like malware, ransomware, theft, phishing assaults, and bots. Cloud infrastructure security should specifically handle layers such as physical assets, applications, networks, and data for complete protection against security threats.
Questions to Answer
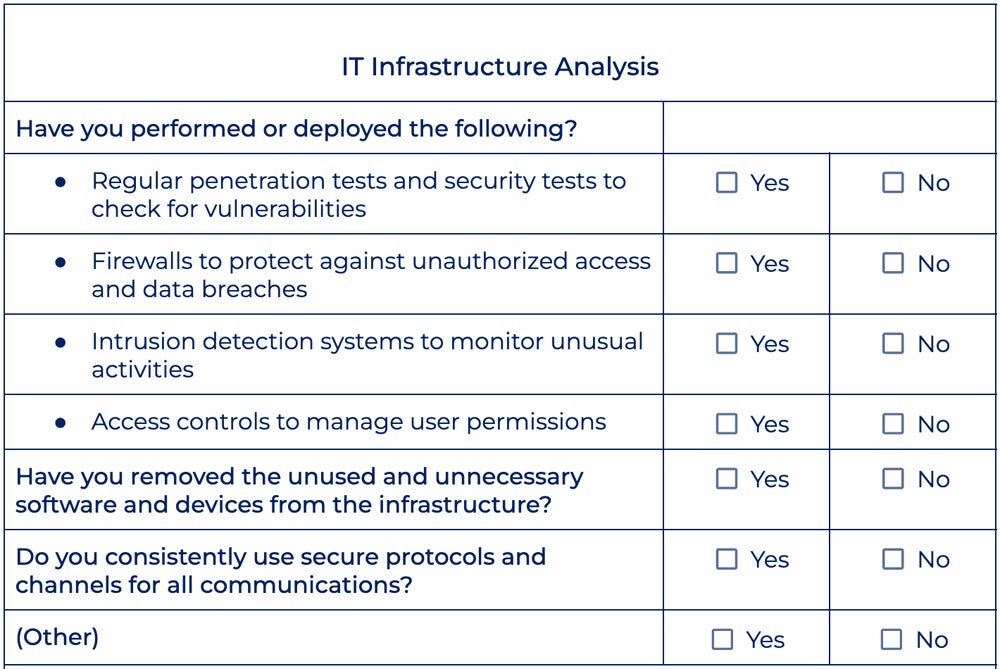
When assessing your IT infrastructure, here are several key factors to consider:
- Have regular penetration and security testing been performed to identify vulnerabilities?
- Have all unused and unnecessary software and equipment been removed from the infrastructure?
- Are secure protocols and channels utilized consistently across all communications?
- Are access restrictions in place and periodically assessed to efficiently manage user permissions?
- Are firewalls configured and maintained to prevent unwanted access and data breaches?
- Have intrusion detection systems been established and maintained so that any security risks can be detected and addressed quickly?
How to Conduct an IT Infrastructure Analysis
Gain insights into your infrastructure to make informed decisions about the solutions your organization needs. Follow these guidelines below:
- Create a software and device inventory: Make a complete list of all software programs and devices in the infrastructure. Identify any unnecessary or obsolete software and devices through the inventory process.
- Evaluate the network architecture: Determine whether the SaaS provider uses network segmentation to separate client data and apps from one another, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement in the event of a security breach.
- Assess the physical security measures: Evaluate access controls, surveillance systems, and environmental controls. Check that the data centers’ physical security meets industry requirements, as well as their redundancy and failover capabilities.
- Review storage and customer data protection methods: Make sure your provider uses robust encryption techniques and key management practices to preserve data confidentiality and integrity.
- Examine security monitoring capabilities: Inquire about the tools and procedures used to detect and respond to security issues in real time, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Explore the IT infrastructure analysis portion of our security checklist:
Cybersecurity Training
Cybersecurity training is a workforce initiative that helps all employees identify threats and potential attacks. Social engineering, for example, is a threat that makes use of human vulnerabilities for illegal access. Internal actors also play a substantial role in cybersecurity breaches. Ongoing training initiatives can cover security factors beyond basic awareness, enabling personnel to spot and mitigate possible cyber risks efficiently.
Questions to Answer
Check the following to see if your cybersecurity training policies are properly executed:
- Have employees been informed of risky cybersecurity behaviors, such as accessing public Wi-Fi or unsecured personal devices for work-related tasks?
- Is there cybersecurity training on best practices, including setting strong passwords in accordance with the organization’s policy?
- Have employees been informed of basic security risks like malware, phishing, and hardware loss, all of which take advantage of human errors?
- Is multi-factor authentication established, and are staff instructed on how to use it?
- Is there a human-factor cybersecurity evaluation strategy in place to regularly examine workforce cybersecurity threats?
- Are staff routinely assessed on their cybersecurity knowledge and awareness using tests or simulations?
How to Implement Proper Cybersecurity Training
Effective cybersecurity training should educate employees of the potential risks and best practices for using SaaS applications securely. Here are five tips to help you conduct these trainings efficiently:
- Customize the training materials: Address the unique security concerns of your organization and cover topics like data encryption, access controls, authentication systems, and data privacy rules.
- Emphasize phishing awareness: Set a portion of the training to teach staff about phishing threats and how to identify and report suspicious emails, links, or attachments. Teach them how to verify the sender’s address and URL.
- Encourage strong password practices: Provide tips on how to create complex passwords and use password management tools. Emphasize the need to change passwords on a regular basis to reduce the risk of credential-based attacks.
- Train employees on secure data handling practices: Encourage employees to minimize the use of personal accounts for work-related activities and report any suspicious or illegal access to sensitive data as soon as possible.
- Provide regular updates and reinforcement: Schedule regular cybersecurity awareness courses, workshops, or newsletters to reinforce key principles, provide recent security incidents or trends, and offer online safety recommendations.
Here’s a peek at the cybersecurity training checklist from our template:

Disaster Response
Developing a disaster response strategy contributes to effective risk management against cyberattacks. Check cybersecurity authorities’ recommendations and develop a plan that includes preventive measures, incident response methods, and communication techniques. This method prepares you for an attack and facilitates effective coordination during situations of crisis. It also minimizes potential damages, safeguards assets, and sustains business continuity.
Questions to Answer
To examine your disaster response preparedness, check the following:
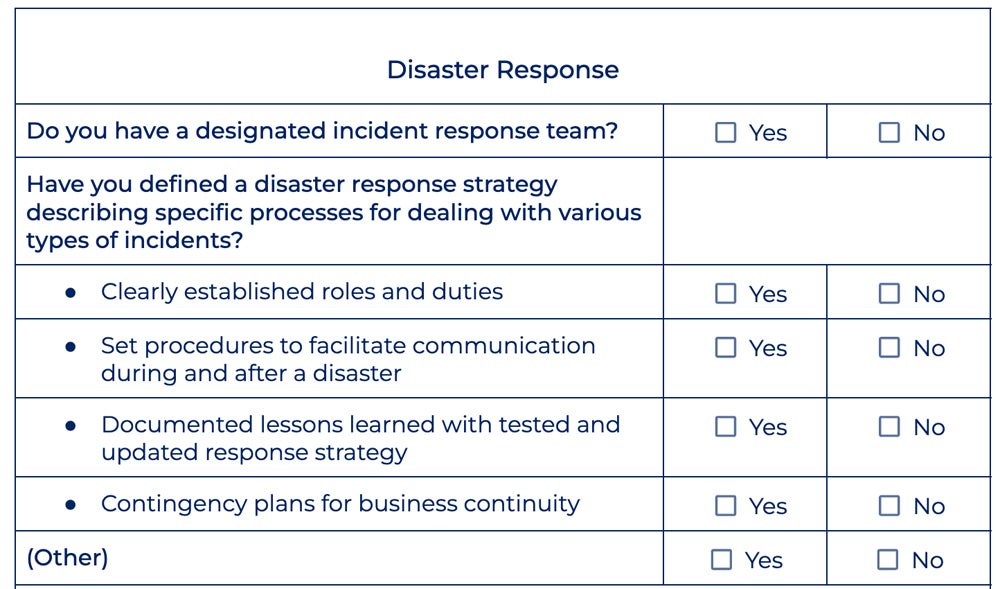
- Is there a designated incident response team that’s trained and equipped to carry out the response plan effectively?
- Is there a defined disaster response strategy describing specific processes for dealing with various types of incidents?
- Are roles and duties clearly established in the response plan?
- Are there systems in place to facilitate communication and cooperation during and after a disaster?
- Has the response strategy been tested and updated on a regular basis, taking into account lessons learned?
- Are contingency plans in place for business continuity during and after a disaster?
How to Achieve Disaster Response Preparedness
A good disaster response strategy mitigates the impact of security incidents and operation disruptions. Conduct an efficient disaster response plan with these methods:
- Identify critical apps and data: Perform a thorough review to prioritize the relevance of each application and data set based on considerations such as business impact, regulatory compliance, and consumer expectations.
- Implement redundancy and backup procedures: Use redundant SaaS or alternative service providers to reduce single points of failure and spread your risk exposure. Backup crucial data and configurations on a regular basis to a safe remote location.
- Create thorough incident response plans: Define roles and duties for key staff, establish communication channels, and document escalation procedures. Conduct regular tabletop exercises to assess its effectiveness.
- Deploy continuous monitoring and alerts: Set up alerts and notifications for potential security issues such as unauthorized access, data breaches, or service outages. Invest in solutions that automate threat detection and response procedures.
- Develop clear communication and coordination protocols: Define communication routes, escalation paths, and key stakeholders’ points of contact to foster effective collaboration. Maintain communication for threat intelligence and sharing incident details.
Here’s a preview of the disaster response section included in our template:
Policy Evaluation & Updates
Finally, a retrospective examination of cyber occurrences informs changes to security methods, processes, training, and policies. Organizations can improve their security by recognizing flaws and lessons learned. This iterative process helps them remain adaptable and robust to evolving cyberthreats, always enhancing their security posture to effectively minimize risks.
Questions to Answer
Assess your existing policies and needs for updates based on the questions below:
- Has a formal framework been established for conducting retrospective analysis of cyber incidents?
- Are detected gaps and lessons learned from the analysis documented and addressed in security measure updates?
- Do security processes, procedures, training, and policies get reviewed and updated on a regular basis?
- Is there a dedicated person or team in charge of overseeing the updating of processes?
- Are security updates successfully disseminated to important stakeholders?
- Are there systems in place to track and monitor the deployment of modifications to guarantee consistency?
How to Perform Policy Evaluation & Updates
When doing your policy evaluation and updates, establish system protocols based on lessons learned and plan for any changes. Below are some guidelines on how to conduct policy analysis and updates effectively:
- Document incident details: Include the nature of the attack, the systems or data that were affected, the timeline of events, and the response steps performed. Gather feedback from all stakeholders, including IT, security, and business departments.
- Conduct an exhaustive root cause analysis: Investigate all technical and human reasons that contributed to the incident, such as software vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, insider threats, or a lack of security awareness.
- Evaluate the efficiency of current security protocols: Identify any gaps in the organization’s security posture disclosed by the incident, and see if existing measures were properly implemented. Determine if additional controls need to be implemented.
- Identify points of improvement based on lessons learned: Carry out corrective actions and remedial efforts to close security gaps, tighten controls, and raise security knowledge and readiness within the business.
- Update security protocols, training, and policies: Assess the timeliness and efficacy of incident detection, containment, eradication, and recovery operations, as well as the gaps in communication. Identify ways to streamline and automate your procedures.
Here’s a snippet of the policy evaluation and updates portion of our checklist:

Bottom Line: Create a Solid SaaS Security Checklist
Following the procedures outlined above establishes the groundwork for a solid security posture, including threat protection, regulatory compliance, and data continuity. SaaS security necessitates continued vigilance. There should be continuous training, testing, and monitoring in order to efficiently adapt to emerging cybersecurity threats while maintaining an optimal level of security.
Review your identity and access management (IAM) strategies, among other security methods as prescribed by SaaS industry standards, to safeguard data integrity, availability, and privacy effectively.








