The failed CrowdStrike sensor update that affected Windows systems may have put those computers at risk, but this is just one potential vulnerability during an interesting week. SolarWinds recently patched 13 vulnerabilities, and Ivanti has fixed yet another flaw in its Endpoint Manager product. The CISA requires federal agencies to patch their instances of GeoServer by August 5, and Wiz recently reported on a major AI model training vulnerability.
Regularly update your hardware and software to the most recent approved versions. Also, make sure your security team has a consistent schedule for monitoring industry news and vulnerabilities. This helps you stay on top of updates before threat actors have much time to exploit potential flaws in your infrastructure.
July 1, 2024
Early July Splunk Enterprise Vulnerability Should Be Patched Immediately
Type of vulnerability: Path traversal.
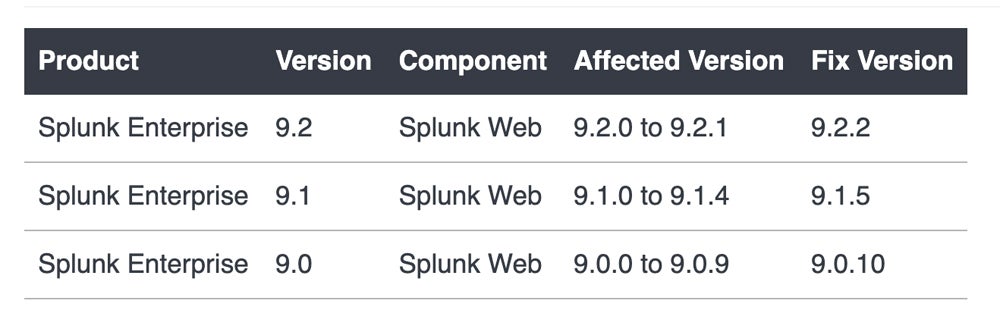
The problem: A vulnerability within Splunk’s Enterprise application allows an attacker to perform a path traversal on the /modules/messaging/ endpoint in Windows installments of Splunk Enterprise. The vulnerability affects app versions below 9.2.2, 9.1.5, and 9.0.10. Splunk released the notice for the vulnerability at the beginning of July, but it’s now getting more attention.
According to the security notice, “The vulnerability exists because the Python os.path.join function removes the drive letter from path tokens if the drive in the token matches the drive in the built path.”
The vulnerability should not affect Splunk Enterprise on non-Windows operating systems, like Linux. A proof of concept is available on GitHub.
The fix: Splunk provides the following chart for fixed versions. Any version higher than 9.2.2, 9.1.5, and 9.0.10 also works.
July 15, 2024
CISA Requires Patches for GeoServer RCE Vulnerability
Type of vulnerability: Remote code execution.
The problem: GeoServer, an open-source server for sharing and processing geospatial data, has a critical vulnerability in its GeoTools library API. When exploited, the flaw allows unauthenticated users to execute code remotely. According to the vulnerability notice:
“The GeoTools library API that GeoServer calls evaluates property/attribute names for feature types in a way that unsafely passes them to the commons-jxpath library, which can execute arbitrary code when evaluating XPath expressions. This XPath evaluation is intended to be used only by complex feature types… but is incorrectly being applied to simple feature types as well, which makes this vulnerability apply to ALL GeoServer instances.”
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has warned users of this vulnerability and now requires federal agencies to apply patches by August 5. It’s currently tracked as CVE-2024-36401.
The fix: Update your GeoServer instance with version 2.23.6, 2.24.4, or 2.25.2, which contain a patch for the issue.
If your business needs dedicated and consistent vulnerability scanning, read our guide to the best scanners next.
July 16, 2024
Ivanti Fixes Another EPM Issue
Type of vulnerability: SQL injection.
The problem: Ivanti recently released a security advisory for an SQL injection vulnerability within Ivanti Endpoint Manager 2024 flat. If exploited, the vulnerability allows a threat actor on the same network as Endpoint Manager to execute code arbitrarily without being properly authenticated.
The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2024-37381 and has a severity rating of 8.4.
The fix: Ivanti provides instructions for downloading a hot patch for EPM 2024 flat within the security advisory:
- Download the linked Security Hot Patch zip files.
- Make sure the two DLL files are unblocked.
- Replace the DLLs within the Core Server with the ones from the Hot Patch in the locations specified.
- If you use the PowerShell script, insert the hotpatch folder into directory C:\Program Files\LANDesk\ManagementSuite\. Use PowerShell as an admin and run JulyEPM2024HotPatch.ps1.
- Either reboot the Core Server or or close the EPM Console and run IISRESET so the new DLLs load properly.
July 17, 2024
Full Effect of Critical Cisco Vulnerability Unknown
Type of vulnerability: Form of authentication bypass.
The problem: Cisco Smart Software Manager On-Prem (SSM On-Prem) has a critical vulnerability in its authentication mechanism. It’s a result of a faulty password change implementation procedure. If a device is affected by the vulnerability, an attacker can send specifically designed HTTP requests to that device.
When exploited successfully, the vulnerability allows the attacker to use compromised privileges to access the target user interface or API. They can then change other users’ passwords, including potential administrative credentials. Experts aren’t sure what could happen within the Cisco network once an attacker manages this, and Cisco hasn’t yet clarified this in a security bulletin.
The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2024-20419 and has a CVSS score of 10, the highest a vulnerability can receive.
The fix: This vulnerability affects Cisco SSM versions 8-202206 and earlier. The first fixed release of the software is 8-202212; upgrade to this version of Cisco SSM as soon as possible. Cisco’s ongoing fixed releases within the security bulletin for this vulnerability.
SolarWinds Fixes 13 Issues in Access Rights Manager
Type of vulnerability: Multiple, including remote code execution.
The problem: SolarWinds has addressed 13 vulnerabilities within its Access Rights Manager software, a user provisioning and access management tool for Active Directory and Azure AD. These include remote command injection, remote code execution, and traversal and information disclosure vulnerabilities. Of the 13, eight are critical and have a CVSS score of 9.6. Each has its own advisory notice from SolarWinds.
Combined, the vulnerabilities allow attackers to use SYSTEM privileges, leak data, and read and delete files arbitrarily without authentication.
Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative partners with SolarWinds and helped it identify the vulnerabilities.
The fix: Download the fixed version of the software, Access Rights Manager 2024.3, to prevent exploitation.
Wiz Report Reveals Weaknesses in SAP AI Core
Type of vulnerability: Arbitrary code execution using AI training models.
The problem: A report by security vendor Wiz discusses isolation issues within AI platforms, particularly SAP AI Core. AI Core facilitates integrations with other cloud services like HANA to access customer data using cloud access keys, according to Wiz. The researchers’ work revealed that they could move laterally and access private customer files and cloud account credentials using SAP’s legitimate AI training procedures.
The researchers were also able to successfully use cluster administrator privileges on the SAP AI Core Kubernetes cluster.
The fix: Wiz reported the vulnerabilities to SAP, which fixed them. Wiz also states that no customer data was compromised. Because training AI models naturally involves running arbitrary code, vulnerabilities are often baked into the AI training process. A long-term fix would mean setting more careful guardrails on this process and doing better sandboxing and isolation, according to Wiz.
July 19, 2024
Failed CrowdStrike Update Creates Opportunity for Hackers
Type of vulnerability: General possibility of exploit when Windows systems are down.
The problem: While this isn’t a specific type of vulnerability or software issue, the update failure of CrowdStrike’s Falcon Sensor last Friday did create the possibility for Windows systems to be attacked while weak. The attempted update to Falcon Sensor created an endless update cycle and the “blue screen of death,” which caused Windows systems globally to crash.
CrowdStrike stated that the issue was not a cyberattack. Its CEO, George Kurtz, initially posted on LinkedIn about the nature of the event — saying that it wasn’t a security incident — and received significant pushback for this statement. While the issue was a software error rather than an attack, it did create a security incident that could lower defenses on Windows systems.
The fix: CrowdStrike isolated the incident and has worked to fix it. It published a video for remote users to self-remediate their Windows laptop if the device is still having issues with the blue screen of death.
July 22, 2024
Open-Source Platform BOINC Spoofed by Threat Actors
Type of vulnerability: Malware payloads.
The problem: Managed security provider Huntress recently published a report on SocGholish malware behavior. SocGholish is now delivering AsyncRAT and Berkeley Open Infrastructure Network Computing Client (BOINC) payloads to victims.
BOINC is an open-source platform for volunteer computing. “The intention is to use ‘donated’ computer resources to contribute to the work of various legitimate science projects,” the Huntress researchers said. Malicious installations of BOINC look like they might route to a legitimate BOINC server that’s actually a different address. Huntress reports that it hasn’t yet noticed the infected hosts executing malicious activity.
This vulnerability does not reside within BOINC; rather, it’s a type of malware that installs malicious versions of BOINC. It is less a standard software vulnerability than a method by which threat actors deliver malicious payloads using open-source software.
The fix: Huntress provides the following indicators of compromise and file indicators:

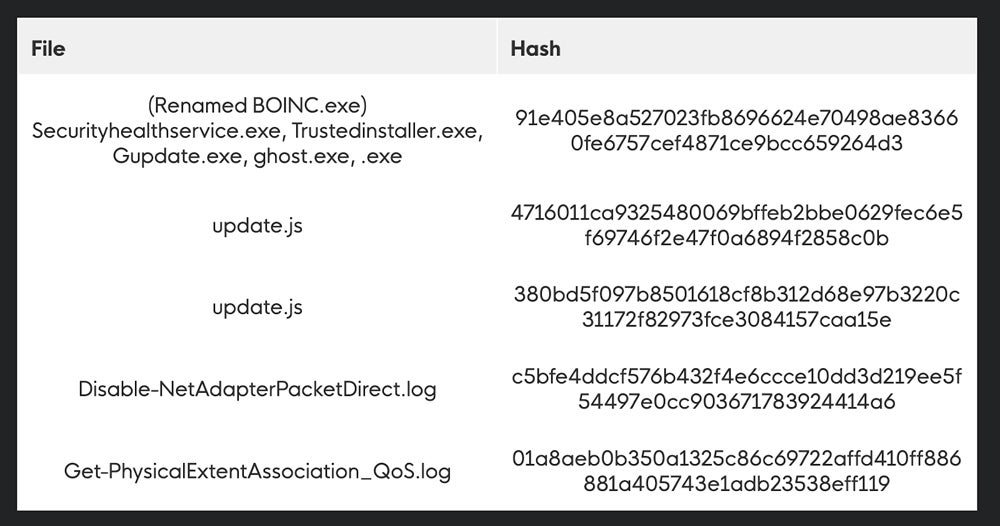
While it’s rare for businesses to use BOINC, watch for any attempted installations of it, which could indicate an attack, according to Huntress.
Read next:
- Vulnerability Recap 7/15/24 — Industry Patches vs Flaw Exploits
- Best Vulnerability Management Software & Systems in 2024








