Private clouds avoid the shared environment of public cloud environments and thus are considered more secure, but users still need to take steps to get private cloud security right.
Private cloud security is the set of techniques, technology, and requirements used to safeguard data and resources in a private cloud environment. We’ll explore the fundamentals of private cloud security, its purpose, benefits, challenges, and how it differs from public cloud security.
Also read: Public Cloud Security Explained: Everything You Need to Know
Table of Contents
What is the Purpose of a Private Cloud?
Private clouds can be hosted in an on-site data center or run by a third-party service provider, but the common theme is they avoid the “multi-tenancy” of public cloud service providers. Private clouds are tailored to a particular business and thus provide better control over security measures. Private clouds are a very good choice for sensitive and regulated data and applications, even as they require high levels of expertise and cost.
Private cloud security is thus the application of best practices and controls to protect data in private cloud environments from unwanted access, data breaches, and cyber threats while ensuring the highest standards of data privacy and confidentiality. Ultimately, the core goal of private cloud security is to allow enterprises to reap the benefits of private cloud computing while preserving the integrity and security of their key assets.
How Private Clouds Work
Private clouds work by providing a specialized cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization, typically one with high security requirements. Cybersecurity is built in from the start through a combination of physical security, network segmentation, encryption, access restrictions, monitoring, and other security measures. Here are the steps involved in setting up a private cloud; many of the elements are designed with security in mind.
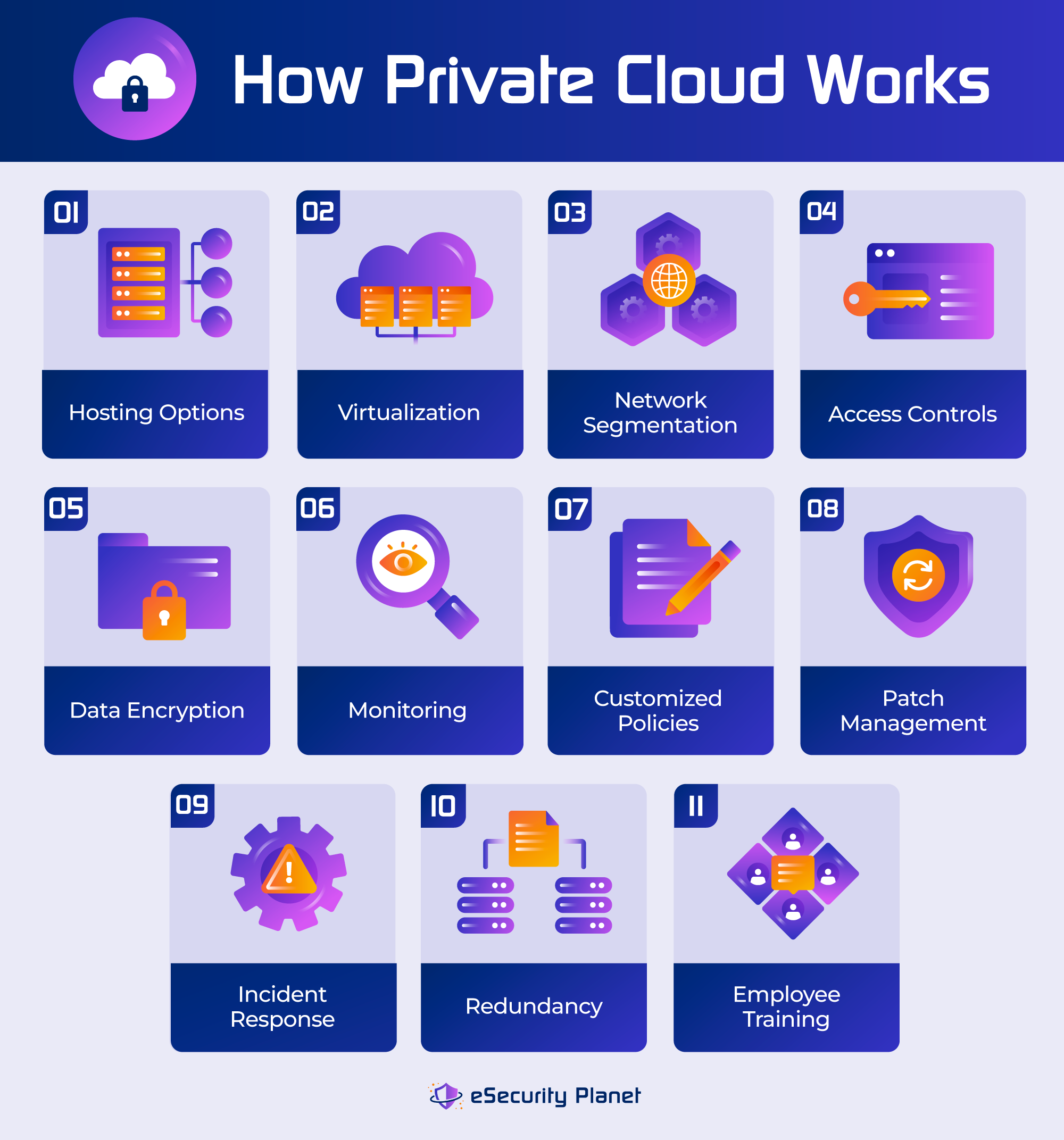
- Setting up a private cloud infrastructure: The process starts with the setup of a private cloud infrastructure. Private cloud configurations can be hosted on-premises or by third-party cloud service providers.
- Optimizing virtualization: Virtualization technologies such as VMware, Hyper-V and containers are used in private clouds to provide flexibility in resource allocation and isolation.
- Implementing network segmentation: VLANs provide network segmentation, which limits the attack surface and helps enforce security policies. Security rules, access restrictions, and firewalls may be customized for each VLAN.
- Setting access rules: Access controls, such as authentication, role-based access controls, and permissions management, limit access to sensitive data and resources.
- Encrypting sensitive data: With secure key management, data encryption protects data in transit and at rest. To avoid unwanted decoding, encryption keys are securely handled.
- Monitoring records and activities: Comprehensive and continuous monitoring and logging technologies detect activity and produce alerts for potential security breaches. For audit and forensics purposes, detailed records are kept.
- Customizing policies for compliance: Private cloud security policies are tailored to an organization’s unique needs and compliance requirements. These policies may be in accordance with industry-specific compliance standards such as HIPAA or PCI DSS, and they may include procedures to enforce data retention, auditing, and reporting obligations.
- Applying patches: Patch management is critical for addressing vulnerabilities, maintaining security, and keeping the private cloud infrastructure and applications up to date with the most recent security updates.
- Implementing incident response: An incident response plan covers security breach detection, containment, mitigation, and recovery processes. The strategy also includes communication channels to keep each stakeholder informed. This guarantees that security breaches are dealt with quickly.
- Ensuring failover mechanisms: Redundancy and disaster recovery systems ensure high availability and data continuity. In case of hardware failures or disasters, redundant systems and data backups are maintained to minimize downtime and data loss.
- Training the team: Employee security training and awareness programs give employees the knowledge they need to help maintain a secure private cloud environment, such as phishing prevention and sensitive data management.
Also read: 13 Cloud Security Best Practices & Tips
Private Cloud Security Standards
For enterprises running private cloud environments, data security and privacy requirements and legal ramifications are key concerns. Compliance with these standards and laws is critical for avoiding legal issues, safeguarding sensitive data, and maintaining stakeholder and customer confidence.
Standards such as ISO 27001 and NIST SP 800-53 indicate a commitment to data security and may be needed for government-related activity. HIPAA and PCI DSS impose strict security and privacy standards on healthcare and payment processing firms, respectively. GDPR imposes data protection and privacy protections for firms managing EU citizen data, regardless of location, and other governments have followed with similar restrictions, such as California’s CCPA. FISMA requires security reporting for private cloud providers that serve government agencies. Strong access controls and data handling standards are required by Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) and a number of other data protection laws.
Private clouds must adhere to numerous security standards and best practices to provide users with the highest level of security. Common security measures include:
- Access restrictions to limit who can access private cloud services and what they can do once inside
- Encrypted data in transit and at rest to further prevent unwanted access
- Segmentation that separates a network into smaller segments to shrink the attack surface and prevents attackers from moving laterally
- Comprehensive monitoring and logging techniques to detect and respond to security issues
Also read: CSPM vs CWPP vs CIEM vs CNAPP: What’s the Difference?
Top 7 Benefits of Private Cloud Security
Private cloud security can give your organization improved data privacy, regulatory compliance, increased control, better performance, customization options, and strong business continuity protections. These potential benefits make secure private clouds an appealing option for enterprises with strict security requirements and legal commitments, as they allow them to secure sensitive data while keeping control and flexibility over their cloud infrastructure.
1. Enhanced Data Privacy
Private cloud systems offer stronger data privacy than public clouds. Data is kept and processed within the organization’s specialized infrastructure in a private cloud, minimizing the danger of illegal access or data disclosure. This increased privacy is especially important for firms that handle sensitive or secret data, such as financial information or personal health records.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Private clouds enable businesses to establish security measures that are tailored to individual regulatory needs. This is especially important in businesses with strict standards, such as healthcare (HIPAA), finance (SOX, FFIEC, GLBA), and payment processing (PCI DSS). Private cloud security solutions may be tailored to satisfy these compliance criteria, lowering the risk of noncompliance and the potential penalties that come with it.
3. Greater Control
Private cloud owners have total control over their cloud infrastructure, including hardware, software, and security rules. With this degree of control, businesses may create and deploy security solutions that are tailored to their specific needs and risk tolerance. Private clouds also enable quick reaction to security risks and incidents.
4. Improved Performance
Private clouds often provide dedicated and guaranteed resources for consistent and predictable application and workload performance. In contrast, public clouds may encounter performance challenges as a result of resource pooling among several users. Improved performance is essential for applications that demand fast data processing and minimal latency.
5. Customization
Private clouds may be tailored to meet individual application, workload, and security needs. Organizations may modify security solutions to safeguard their most important assets while being adaptable to evolving security threats. This customization allows enterprises to achieve the proper balance between security and operational requirements.
6. Reduced Risk of ‘Noisy Neighbors’
Multiple users use the same physical infrastructure in a public cloud environment, which can lead to performance concerns caused by “noisy neighbors.” Private clouds, on the other hand, reduce this risk because resources are committed exclusively to one enterprise, assuring consistent performance and eliminating interruptions.
7. Business Continuity
Many private cloud infrastructures have effective disaster recovery and backup options. These safety features assure data availability and business continuity in the event of unanticipated occurrences like hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. Compared to public clouds, private clouds frequently provide more extensive disaster recovery options, allowing enterprises to swiftly recover from interruptions.
8 Common Private Cloud Security Challenges and Risks
Private cloud systems have several advantages in terms of security, but they also provide a number of challenges. Understanding these issues is critical for businesses to establish successful security plans. To address these issues, a combination of technological solutions, process improvements, and strategic planning is required.
1. Cost
Establishing and sustaining a private cloud infrastructure can be expensive due to large upfront expenditures in hardware, software, data center resources, and experienced staff. Ongoing operational costs, like maintenance and security upgrades, add to the overall cost of ownership.
How to address this challenge: Run a cost-benefit analysis of a private cloud to estimate the total cost of ownership and compare it to the advantages. Investigate cost control methods such as open-source software, resource optimization, and managed private cloud services from providers.
2. Skill Requirements
Managing a private cloud system involves extensive knowledge and experience in cloud technologies, virtualization, and security. Many businesses may experience difficulty in finding and retaining qualified employees, which can affect the efficiency of their security measures.
How to address this challenge: Invest in IT staff training and certification programs to help them gain the skills they need in cloud technologies, virtualization, and security. Consider hiring professionals to handle certain cloud administration responsibilities or working with managed service providers. And promote from within and develop your own talent wherever possible.
3. Scalability
Private clouds have restricted resources, as opposed to public clouds, which have nearly infinite scalability. Scaling a private cloud infrastructure may be complicated and costly, especially during peak demand periods.
How to address this challenge: To avoid performance difficulties, organizations must initially create a scalable design, allowing for the addition of resources as needed. Implement automation and orchestration technologies to distribute resources dynamically based on demand. Consider hybrid cloud solutions, which would enable you to use public cloud resources during peak demand periods.
4. Security Misconfigurations
Human error or misconfigurations may result in security flaws. Access restrictions, firewall rules, or encryption settings that are incorrectly configured might accidentally expose sensitive data or create security flaws that attackers can exploit.
How to address this challenge: Use security automation and configuration management technologies to maintain consistent and secure setups. Conduct security audits and vulnerability assessments regularly to discover and correct misconfigurations.
5. Single Point of Failure
Single points of failure can occur if a private cloud isn’t designed with redundancy in mind. If failover and redundancy strategies are not in place, hardware failures or other disturbances in key components can result in service outage and data loss.
How to address this challenge: Design the private cloud with redundancy in mind, including failover methods and high-availability settings, to handle this difficulty. Load balancing should be used to disperse and adjust traffic over many servers or data centers.
6. Compliance Issues
Compliance with data privacy and security rules and regulations can be difficult to achieve and maintain. Organizations must verify that their private cloud security measures comply with measures like HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, SOX, and others.
How to address this challenge: Stay up to date with the regulations and standards in your industry and geographic region. Consult compliance specialists or auditors to analyze and confirm the compliance status of your private cloud. Consider GRC tools to automate as much as possible.
7. Integration Complexity
It might be difficult to integrate a private cloud with current on-premises systems and apps. Maintaining security and ensuring flawless data flow during integration attempts can pose challenges.
How to address this challenge: Plan integration activities involving cross-functional teams to guarantee smooth data flow. Implement secure APIs and protocols for inter-system data sharing. For infrastructure you own, ensuring interoperability of hardware and software will be under your control and responsibility. If you use a cloud service provider, make sure the infrastructures are compatible. And hire consultants if necessary. With a project this costly and critical, you want to get it right.
8. Monitoring and Incident Response
Security issues, such as illegal access or data breaches, require thorough monitoring systems and well-defined incident response procedures.
How to address this challenge: Deploy reliable monitoring and logging solutions that enable real-time visibility into your private cloud infrastructure to handle this difficulty. If you’re using a service provider’s infrastructure, activate and ingest all available logs and monitor them with a SIEM solution. Create an incident response strategy that includes clearly defined roles and duties, as well as communication channels and remedial methods.
Also read: SIEM vs. SOAR vs. XDR: What Are The Differences?
10 Private Cloud Security Solutions
The following vendors are among those offering private cloud security; some host private clouds while offering additional security features on top of those offerings.

Amazon VPC
Best for: Scalability and Flexibility
Key Features: Amazon Virtual Private Cloud offers scalability, flexibility, and access to a wide range of AWS services, APIs, and tools, providing organizations extensive resources and a unified cloud experience.

Cisco
Best for: Networking Expertise
Key Features: Cisco offers networking expertise and optimization, and seamless integration of private and public clouds with a focus on security and network performance.

Dell Apex Private Cloud
Best for: Customized Private Cloud Solutions
Key Features: Dell provides comprehensive private cloud solutions, including cloud management, security software, consulting services, and tailored virtual private cloud options to meet specific organizational needs.

HPE
Best for: Customizability and Integration
Key Features: Hewlett Packard Enterprise offers high customizability, seamless integration between private and public clouds, and a strong focus on security to ensure data protection and compliance.

IBM
Best for: Flexibility and Open Standards
Key Features: IBM’s private cloud offerings are built on open-source frameworks, emphasizing flexibility and open standards, with a wide range of private cloud infrastructure and management solutions.
Microsoft
Best for: Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem
Key Features: Offers tight integration with the Microsoft ecosystem and the Azure Stack for on-premises private cloud deployments, with a focus on hybrid cloud scenarios, security, and compliance.

NetApp
Best for: Storage and Data Management
Key Features: NetApp specializes in storage, data management, and data protection, offering scalability and seamless data management between on-premises and cloud environments.

Oracle
Best for: Scalable Private Clouds
Key Features: Oracle offers a scalable Private Cloud Appliance for mixed workloads and a comprehensive suite of private cloud solutions, including infrastructure, applications, and integration services.

Red Hat
Best for: Open-Source Environments
Key Features: Red Hat provides open-source private cloud solutions based on Red Hat OpenStack and Virtualization, offering flexibility, customization, and integration with open-source technologies.

VMware
Best for: Virtualization and Cloud Management
Key Features: VMware offers widely used virtualization software, robust cloud management capabilities, and a range of private and hybrid cloud solutions, including VMware Cloud Foundation for optimized private cloud deployments.
What Is the Difference Between Private and Public Cloud Security?
The chart below highlights some of the key differences between public and private cloud security.
| Aspect | Private Cloud Security | Public Cloud Security |
|---|---|---|
| Data Control | Full control of data and infrastructure | Shared responsibility model |
| Multi-Tenancy | Single organization | Shared among several organizations |
| Compliance Flexibility | Adjustable for compliance | Limited customization for compliance |
| Cost | Higher initial setup and upkeep | Pay-as-you-go model, potentially lower cost |
| Resource Allocation | Specialized resources | Shared resources among multiple tenants |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable and flexible |
| Security Responsibility | User is fully responsible for security | Cloud provider and user have shared responsibilities |
Bottom Line: Enhance Your Private Cloud Security Strategy
Private clouds offer enterprises greater control, privacy, and security than they would get in a public cloud. While public clouds come with their own challenges — not the least of which is higher cost — the benefits of a private cloud can outweigh the downsides, especially for enterprises with stringent security and compliance needs. Understanding the complexities of private cloud security and the available controls are critical for enterprises looking to maximize the benefits of an agile cloud environment while keeping their data safe and secure.
Read next:








