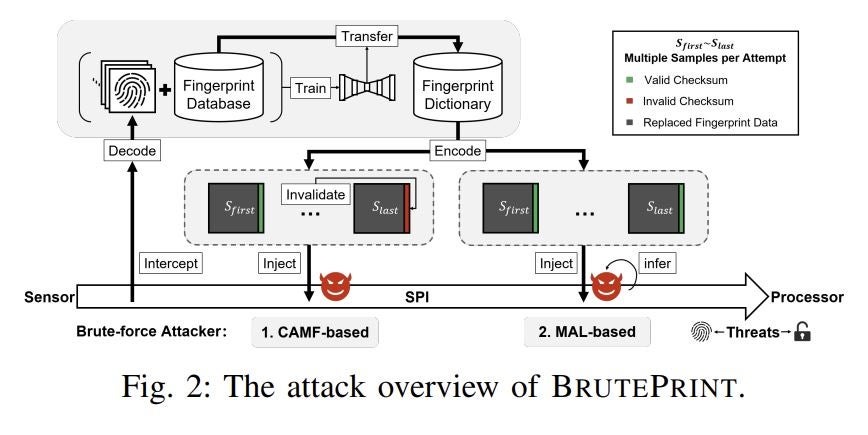
The modern enterprise is mobile and employees are no longer tethered to their corporate owned and provisioned computing equipment. As is the case in the wired world, mobile end-user devices need to be managed to improve employee productivity and to reduce enterprise security risks. That’s the world that Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) inhabits.
What is EMM?
The term Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) is an evolution of the technology used to help control and manage mobile devices.
EMM is an evolution of the Bring Your Device (BYOD) phenomenon that has been going on for well over a decade in organizations around the world. The emergence of Apple’s iPhone a decade ago was a real catalyst in the movement, as employees chose to use their own iPhones over corporate provided devices. The first generation of BYOD management platforms was known as Mobile Device Management (MDM) and originally focused largely on the hardware enrollment and access part of the BYOD challenge.
The Mobile Application Management (MAM) categorization of mobile management technologies was initially all about helping organizations manage the software piece, specifically client-side applications running on mobile devices.
The early promise of MAM was to provide capabilities that were not in MDM, namely the application piece, providing curated app stores for corporate use as well as data management policies. While MDM initially was all about hardware and MAM was about the software, the term Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) is a superset of both MDM and MAM capabilities as well as adding mobile information management.
EMM features
A full EMM platform contains multiple capabilities to help secure mobile device usage in an enterprise environment.
- Access: EMM can help enforce access rules based on device and policy.
- Data protection: Data that is on a mobile device that is protected by an EMM can be encrypted, with options for remote lock and wipe.
- App management: An EMM platform can provide enterprise app ‘stores’ or enterprise application catalogues, serving as a curated repository of enterprise applications that can be easily downloaded by enrolled devices.
- Threat management:The ability to scan devices for known issues as well as offering proactive threat management is sometimes part of EMM solutions.
- Separation of work and personal: Some EMM solutions help solve the challenge of commingling of data on a BYOD device with some form of isolated area, on the device, to help keep work data separate from personal data.
- Visibility and control: EMM systems also offer visibility into the devices that are connecting to a network and what resources they are consuming.
Setting up EMM
Different vendors have different approaches to EMM platform deployment. Some deployments can be done as an on-premises software installation, though many vendors today offer some form of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) cloud-hosted EMM application.
Once the EMM platform is set up (either on-premises or in the cloud), the process of getting devices controlled is referred to as device enrollment.
Device enrollment can be done via:
- SMS
- URL enrollment
The actual EMM control often involves the use of a client-side download application, and some solutions will also include some form of network gateway or proxy control as well.
While many vendors provide a bulk enrollment capability, many will also offer a user self-service portal that enables users to request access.
EMM products
EMM vendors include:
- VMware AirWatch
- Mobile Iron
- IBM MaaS 360
- Citrix Xen Mobile
- Landesk Mobility Suite
- Blackberry EMM / Good Secure EMM Suite
- Microsoft Enterprise Mobility Suite
See our picks for the 5 top EMM solutions.