The post How to Perform a Cloud Security Assessment: Checklist & Guide appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>Why Do You Need a Cloud Security Assessment?
Assessing your cloud security posture guarantees that the organization correctly configures networks and assets, ensuring they’re secure and free of any current threats. The comprehensive evaluation detects flaws in the organization’s architecture and makes precise recommendations to strengthen defenses and boost future capabilities. Conduct a cloud security assessment if your business needs to:
- Minimize risks: Use a strong cloud-based testing plan to methodically discover, analyze, and manage any dangers.
- Limit accidental misconfiguration: Implement the specific configuration modifications advised in the assessment. Limit the attack surface as you migrate to the cloud.
- Prevent missed notifications: Enhance your ability to detect and respond to compromises, ensuring that minor errors in your cloud won’t result in major breaches.
- Improve resilience: Follow the assessment team’s recommendations to help your firm recover faster and more efficiently from cloud breaches.
- Boost speed: Perform efficient cloud security testing with parallel scans across several locations, lowering the time for security tests as your cloud infrastructure scales.
- Detect past compromise: Identify deviations from the usual in your cloud configuration that may indicate previous breaches, even if this is not a full compromise evaluation.
- Optimize account management efficiency: Streamline identity architectures to reduce the time your company spends on account and privilege management.
- Ensure compliance: Create an even balance of compliance and security to protect your company from penalties and other adverse effects.
- Enhance financial resilience: Implement proactive strategies that result in significant cost reductions for your company’s cloud operations.
- Scale solutions: Use scalable solutions, either in-house or from trustworthy vendors, to keep up with your company’s cloud growth and objectives.
- Maintain quality: Produce accurate and comprehensible data that clearly shows your company’s cloud security posture.
Understanding the Basics of Cloud Security Assessment
These core aspects of a cloud security assessment should cover the security evaluation process, identity and access, network security, data storage security, incident response, platform security, and workload protection. Understanding the fundamental cloud security elements offers a thorough examination of an organization’s cloud infrastructure and aids in identifying and mitigating any security threats, resulting in a secure cloud environment.
- Comprehensive security evaluation: Conduct interviews and analyze data to evaluate the security measures in place for cloud infrastructure, including existing policies, controls, and potential gaps.
- Identity and access control: Review identity and access control methods, such as user roles, account settings, and key management policies, to verify that only authorized users can access sensitive cloud resources.
- Network defense mechanisms: Examine firewall setups and network segmentation to look for vulnerabilities. Proper segmentation and firewall configurations help to reduce unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data storage protection: Assess the security of your cloud storage solution or its alternatives, including object storage, block storage, and data snapshots, to prevent unauthorized access and data loss.
- Incident response protocols: Analyze policies and procedures for responding to cloud security incidents. Effective protocols should ensure prompt and efficient response and recovery from breaches.
- Platform services: Check the security settings of advanced cloud services from specific providers to ensure that database services, machine learning platforms, and other specialized services are configured securely.
- Workload protection: Explore the security protocols for virtual servers, hosted containers, functions, and serverless applications. Address every specific requirement of each workload to maintain overall cloud workload security.
Preparing for a Cloud Security Assessment
To prepare for a cloud security assessment, begin by evaluating your existing infrastructure and security measures. This could help you easily define your objectives. Allocate resources and set a dedicated period for assessment. Lastly, evaluate your budget to set limits and see which solutions suit your business. These procedures guarantee a thorough and effective assessment process.
Analyze Existing Infrastructure
Consider your IT stack and evaluate the cloud services in use. Assess the performance and delivery of your security controls. Use suitable cloud assessment tools to thoroughly understand the elements that influence security.
Assess Current Security Measures
Begin by analyzing your current defenses to determine and record the security mechanisms in place in your cloud environment. Next, identify gaps or weaknesses in your current security system to determine which areas require improvement.
Identify & Define Future Security Objectives
Determine the anticipated state of your cloud infrastructure based on your current and future requirements. Establish the security procedures and controls required to attain this future state, ensuring they align with your company objectives.
Allocate Resources
Set aside the required resources to focus on the assessment without jeopardizing your other activities and operations. Dedicate a period to prioritize the assessment so that it receives the required time and focus.
Plan Assessment Duration
Allow 10-15% of your time to map your existing environment, 65-70% to evaluate the current environment, and 10-15% to plan for the future state. Prepare to adapt your timetable based on evaluation results to guarantee thoroughness.
Evaluate Financial Implications
Understand the cost dynamics and budget carefully by choosing evaluation tools that offer good value for money within your budget. Ensure that your resource and security requirements budget align with your financial capacity. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis of the security tools and services. Then, confirm that the solutions you choose are within your budget while still meeting your security requirements.
Cloud Security Assessment Checklist
Use a cloud security assessment checklist to systematically evaluate your cloud security posture and ensure comprehensive protection of your cloud environment. To help you create a checklist for your own security assessment, here’s a snippet of our customizable template. Click the image below to download, make your own copy, and modify it as needed. Then, refer to the section below to understand how to execute the tasks included in the checklist.

Review Existing Policies & Procedures
Implement the methods listed below.
- Assess access control and authentication: Evaluate policies for restricting user access and authentication techniques, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Examine data protection and encryption: Confirm that rules include data encryption at rest and in transit, as well as data protection procedures.
- Check incident response and disaster recovery: Check that the processes for dealing with security events and recovering from disasters are in place.
- Evaluate auditing and logging: Ensure that policies incorporate logging and auditing techniques for monitoring and recording actions.
- Inspect monitoring and reporting: Verify the rules, including regular monitoring and reporting of security events.
- Ensure regulation compliance: Confirm that policies adhere to relevant industry regulations and standards.
Control Access
Use the following approaches to manage access:
- Limit access to authorized personnel: Make sure that access is confined to only authorized persons.
- Implement authentication: Check that all accounts have activated two-factor authentication or MFA.
- Enforce strong password policies: Maintain that every company user meets strong password standards.
- Perform regular account reviews: Ensure that the admin examines user accounts and deactivates inactive, unauthorized accounts.
- Manage temporary access: Review the protocols for granting and terminating temporary access.
- Implement role-based access controls: Limit access to sensitive data based on employment role.
- Monitor third-party access: Examine the controls and restrictions in place for third-party vendor access.
Secure the Network
Check your network security by doing the following:
- Deploy and configure firewalls: Assess the installation and configuration of firewalls that defend your cloud environment.
- Encrypt data in transit: Use encryption tools to ensure security and prevent unauthorized access to data while it travels between locations.
- Use intrusion detection tools: Confirm the deployment of IDPS to monitor network traffic for suspicious behavior and prevent unwanted access.
- Secure remote access: Employ VPNs to encrypt communications, ensuring secure and private remote access to your network.
- Implement network segmentation strategies: Isolate critical data to lower the risk of illegal access and mitigate potential damage.
Manage Directory Services
To manage directory services, make sure you’ve followed these practices:
- Administer user access and permissions: Ensure that directory services control user access and permissions.
- Update directory services: Schedule regular intervals to review and modify your directory services.
- Restrict access to sensitive data: Verify that your privilege controls limit access to confidential information and systems.
Prevent Data Loss & Ensure Backup
Adopt the following measures:
- Classify sensitive data: Determine and categorize sensitive data to ensure it gets the necessary level of protection and meets regulatory standards.
- Encrypt data at rest: Encrypt sensitive data saved on devices or servers to prevent unauthorized access and preserve data integrity.
- Create a backup policy: Develop a comprehensive backup strategy for speedy and successful data restoration during a disaster or data loss.
- Secure backup storage: Store backups securely offsite. Utilize encryption and physical security measures to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Enhance Security Operations
Apply the listed tasks below:
- Monitor and look into security alerts: Ensure that you regularly monitor and examine security alerts to detect and handle potential risks.
- Report and escalate events: Make sure that you quickly report and appropriately escalate security incidents to allow a fast and successful resolution.
- Respond and remediate incidents: Create a clear methodology for responding to and remediating security incidents to reduce damage and restore normal operations.
Verify Data Encryption Methods
Ensure strong encryption and data protection by carrying out the following actions:
- Secure data at rest: Use industry-standard techniques to encrypt data saved on devices, preventing unauthorized access.
- Safeguard data in transit: Encrypt data as it travels across networks to prevent eavesdropping and unwanted access.
- Manage encryption keys: Establish a comprehensive procedure for managing encryption keys. Confirm that they’re secure and available only to authorized users.
Monitor Cloud Security Status
Follow these procedures:
- Monitor security events and logs: Constantly monitor security events and logs to rapidly detect and respond to potential incidents.
- Conduct compliance audits: Perform audits periodically to ensure that you meet the industry and regulatory standards, simultaneously upholding strong security measures.
- Update security controls: Assess and revise security controls frequently to keep up with the changing threat landscape and improve protective measures.
How to Conduct Cloud Security Assessment in 10 Steps
After creating a cloud security assessment checklist, you can now begin the assessment by setting boundaries, identifying requirements, and defining responsibility divisions. Evaluate potential risks and security measures, choose testing techniques, and run environmental tests. To guarantee effective security, record and report results, develop remediation procedures, review and improve plans, and continue monitoring and evaluations.
Establish Assessment Boundaries
Define the scope by specifying the cloud assets, apps, and data that will be analyzed. Set specific security goals connected with your organization’s strategy, and use frameworks such as OWASP SAMM or AWS CIS to ensure full coverage. Set boundaries and align with legal requirements and industry standards.
Identify Cloud Resources & Requirements
List all cloud assets, including data and configurations. Examine these assets for vulnerabilities and collect information about setups, network architecture, and access controls. Determine security requirements using compliance frameworks and corporate policies to ensure your cloud infrastructure is secure and compliant.
Clarify Responsibility Divisions
Engage with your cloud provider to better understand their shared responsibility model. To avoid gaps, define security roles for both providers and organizations. Create internal responsibility for cloud security testing and ways to ensure compliance with security policies and duties.
Assess Risks & Security Measures
Evaluate the risks associated with each asset and vulnerability, prioritizing them according to their impact. Examine existing security mechanisms to determine their efficacy. Create a risk-scoring system and threat models to help guide your evaluation, focusing on cloud-specific hazards and tailored testing efforts.
Select Testing Methods
Choose relevant security testing methods, such as:
- Vulnerability assessment: Uses automated tools to recognize known problems.
- Penetration testing: Involves simulating assaults to identify exploitable flaws.
- Source code analysis: Checks the code for security issues.
- Dynamic analysis: Identifies problems during actual use.
- Configuration analysis: Discovers configuration issues.
Perform Environment Testing
Conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration tests to identify potential threats and weaknesses. Use several approaches:
- Black box: Tests without any prior information about the surroundings.
- Gray box: Uses limited knowledge to simulate insider threats.
- White box: Evaluate with full information to identify specific vulnerabilities.
Record & Report Findings
Document all vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and potential exploits encountered during testing. Provide concrete remedial recommendations and executive summaries to ensure stakeholders understand the results, risks, and business effects.
Develop Remediation Strategies
Create a priority-based plan to address identified vulnerabilities. Include suggestions for enhancing access controls, conducting additional testing, and revising security plans. Collaborate with development teams to make fixes and ensure their effectiveness through retesting.
Conduct Review & Improvement Plans
Perform a post-testing evaluation to identify the lessons learned and opportunities for improvement. Update your cloud security plan to include new technologies, risks, and best practices. Use the information gathered to improve future assessments and overall security posture.
Implement Ongoing Evaluation
Treat cloud security assessments as a continuous procedure. Keep up with evolving threats by reviewing and updating your assessment processes periodically. Employ continuous monitoring, such as intrusion detection systems and threat intelligence, to ensure the cloud environment’s security and resilience.
Cloud Security Assessment Best Practices & Recommendations
The recommended practices for cloud security assessments include examining documentation, conducting interviews, and completing both automated and manual tests. Create specific recommendations based on the findings, collaborate on your findings, and use cloud security services. Likewise, automate and integrate security testing processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness in implementing strong cloud security measures.
Review Existing Documentation & Conduct Stakeholder Interviews
Begin by analyzing current documentation and conducting interviews with key stakeholders to better understand the client’s business objectives, cloud architecture, and anticipated changes. This guarantees that the assessment is tailored to their individual requirements and future revisions.
Perform Automated & Manual Testing
Use automated tools to search for misconfigurations and irregularities in the cloud environment. Combine this with manual testing to look for potential attack vectors. Combining these methodologies enables a thorough review, revealing both technical defects and security vulnerabilities that automated tools may overlook, resulting in a more comprehensive evaluation of the cloud’s security posture.
Develop Tailored Recommendations
Analyze vulnerabilities and issues discovered during testing to create tailored suggestions. Present them to other security teams. Ensure that they address specific risks and are consistent with the client’s demands and security goals.
Collaborate on Findings & Recommendations
Review the findings and recommendations with internal stakeholders, providing full explanations and answering any concerns. This collaborative approach ensures a comprehensive grasp of the issues and recommendations, facilitating the effective implementation of the offered actions and solutions. Engage in open communication to establish alignment and resolve any concerns or misconceptions.
Utilize Cloud Security Services
Use specialized cloud security services to improve your security. Perform incident response to analyze breaches and implement response strategies. Execute compromise assessments to identify any current or previous breaches. Simulate red team/blue team exercises to test and develop defenses with controlled, focused attacks. This assures overall security and preparedness for prospective threats.
Automate & Integrate Security Testing
Automate vulnerability scanning, code analysis, and security inspections to ensure uniform coverage and timely response. Integrate these technologies into CI/CD pipelines to detect vulnerabilities early on. This process allows for immediate correction and ensures strong security throughout the development lifecycle.
For a stronger cloud protection approach, integrate this security assessment-specific best practices with the overall cloud security best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is a Cloud Security Checklist?
A cloud security checklist can help you review and prepare for cloud security assessments. Multiple teams collaborate to develop or audit security rules, secure data, verify compliance, and preserve customer trust. This tool gives a road map for secure cloud access and assesses the efficiency of current security measures.
What Are the 4 Types of Cloud Security Controls?
There are four main types of cloud security controls. Deterrent controls seek to deter attackers by indicating the consequences of destructive behavior. Preventive controls increase defenses by implementing measures such as MFA and secure coding techniques. Detective controls use techniques such as intrusion detection systems to discover and respond to threats. Corrective controls limit harm by restarting systems and isolating infected servers.
What Is Included in a Cloud Security Assessment?
A cloud security assessment may include evaluating data encryption for transit and rest, implementing strong access controls, using multi-factor authentication, and configuring logging and monitoring. It also includes applying security patches, developing an incident response plan, ensuring compliance, establishing data backup and recovery strategies, assessing vendor security, and providing employee security training.
Bottom Line: Assess Your Cloud Security Posture Now
A cloud security assessment is fundamental for overall cloud security but must be maintained, monitored, and updated regularly. Use the available technologies to expedite assessments and incorporate them into your overall cloud security strategy. This method improves the protection of your cloud environments by ensuring that security measures adapt to emerging threats and changes in your cloud architecture.
After cloud security assessment comes cloud security management. Manage and maintain your cloud infrastructure by exploring our guide covering the cloud security management types, strategies, risks, and best practices.
The post How to Perform a Cloud Security Assessment: Checklist & Guide appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post Cloud Security Strategy: Building a Robust Policy in 2024 appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>Understanding the Basics of Cloud Security Strategy
Knowing the cloud service types, OSI model layers, shared responsibility, deployment models, and DevSecOps will help you create a more effective cloud security strategy. It improves your company’s threat response and enables you to apply best practices more efficiently. Mastering these areas ensures a comprehensive and adaptable approach to cloud security.
Cloud Service Types
Cloud security delivers a variety of service options to meet different company demands. These cloud service models are broadly classified into three types: infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS). Each of these models offers the customer various levels of control and responsibility.
- IaaS: Uses virtualized computing resources online, allowing users to manage operating systems, storage, and applications while the vendor handles hardware and networking.
- PaaS: Creates a platform enabling clients to design, run, and manage apps using vendor tools without having to manage the underlying infrastructure and middleware.
- SaaS: Includes ready-to-use software applications via the internet, controlled entirely by the vendor, with little customer configuration and maintenance requirements.
The OSI Model
The OSI Model’s layers help develop a safe cloud environment. Understanding the relationship between the OSI Model Layers and your cloud security strategy allows you to simplify intricate security concepts, make more informed security decisions, and boost collaboration and interaction. Effective cloud security is established layer by layer. The following describes how each layer of the OSI Model relates to cloud security:
- Physical layer: Enables physical protection for data centers, guarding against unwanted access and physical harm.
- Data link layer: Uses VLANs and MAC filtering to regulate access and ensure secure communication between nodes.
- Network layer: Protects data in transit and ensures safe network paths by utilizing firewalls, VPNs, and secure routing protocols.
- Transport layer: Employs SSL/TLS to ensure data integrity and confidentiality during transmission.
- Session layer: Manages secure sessions by utilizing authentication protocols and session management mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
- Presentation layer: Utilizes encryption and data formatting standards to ensure data confidentiality and integrity throughout processing and storage.
- Application layer: Includes app-level security features such as API, web application firewalls (WAFs), and endpoint protection to protect user interactions and app data.
The Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model assigns cloud security tasks to both the vendor and the customer. Customers safeguard data, applications, and configurations; providers secure the infrastructure. Understanding this division of responsibility results in good cloud security management, ensuring each party implements appropriate measures to reduce risks.
Cloud Deployment Models
Understanding the many types of cloud environments enables you to choose the appropriate deployment option for your organization’s needs. Here are the five main cloud deployment models:
- Public cloud: Managed by third-party companies that provide services over the internet with multi-tenancy, in which clients share server space with other enterprises.
- Private cloud: Utilized by a single business and can be hosted on-premises or in a provider’s data center, ensuring internal multi-tenancy.
- Hybrid cloud: Combines several cloud instances (public or private) with portability, typically provided by solutions such as Microsoft’s Azure Stack or VMware on AWS.
- Multi-cloud: Uses many public and private clouds simultaneously, distributing apps and data across multiple providers.
- Multi-tenant cloud: A public cloud architecture feature that allows multiple clients to share the same environment while keeping their data segregated.
Explore how to protect your cloud deployment by reading our guide on how to secure the five cloud environment types, the risks, and prevention methods.
DevSecOps
Integrating security into the SDLC is fundamental to cloud resilience. DevSecOps integrates security into development, deployment, and operations, proactively finding vulnerabilities. DevSecOps supports collaboration by bringing together development, operations, and security teams, resulting in secure, dependable systems delivered at modern business speeds. This strategy addresses cloud security needs by building a comprehensive, adaptive security culture.
Why Is Cloud Security Strategy Important?
Any business that wants to benefit from cloud computing while keeping its data safe and secure needs a secure cloud strategy. Organizations can defend their assets and maintain consumer trust by addressing cyber risks, obtaining a competitive edge, assuring full-stack visibility, adopting proactive security, and allowing business agility.
- Mitigates cyber threats: Implements strong security procedures to prevent data breaches, income loss, and reputational damage. Protects sensitive data against unauthorized access.
- Gains a competitive advantage: Emphasizes data protection methods integrated into a well-designed cloud security strategy to foster client trust and sets it apart from the competition.
- Ensures full-stack visibility: Provides complete visibility across your cloud infrastructure, allowing you to identify and solve security concerns. Detects anomalies and responds quickly, with a comprehensive view of all resources.
- Adopts proactive security: Uses automated technologies for vulnerability scans and misconfiguration checks to identify and address threats before they arise. Prevents mishaps and reduces the severity of threats.
- Enables corporate agility: Integrates new cloud services and scales security operations to meet changing business needs. Maintain flexibility in your security plan to meet the changing business needs.
Core Components of a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
To properly secure your cloud environment, prioritize five key cloud security strategy components: visibility, exposure management, prevention, detection, and response. Focusing on these components allows organizations to develop a comprehensive and successful cloud security strategy to protect their assets and operations.
- Visibility: Maintain complete insight into your cloud architecture to effectively manage and secure dynamic resources. Without visibility, you risk being exposed to security risks since you can’t protect what you can’t see.
- Exposure management: Reduce risk by resolving vulnerabilities and coordinating the IT and security teams. Effective exposure management necessitates teamwork to prioritize and reduce risks that may interrupt corporate operations.
- Prevention controls: Implement security controls that are specifically designed for cloud environments. As you adapt to the cloud, ensure that existing tools are compatible and that controls are updated to handle new attack vectors and emerging risks.
- Detection: Quickly detect security breaches to limit their damage. Given the scarcity of cybersecurity experts, use automated systems or third-party services to monitor and detect irregularities in your environment constantly.
- Response: Create and maintain a documented response plan that specifies roles, responsibilities, and processes for handling breaches. Regularly test, review, and update this strategy to ensure it’s ready for successful event management and recovery.
7 Steps in Building a Robust Cloud Security Strategy (+ Template)
Creating a strong cloud security strategy requires an integrated strategy that includes reviewing your current environment, assessing costs, establishing security objectives, designing your architecture, creating policies, implementing solutions, and conducting ongoing testing. This takes care of your organization’s data and apps as you transition to and operate in the cloud.
To guarantee that your strategy remains effective, it must be dynamic and adaptable to new services, features, and threats. Here’s a systematic way to develop and sustain a complete cloud security plan.
Assess Your Current Cloud Environment
Begin by assessing the condition of your IT ecosystem. Identify inefficiencies and create a baseline for comparison with the existing infrastructure. Determine which applications are appropriate for cloud transfer. Consider storage capacity, data type, network environment, and analytics applications. This study will help inform migration decisions and plan creation.
Evaluate Costs & Resources
Assess the costs and resources involved with your current IT infrastructure. Examine the associated expenses of physical servers, maintenance, and manpower. Compare these expenditures against the potential savings and efficiencies from cloud migration. Your assessment helps your business justify the transition to the cloud and shows potential productivity and cost-effectiveness gains.
Define Security Objectives & Requirements
Set specific security goals and standards depending on your organization’s needs and regulatory constraints. Define what you want to protect, the level of security required, and the compliance standards to achieve. This stage ensures that your security plan is aligned with company objectives and meets specific security requirements.
Design Your Cloud Security Architecture
Build a security architecture for your cloud environment. Consider network security, data protection, identity management, and access controls during the design process. A well-structured architecture serves as a solid platform for applying security measures and efficiently protecting your cloud resources.
Develop Security Policies & Procedures
Create comprehensive security policies and procedures to help guide your cloud operations. Include policies on data security, incident response, access management, and compliance. Clear policies guarantee that security techniques are used consistently and help to manage risks methodically.
Implement Security Measures
Implement the security measures outlined in your strategy. This includes deploying technologies for encryption, monitoring, vulnerability management, and threat detection. Implementing these procedures secures your cloud environment against potential attacks and weaknesses.
Test & Refine Your Strategy
To guarantee that your cloud security plan is effective, review and improve it regularly. Conduct vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and simulated security incidents. Use the data to continually upgrade and enhance your security posture to respond to new threats and changes in your cloud environment.
Cloud Security Strategy Template
This downloadable template will assist your business in developing a customized cloud security strategy to meet your specific requirements. Use the document as a full or partial guidance to create your own approach. Click the image below to download and modify your copy.

Common Cloud Security Strategy Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities such as data breaches, misconfigurations, insider threats, and DDoS attacks all weaken the effectiveness of your cloud security approach. Organizations can reduce these risks and improve their cloud security posture by implementing preventive measures such as strong access controls, automated configuration management, effective IAM policies, and DDoS protection.
Data breaches
Data breaches occur through various means, including cyberattacks, insider threats, or weaknesses in cloud services. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities to access confidential information, resulting in unauthorized disclosure.
To mitigate data breaches, use robust access controls, encryption, and continual monitoring. Regularly update security processes and conduct vulnerability assessments to detect and remedy potential flaws before they’re exploited.
Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations happen when cloud resources or services aren’t correctly configured, which is generally due to human mistakes or a lack of knowledge. This can expose data unintentionally and pose security issues.
To avoid misconfigurations, use automated tools to detect and rectify mistakes. Establish and enforce configuration management standards, and encourage employees to follow the best practices for cloud setup and maintenance.
Insider Threats
Insider threats refer to unlawful or careless actions by workers or contractors who have access to cloud systems and data. These individuals may purposefully or unintentionally cause data breaches or other security vulnerabilities.
To reduce insider threats, establish strong identity and access management (IAM) policies, such as least privilege access and regular access reviews. Educate personnel about security practices and keep an eye out for unusual conduct.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks flood cloud services with traffic, making them inaccessible to authorized users. Attackers employ botnets to flood resources, creating service outages.
Reduce DDoS attacks by implementing DDoS defense technologies and traffic filtering mechanisms. Work with cloud service providers that provide DDoS mitigation services, and design your architecture to withstand high traffic volumes and attacks.
Explore our guide on the top cloud security issues and recognize the differences in cloud threats, risks, and challenges. Learn how to properly prevent each risk to improve your cloud security approach.
Common Challenges & Pitfalls in Building a Cloud Security Strategy
Creating an effective cloud security strategy involves many challenges, including a lack of visibility, misconfigurations, and human error, compliance issues, shared responsibility model issues, complicated cloud environments, and adapting to continuously evolving cloud tools. Address these issues with effective tools and techniques to develop a strong cloud security plan that adapts to the changing cloud landscape while protecting your assets.
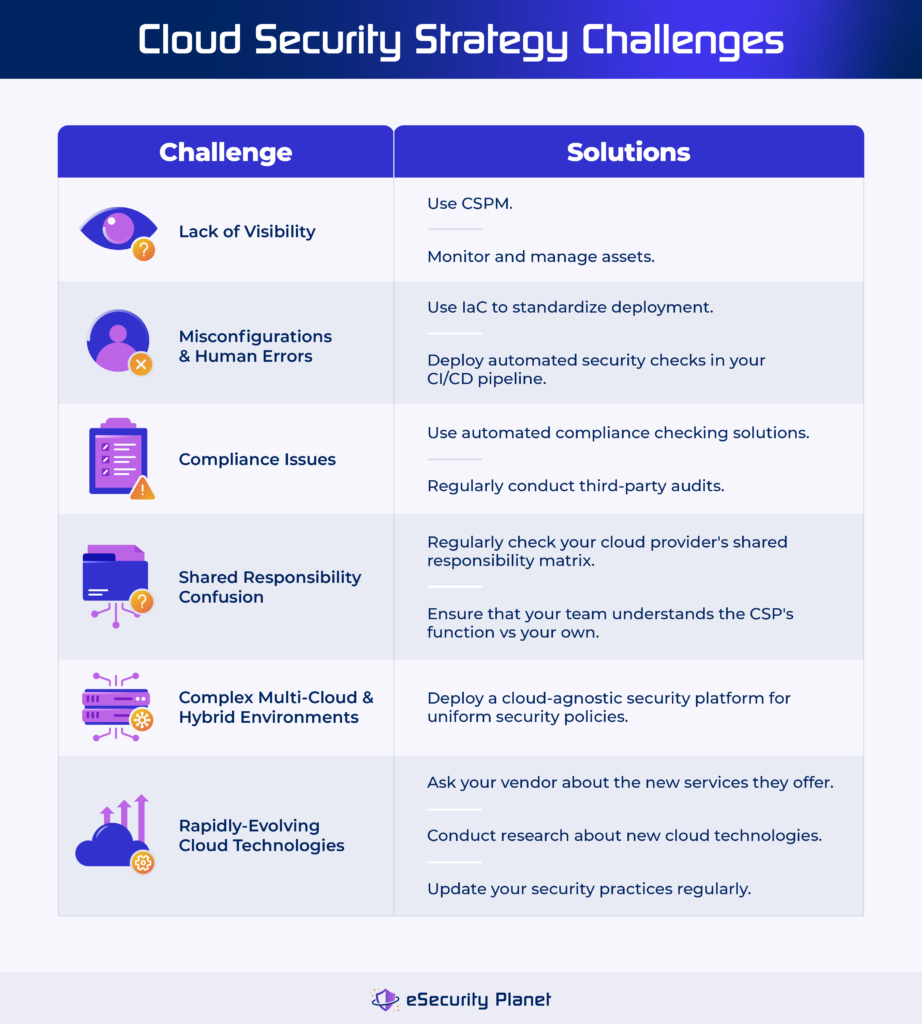
Lack of Visibility
Enterprises moving to the cloud frequently lose complete visibility over their assets. This can lead to vulnerable endpoints, misconfigured resources, and shadow IT concerns where staff use unauthorized applications.
Solution: Use cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to acquire visibility into your cloud environment. By properly monitoring and managing cloud assets, these technologies aid in identifying security concerns and the overall security of the cloud.
Misconfigurations & Human Errors
The level of complexity and speed of cloud provisioning can lead to setup errors, which attackers frequently exploit. Human errors during setup might also lead to security vulnerabilities.
Solution: Use infrastructure-as-code (IaC) to standardize and automate deployment. Implement automated security checks in your CI/CD pipeline to detect and remediate misconfigurations before going live.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Adhering to multiple laws and regulations can be difficult, especially given the dynamic nature of cloud infrastructures. Keeping up with compliance regulations across several areas and industries can be difficult.
Solution: Employ automated compliance checking solutions that are adapted to individual regulatory requirements. Conduct third-party audits regularly to verify that compliance assessments are objective and complete.
Shared Responsibility Model Confusion
The shared responsibility model allocates security responsibilities to the cloud provider and the customer. Misunderstanding this distinction might result in gaps in security coverage, leaving crucial areas vulnerable.
Solution: Refer to your cloud provider’s shared responsibility matrix regularly to understand your security duties. To properly cover all aspects of security, ensure that your staff understands the provider’s function in relation to your own.
Complex Multi-Cloud & Hybrid Environments
Managing numerous cloud providers or mixing on-premises and cloud solutions can result in inconsistencies in security postures, making it difficult to enforce consistent security standards.
Solution: Deploy a cloud-agnostic security platform to establish uniform security policies across many environments. This technique ensures consistent protection and simplifies security management across various cloud and hybrid deployments.
Rapidly-Evolving Cloud Technologies
The quick expansion of cloud services brings new features and potential problems. Staying ahead of these changes ensures a secure cloud strategy.
Solution: Ask your existing vendor or research cloud security technologies to discover new services and the potential risks they introduce. To handle emerging risks and remain proactive, update your security practices regularly.
9 Cloud Security Strategy Best Practices
Implementing effective cloud security strategies and best practices protects your data and apps in the cloud. Understanding your environment, getting visibility, recognizing risks, adhering to governance frameworks, and implementing multi-layer security solutions will help you effectively secure your data and applications from potential threats.
Understand Your Cloud Environment
Before developing a security strategy, thoroughly understand your cloud environment. To effectively design your security measures, identify the types of data and applications you hold and the associated risks and vulnerabilities.
Gain Full Cloud Visibility
Gain complete access to your cloud infrastructure. Ensure 100% visibility across all cloud architectures, including team-specific normalization and segmentation. Implement features like RBAC, full inventory, automated detection, and configuration visibility. Automated, continuous visibility allows you to monitor the proportion of your surroundings.
Identify & Remediate Critical Cloud Risks
Understand workload and cloud risks, identify attack vectors, and prioritize essential concerns. Implement cloud tool features such as exposure analysis, misconfiguration, and vulnerability management, secure secret storage, and attack route analysis. Monitor the number of open critical issues and assess overall decreases over time.
Recognize the Common Cloud Threats
Identify internal and external threats in your cloud environment. This includes malicious insiders, hackers, and cybercriminals. Use threat intelligence to remain on top of prospective threats and adjust your security posture accordingly.
Establish a Cloud Governance Framework
Create a cloud governance framework to oversee data security, system integration, and cloud deployment. This provides risk management, data protection, and conformity to regulatory requirements. Regularly update your governance policies to reflect changing compliance requirements.
Employ a “Shift Left” Approach
Implement security protections early in the application development lifecycle using a “shift left” technique. Integrate pre-production security testing, vulnerability scanning, and compliance assessments directly into CI/CD pipelines to anticipate and resolve issues.
Implement Multi-Layer Security
Use a multi-layered security technique to protect your cloud environment. To ensure complete network and data security, deploy firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) tools.
Encrypt Your Data
Utilize encryption tools to protect sensitive data in the cloud. Ensure that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Make it a necessary part of your security strategy to prevent unauthorized access.
Monitor & Audit Your Infrastructure
Perform regular monitoring and auditing of your cloud infrastructure. To discover and respond to security problems quickly, review logs and security alerts, and conduct frequent vulnerability assessments.
Integrate the best practices above with the general cloud security best practices to achieve an enhanced cloud protection.
Case Studies & Real-World Examples
Real-world cloud incidents, such as Toyota’s data breach, Atlassian Jira’s database issues, and Microsoft outages, highlight the crucial need for strong security measures. These situations demonstrate how gaps in cloud security can cause severe disruptions.
According to the Cybersecurity Insiders 2023 cloud report, 95% of security experts are deeply concerned about public cloud security. This emphasizes the importance of continual education, adaptable solutions, and effective techniques for addressing underappreciated hazards. To strengthen cloud security, install comprehensive protection measures, invest in ongoing training, and modify your strategies to reduce risks and the impact of interruptions.
Toyota Exposed 260,000 Customer Data in 2023
Toyota faced a breach in June 2023 due to a misconfigured cloud environment, which exposed data from 260,000 customers. The intrusion went undiscovered for several years, exposing sensitive information like in-vehicle device IDs and map data updates.
How a secure cloud strategy could help:
- Configuration management: Use IaC and automated configuration management to avoid misconfiguration. Review and update configuration settings regularly.
- Continuous monitoring: Employ CSPM tools to constantly monitor configurations and discover anomalies that may signal a misconfiguration.
- Incident detection and response: Implement effective incident detection techniques to detect breaches early and shorten exposure time.
Database Upgrade Affects Atlassian Jira
Atlassian’s Jira project management platform experienced failure and downtime in January 2024 due to issues related to a scheduled database upgrade. This affected many Jira services, causing them to be unavailable for almost four hours.
How a secure cloud strategy could help:
- Change management: Include extensive testing and validation of modifications prior to deployment. Make sure your backup and rollback protocols are in place.
- Disaster recovery: Create and test a disaster recovery strategy regularly to ensure that services are restored, and redundancy and failover solutions are in place.
- Performance monitoring: Use performance monitoring technologies to identify and resolve issues before they affect end users.
A Series of Microsoft Outages in 2024
In July 2024, Microsoft had massive outages affecting various Azure services and Microsoft 365. On July 13, a configuration update in Azure’s OpenAI service caused problems owing to the elimination of unused resources, affecting both storage and compute resources. This problem was followed by more outages on July 18-19, which impacted connection and service management operations in the Central US region.
Additionally, the issue caused disruptions to Microsoft’s status page and other services. These disruptions were heightened by a faulty CrowdStrike update, which created confusion about the root cause.
How a secure cloud strategy could help:
- Configuration management: Set up a robust configuration management strategy to handle updates and changes methodically. Use automated tools to validate configuration changes before they go live.
- Resilience and redundancy: Include redundancy in cloud architecture to maintain service continuity during outages. Use multi-region deployments to alleviate the effects of regional difficulties.
- Incident communication: Maintain clear communication lines with users during outages. Provide timely status updates to all affected users, including all the mitigation actions your team performed.
- Redundancy and failover planning: Develop a strategy that includes redundancy and failover measures to reduce the effect of failures by maintaining continuous service availability and automated traffic rerouting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is a Cloud-First Strategy?
A cloud-first approach prioritizes cloud-based solutions above on-premises infrastructure. Organizations choose to use external cloud services rather than build and manage their own technology infrastructure. This method uses the provider’s infrastructure to provide efficient, high-quality services, promoting scalability, flexibility, and lower maintenance costs than in-house operations.
What Are the 4cs of Cloud-Native Security?
The four Cs of cloud-native security — code, container, cluster, and cloud — comprise a layered security strategy. Code security entails protecting application code and APIs. Container security focuses on safeguarding container runtimes such as Docker and Kubernetes. Cluster security focuses on the infrastructure that runs containers. Cloud security ensures that the underlying cloud infrastructure is secure.
What Are the 5 Pillars of Cloud Security?
Cloud security is built on five pillars: identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, network security, compliance and governance, and incident response and recovery.
- IAM: Manages user access to cloud resources by enforcing the least privilege principle through authentication and authorization, and constant monitoring for suspicious activity.
- Data encryption: Encrypts data at rest and in transit, including end-to-end encryption, and uses secure key management to keep data unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Network security: Uses firewalls, Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), network segmentation, and security groups to prevent unauthorized access and regulate traffic.
- Compliance and governance: Ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards by using audit trails, compliance frameworks, and automated checks.
- Security incident response and recovery: Manages security incidents using detection tools, response plans, communication protocols, recovery methods, and post-analysis.
Bottom Line: Enhance Protection with a Secure Cloud Strategy
A cloud security strategy ensures that businesses continue to operate regardless of outages. However, it only provides one layer of protection. Integrate cloud protection with existing network security measures, identify potential risks, and use the appropriate technologies. This comprehensive method offers strong disruption defense, protecting both your cloud environment and your entire network.
Discover how to protect your organization with this comprehensive guide to cloud security fundamentals. Learn about data protection, regulatory compliance, and access control to effectively address challenges and apply best practices.
The post Cloud Security Strategy: Building a Robust Policy in 2024 appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post What Is Cloud Migration Security? Implementation + Checklist appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>How Cloud Migration Security Works
A complete cloud migration security strategy consists of three main stages: pre-migration, migration, and post-migration.
Pre-migration security focuses on evaluating the current infrastructure, identifying weaknesses, and establishing security objectives. This stage entails completing a detailed risk assessment, reviewing present systems, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure a secure move.
Cloud migration security involves securing data in transit and facilitating access control. It includes encrypting data to prevent unwanted access, adopting strong identity and access management (IAM) protocols to manage user rights, and continuously monitoring activity to detect and mitigate any threats in real time.
Post-migration security requires enhancing cloud resources for increased security, regularly monitoring performance, and verifying compliance with the applicable regulations. In this stage, you perform frequent security audits, fine-tune resource allocation to prevent vulnerabilities, ensure compliance standards are met, and apply your incident response strategy to address any security breaches as soon as possible.
2 Types of Cloud Migration
The two types of cloud migration are on-premise to cloud and cloud to cloud. An on-premise to cloud migration (lift and shift) works well for rapid conversions with minimum adjustments. Cloud to cloud migration allows greater flexibility and optimization when moving cloud providers. Choosing an appropriate type of cloud migration depends on your specific demands and goals. Regardless of the method used, properly plan and execute secure ways for a safe migration.
On-Premise to Cloud
On-premise to cloud migration is also known as “Lift and Shift,” a fundamental cloud migration type. The process includes moving data and applications from an on-premise data center to a cloud environment. This can be done manually or using migration software.
This method is often faster and less difficult, requiring just minor adaptations for applications and data. It enables fast deployment and lowers infrastructure expenses by eliminating the need to maintain on-premise hardware. However, it may not completely optimize programs for cloud performance and may encounter compatibility concerns.
Cloud to Cloud
Cloud to cloud migration is the process of migrating data, workloads, and applications from one cloud environment to another. This type of migration is expected when firms change cloud providers or combine different cloud services. Applications and data may need to be reconfigured to fit into the new cloud environment.
It allows businesses greater flexibility in leveraging better pricing, features, or performance from a new cloud provider. It also enables enterprises to use more advanced cloud services while reducing reliance on a single cloud provider. Still, data movement across clouds can be complex and time-consuming, with the possibility of outages and security issues.
Benefits of Cloud Migration Security
Cloud migration security benefits businesses by improving security, scalability, flexibility, productivity, and compliance. It lays a solid basis for you to safeguard their data, manage resources efficiently, and quickly respond to new opportunities.
- Strengthens security: Applies advanced security technologies to safeguard data from breaches, unauthorized access, and cyber threats.
- Improves scalability: Easily adjusts scales up or down based on demand, resulting in more efficient management and lower costs.
- Increases flexibility: Rapidly launches new applications and services, allowing for quick responses to market changes and client needs.
- Improves productivity: Enables remote work and collaboration by granting secure access to data and applications from anywhere.
- Maintains compliance: Uses strong security methods and controls to meet industry requirements and standards while protecting data integrity and privacy.
According to Gartner’s cloud predictions, by 2026, three out of four businesses will undergo a digital transformation based on cloud computing. This implies that businesses should start investing in cloud to gain the benefits above.
Risks & Challenges of Secure Cloud Migration
Despite the benefits, migrating to the cloud involves risks and challenges that businesses should be aware of. Cloud migration risks are direct threats to data and systems, potentially resulting in breaches or data loss. Challenges, on the other hand, such as regulatory difficulties and skill shortages, impede successful security implementation. Managing risks and challenges reduces vulnerabilities and enables a seamless transition to the cloud.
Cloud Migration Security Risks
Cloud migration security risks are potential threats to data integrity, confidentiality, and availability during and after transfer to the cloud. Address data breaches, IAM lapses, API flaws, key management issues, and insider threats through implementing different mitigation methods.
| Risk | Causes | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Data compromise | • Misconfigured cloud resources. • Inadequate security measures during data transmission. | • Implement effective security setups. • Use robust encryption for data in transit and at rest. • Conduct frequent security audits. • Utilize DLP tools. |
| Identity and access management (IAM) lapses | • Oversight in access privileges. • Poorly configured IAM controls. | • Implement strict IAM policies. • Enable multi-factor authentication. • Review and update the access controls. • Use IAM tools. • Enforce the least privilege principles. • Check access records for any unusual activity. |
| API vulnerabilities | • Inadequate application protection measures. | • Create and enforce a robust API gateway implementation. • Security testing occurs on a regular basis. • Keep track of any unexpected API activity. • Ensure that APIs use proper authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms. |
| Weak encryption and inadequate key management | • Using outdated encryption algorithms. • Poor management of encryption keys. • Using default or shared keys. | • Use strong encryption techniques. • Adopt strict key management practices. • Rotate encryption keys using dedicated key management services (KMS). |
| Insider threats | • Malicious actions by disgruntled employees. • Negligent behaviors | • Conduct a comprehensive background check upon hiring. • Implement stringent access controls. • Regularly audit user activity. • Offer comprehensive security training. • Develop clear offboarding procedures for departing staff. |
Cloud Migration Security Challenges
Cloud migration challenges — such as proliferating environments, monitoring issues, skills shortage, new compliance requirements, and misunderstanding the shared responsibility — affect business continuity. Fortunately, there are several ways to manage these challenges.
| Challenge | Impact to Businesses | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Uncontrolled environments proliferation | • Security blind spots in threat detection. | • Implement cloud management and governance frameworks. • Maintain control of cloud resources. • Use cloud security posture management tools. |
| Monitoring issues | • Difficulty in maintaining visibility for potential security incidents. | • Deploy security information and event management systems. • Monitor cloud activity. • Adjust the monitoring configurations. |
| Cloud security skills shortage | • Hampers effective incident handling and security management. | • Invest in training programs for your existing personnel. • Engage with managed security service providers (MSSPs). • Use automation and AI-powered security tools. |
| New compliance requirements | • Compliance gaps | • Stay updated on applicable rules. • Work with compliance specialists. • Implement cloud governance frameworks. • Conduct internal and external audits regularly. |
| Misunderstanding the shared responsibility | • Security gaps • Compliance issues | • Define and document the shared responsibility model with your CSP. • Evaluate and modify security policies. • Ensure that all parties understand their roles and obligations. |
Cloud issues exist not just in cloud migration, but also while implementing your overall cloud security. Explore our guide to learn more about the top cloud security issues and the different methods to mitigate them.
How to Implement Cloud Migration Security (+ Checklist)
To integrate security into the whole cloud migration process, begin with extensive pre-migration evaluations and planning. Then, assure application readiness, securely migrate data and infrastructure, rigorously test and verify, and execute a smooth go-live process. Finally, maintain post-migration optimization by managing your cloud environment.
We’ve created a sample checklist for implementing secure cloud migration processes. Click the image below to download the file and customize your own cloud migration security checklist. Then, continue reading below to see our step-by-step explanation on how to perform each task on the checklist.

1. Conduct Pre-Migration Assessment & Planning
Before you begin your cloud migration, do the following steps to assess your readiness:
- Evaluate your current IT infrastructure and network security: Create a complete inventory of all your data center’s hardware, software, network infrastructure, firewalls, and security measures.
- Assess potential risks: Identify and plan for any security risks and problems during the relocation process. Then, conduct a risk assessment to identify weaknesses and potential threats.
- Define migration goals and KPIs: Establish specific objectives and success indicators to drive the migration process. Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals and KPIs.
- Assess vendors and choose a cloud provider: Choose a cloud provider that fulfills your requirements and provides dependable services. Compare providers based on reliability, scalability, pricing, support, and compliance capabilities.
- Select migration team: Put together a professional team to oversee the migration process successfully. Determine essential positions (e.g., project managers, cloud architects, security specialists) and delegate duties.
- Prepare backup and disaster recovery plans: Ensure your data integrity and availability in the event of an unforeseen issue. Create a robust backup and disaster recovery plan to prevent data loss.
2. Evaluate Your Application Readiness
Prepare for the cloud migration process by assessing your apps through these actions:
- Assess application suitability: Determine whether apps are compatible with your cloud environment.
- Identify dependencies and integrations: Map out interdependencies and necessary integrations.
- Plan integration strategies: Create detailed plans to integrate different applications with new cloud systems.
- Examine application architecture: Ensure that your app architecture supports scalability, dependability, and performance.
3. Perform a Secure Cloud Data Migration
Conduct a secure data migration and check if you’ve performed the following:
- Identify the data to be migrated: Ensure that all necessary data is included in the migration. Collaborate with teams to identify key data sources and eliminate data silos.
- Choose a migration method: Determine the best way for migrating data to the cloud. Choose based on data volume, complexity, and downtime tolerance.
- Encrypt data: Preserve data privacy policies and integrity during transmission. Use encryption tools to secure data in transit and at rest.
- Control access to cloud resources: Use identity and access management protocols that govern user rights and responsibilities.
- Use multi-factor authentication: Require multiple verifications. Enable MFA to ensure that only authorized users can access the cloud environment.
4. Secure Your Infrastructure Migration
Do these methods to safely conduct infrastructure migration:
- Replicate or reconfigure infrastructure: Create a cloud architecture that mirrors or improves on your current configuration.
- Double check your infrastructure: Identify gaps, check for scalability and performance, and test new configurations.
5. Test & Validate Your Environments & Apps
Perform testing and validate your environments by doing the processes below:
- Apply functional testing: Verify that apps work as intended in the new environment. Create test cases and scenarios to validate all important features.
- Conduct performance testing: Determine how apps function under various scenarios. To evaluate system performance, test it under load, stress, and endurance.
- Validate security and compliance: Ensure that the migrated environment fulfills security and regulatory standards. Perform scans, vulnerability assessments, and audits.
6. Go Live
Take these steps to ensure security while going live:
- Verify data accuracy: Ensure that all data has been sent correctly and consistently. Perform data validation checks after migration.
- Perform final data synchronization: Record any changes made during migration. Synchronize the final data to maintain uniformity across systems.
7. Manage & Maintain Secure Cloud Environment Post-Migration
Monitor and analyze the post-migration performance of your cloud environment using these methods:
- Update DNS and network parameters: Reroute traffic to the new cloud environment. Validate DNS and network setups.
- Validate connectivity: Confirm that all users can connect seamlessly. Check and confirm network connectivity.
- Optimize resource allocation with cloud tools: Maximize the use of cloud resources. Use cloud provider tools for dynamic scaling and cost optimization.
- Performance monitoring and fine-tuning: Ensure that the system is performing optimally and securely. Set up monitoring systems and modify resources.
- Verify and update new compliance and regulation adherence: Maintain continuing compliance with applicable rules. Conduct regular audits and updates to policies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Do I Protect Data During Cloud Migration?
To maintain cloud data security during transfer, categorize it according to its criticality. Encrypt data in transit and at rest to protect its security. Use strong identity and access management and multi-factor authentication to govern and safeguard access to critical data.
What Are the 4 Phases of Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration consists of four phases: assessment, planning, execution, and post-migration.
- Assessment: Determines whether workloads are eligible for migration by examining current infrastructure and gathering data.
- Planning: Includes designing the cloud environment, mapping migration stages, and selecting the appropriate cloud service provider.
- Execution: Completes the migration, configures the new environment, and tests apps to ensure correct functionality.
- Post-migration: Monitors performance, backs up data, and handles any issues or dangers that arise.
What Are the 7 Cloud Migration Strategies?
AWS’s 7 Rs migration model for cloud migration includes rehost, relocate, replatform, refactor, repurchase, retire, and retain.
- Rehost: Transfers existing IT assets to the cloud with little adjustments, also known as “Lift and Shift.”
- Relocate: Moves your whole virtualized environment to the cloud with no changes to the hypervisor, resulting in increased efficiency and performance.
- Replatforming: Involves migrating apps to the cloud with some adjustments to take use of cloud-native features, also known as “Lift and Reshape.”
- Refactor: Redesigns apps to fully leverage cloud capabilities, including secure coding principles and cloud platform features.
- Repurchase: Replaces current apps with cloud-based SaaS products that take advantage of the SaaS provider’s security controls.
- Retire: During migration, decommission any old or non-essential programs to reduce your threat surface and simplify security administration.
- Retain: Keep certain programs on-premises due to security concerns or technical restrictions, carefully weighing the risks and advantages.
Bottom Line: Apply Cloud Migration Security Practices for Enhanced Data Protection
Security in cloud migration should be performed across all integral phases, from initial planning to execution and post-migration. Different cloud tools are easily accessible now, so utilize these to enhance your cloud protection methods. Integrate cloud migration security with the broader cloud security strategies so your business can establish a cohesive defense architecture that successfully protects data, apps, and infrastructure from both common and new threats.
After a successful cloud migration, a post-migration practice requires maintaining and managing your cloud data. Read our review of the top cloud data management solutions and compare their key features, strengths, weaknesses to evaluate which is best for you.
The post What Is Cloud Migration Security? Implementation + Checklist appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post What Is Cloud Database Security? Types, Best Practices & Tools appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>How Cloud Database Security Works
Cloud database security often entails identifying sensitive data, setting policies, utilizing encryption, installing access restrictions, auditing, monitoring logs, and more, but this may vary depending on the company’s resources. It’s a shared responsibility of the company (network, DBA, security, apps, compliance, and infrastructure teams) and its cloud provider, and it requires regular evaluations and adjustments.
Here’s an overview of how cloud database security works and who are typically responsible for implementing these methods:
| Step | Responsible Role | Execution |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Identify any sensitive data in the database. | • Database administrator (DBA) • Security team • Compliance team | • Create sensitive information inventory. • Utilize data classification frameworks. • Use database schema diagrams and flowcharts. • Deploy data discovery tools. |
| 2. Create and implement database security policies and processes. | • Security team • Compliance team • Legal • Staff | • Document and align policies with company goals. • Utilize policy templates and industry regulations. • Maximize collaborative platforms. |
| 3. Establish encrypted connections for data transmission. | • Network team • Security team • Infrastructure team | • Employ secure communication protocols (HTTPS and SSL/TLS). • Use certificates. • Consult the encryption guidelines. |
| 4. Set access controls. | • Security team • DBA • Infrastructure team | • Manage access control lists and policies. • Use access control frameworks. • Apply RBAC models. • Implement IAM systems. |
| 5. Perform database auditing. | • DBA • Security team | • Configure the audit logs. • Apply log management tools. • Define procedures for log review and investigation. |
| 6. Monitor the database activity logs. | • Security team • Incident response team | • Install log analysis tools. • Define the baseline patterns. • Engage security personnel in log review. |
| 7. Check for SQL injections and other vulnerabilities. | • Security team • Apps team • Penetration testers | • Deploy vulnerability scanning tools and pentesting frameworks. • Follow the secure coding principles. |
| 8. Plan for backups and restoration. | • DBA • Infrastructure Team | • Setup backup and recovery software. • Define the backup frequency. • Evaluate the recovery techniques. |
| 9. Develop disaster recovery and incident response plans. | • Security team • DBA • Infrastructure team • Incident Response Team | • Build disaster recovery templates. • Set communication channels. • Test plans through exercises. |
| 10. Schedule periodic security inspections and updates. | • Security team • Compliance team | • Determine the assessment. • Update the procedures. • Maintain cloud security practices. |
For a thorough approach to cloud database security, you should have a deeper grasp of its functions, types, benefits, and threats in order to make informed decisions. Recognizing common dangers also aids in risk reduction through applying best practices and using appropriate cloud tools. By employing a holistic, secure cloud database practice, you maximize the benefits of cloud computing for your organization.
Who Should Use Cloud Database Security?
Cloud database security is not just a preventative measure; it’s a strategic investment for enterprises. Any organization that handles sensitive data should employ cloud security practices to avoid data breaches and the associated costs of legal fees, system repair, victim compensation, and noncompliance fines.
- Companies that value data protection: Prioritizing the application of cloud database security practices guarantees that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized data access and breaches.
- Businesses wanting to enhance customer trust: Securing your cloud database improves customer trust by displaying your commitment to cloud data security, boosting your reputation, and promoting customer loyalty.
- Corporations enhancing operational continuity: By preventing disruptions, a secure cloud database protects revenue streams and maintains smooth corporate operations, even in the face of potential cyber threats.
- Organizations adhering to regulatory requirements: Implementing cloud database security enables you to effectively comply with regulations and avoid penalties and legal liability associated with data breaches.
- Firms wanting to reduce financial risks: Preventing the costs of breach recovery, including potential ransomware payments, can save your company a substantial amount of money and resources.
4 Types of Cloud Database Security
Each type of cloud database security — network security, access management, threat protection, and information protection — ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These types are layered security that work together to create a fully secure architecture that reduces risks and secures sensitive data in cloud settings from attacks and vulnerabilities.
Network Security
Network security is the first layer of protection in cloud databases that employs firewalls to prevent unwanted access. Firewalls help you comply with cloud data security policies by regulating incoming and outgoing traffic using software, hardware, or cloud technologies. By implementing strong network security measures, you can avoid breaches and illegal data access, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of your cloud data.
Access Management
Another type of cloud database security is access management, which guarantees that only authorized users have access to sensitive data in the cloud. Authentication validates user identities, while authorization allows particular data access based on preset roles and permissions. It reduces the danger of data breaches by limiting information access to just authorized workers, improving data security and compliance with privacy requirements.
Threat Protection
Threat protection involves taking proactive measures to detect, assess, and respond to any threats to the cloud database. Use auditing tools to monitor and analyze database activities for anomalies, sending managers real-time notifications about suspicious activity or potential breaches. The ongoing monitoring maintains compliance with security requirements and allows for timely responses to mitigate threats and maintain data integrity.
Information Security
This security layer focuses on safeguarding data stored in a cloud database. Encryption techniques turn sensitive data into unreadable formats, guaranteeing that even if it’s intercepted, unauthorized people cannot access it. Additionally, it uses regular backups and disaster recovery strategies to assure data availability in the event of deletion, corruption, or cyber-attacks.
Cloud Database Security Benefits
Cloud database security provides a comprehensive set of benefits that solve key database concerns such as data protection, accessibility, and resilience. It also promotes agile corporate growth and innovation by delivering scalable, secure, and dependable data management solutions. By leveraging the following advantages, you can improve operational efficiency, bolster security posture, and better manage data assets:
- Scalability: Adjusts database size and performance to accommodate changing business requirements without incurring costly upgrades or disruptions.
- Increased visibility: Enables better monitoring of internal operations, data locations, user actions, and access kinds.
- Efficient native apps integration: Allows developers to create efficient native applications that use cloud-stored data, resulting in faster app deployment processes.
- Secure data encryption: Uses advanced encryption algorithms to maintain safe data in transit, in storage, and while sharing.
- Convenient access: Encourages flexibility and collaboration across distant teams, resulting in smooth data exchange and collaboration without jeopardizing security.
- Reliable disaster recovery: Includes safe backups maintained on external servers, allowing enterprises to quickly restore data and continue operations.
Cloud Database Security Threats
Despite its benefits, cloud databases are vulnerable to dangers such as API flaws, data breaches, data leaking, DoS attacks, malware, and unauthorized access. These dangers, inherent in modern systems, threaten data security, potentially causing serious damage. Fortunately, there are ways to mitigate these threats.
API Vulnerabilities
Insecure APIs can be used by attackers to obtain unauthorized access to the database. API design or implementation flaws, such as insufficient authentication or incorrect input validation, can be used to modify data or access sensitive information.
To avoid API vulnerabilities, use strong authentication methods such as OAuth or API keys, encrypt data in transit, update APIs on a regular basis, and monitor usage trends to detect unwanted access attempts quickly.
Data Breaches
Unauthorized access to sensitive information can result in theft, corruption, or exposure. It can happen through exploiting weaknesses in databases, apps, or compromised credentials. To mitigate the threat, encrypt sensitive data, implement rigorous access rules, and monitor database access logs. Conduct frequent security audits to detect and remediate issues in advance.
Data Leakage
Data leaking occurs as a result of sensitive data being exposed outside of the organization’s network, either accidentally or on purpose. This is generally caused by insecure settings, careless personnel practices, or insider threats.
Reduce data leakage by implementing strong data governance principles. Then, deploy data loss prevention solutions, encrypt critical data, and provide frequent security training to prevent accidental or intentional data exposure.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks attempt to interrupt database systems by flooding them with malicious traffic, rendering them unreachable to normal users. It causes downtime and loss of service. To prevent DoS attacks, implement network security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS). Apply rate restriction and traffic filtering, use content delivery networks (CDNs) for traffic distribution, and monitor network traffic for unusual activities.
Malware Distribution via Cloud Services
Attackers exploit cloud synchronization services or compromised accounts to spread malware across multiple devices and platforms. Malware uploaded to cloud storage results in widespread infection and compromise.
To prevent malware transmission via cloud synchronization, use strong endpoint security, impose strict cloud service rules, educate staff about phishing dangers, and keep antivirus software up to date.
Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access happens when malicious actors obtain access to a database via stealing credentials, exploiting flaws in authentication mechanisms, or circumventing access rules. Implement strong access restrictions and authentication techniques like MFA and RBAC, review and update user permissions on a regular basis, monitor database access logs, and perform security audits and penetration testing to quickly eliminate unauthorized access threats.
A cloud security posture management tool can help you discover and manage cloud environment threats. Read our in-depth guide on CSPM, covering how it works and the best available solutions in the market.
Best Practices for Cloud Database Security
Securing cloud databases requires the use of strong access controls, data encryption, updated database software, zero trust security approach, and more. By incorporating these best practices into your approach, you can effectively minimize the risks associated with unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats, assuring the security of sensitive data contained in your cloud environment.
Implement Strong Access Controls & Authentication Mechanisms
Strong access controls are implemented using multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls (RBAC). To reduce the danger of unauthorized access, review and modify your access rights on a regular basis, following least privilege principles.
Encrypt Sensitive Data at Rest & in Transit
Utilize strong encryption techniques, such as AES-256, to secure data at rest and in transit. Implementing secure key management procedures safeguard encryption keys while guaranteeing data confidentiality. It guards sensitive information from unauthorized access while also ensuring compliance with data protection standards.
Utilize Firewalls & Network Security Tools
Use firewalls to monitor and filter both incoming and outgoing network traffic, which improves security by blocking unauthorized access attempts. Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to increase defenses by identifying and stopping hostile activity in real time. This layered method efficiently protects networks and sensitive data against cyber attacks.
Keep Your Database Software Updated
To maintain security, apply patches and upgrades supplied by your database provider on a regular basis. Monitor vulnerability reports and security advisories to make sure that you address reported flaws as soon as possible. Doing this strengthens database protections against possible exploits. It also ensures that your database infrastructure is resilient and secure against new threats and vulnerabilities.
Regularly Back Up Your Data
You should plan automated backups on a regular basis and guarantee redundancy in several locations or cloud regions. Periodically test backup restoration procedures to maintain data integrity and availability in the event of data loss or corruption. With this approach, you can support the continuity of operations and enhance the defenses of your cloud management systems against any disruptions.
Monitor & Audit Database Activities
Implement logging and auditing methods to monitor user activity, data changes, and system events. Use complementary cloud technologies to automate and monitor logs, detect suspicious activity in real time, generate alerts, and respond quickly to any security issues. Improve your overall security posture by allowing for quick detection and mitigation of threats in your environment.
Encourage Company-Wide Security Awareness
Train your employees about data protection policies, phishing awareness, and incident response protocols. Utilize cybersecurity training programs to easily manage your workforce’s security campaigns and user education. Conduct phishing simulations to test people’s response and cover strong password policies and protection in your training guides. Also, provide a dedicated space for conversations about security to encourage long-term security behaviors.
Adopt a Zero Trust Security Model
Use zero trust solutions and follow zero trust’s principles: “All entities are untrusted by default; least privilege access is enforced; and comprehensive security monitoring is implemented.” Regardless of origin or resource, verify each access request with continuous authentication and authorization checks. To avoid unwanted access and data breaches, use micro-segmentation and stringent access controls based on dynamic risk assessments and behavioral analysis.
Use Distinct Set of Credentials
Restrict the scope of permissions granted to each organization to reduce the impact of a compromised account or fraudulent activity. It’s particularly crucial when the application code is prone to vulnerabilities such as SQL injection. By isolating authentication accounts, you can reduce the risks of unwanted access and data breaches.
Best Cloud Database Security Tools
Oracle Data Safe, IBM Guardium, and Imperva Data Security are three of the top cloud database security tools available in the market today. Remember that when choosing a cloud database service, you must analyze potential provider’s security procedures, licenses, and compliance to check if they meet your security requirements. This due diligence guarantees that the chosen services meet your cloud protection and regulatory compliance criteria.

Oracle Data Safe
Oracle Data Safe is designed specifically for Oracle databases. It includes advanced security features such as alert policies, least privilege enforcement, and compliance reporting. It has an agentless operation, ensuring that data is not captured by software agents. Oracle Data Safe is suited for teams that utilize Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Price starts at $50 per month for over 500 target databases, with a 30-day free trial available.

IBM Guardium
IBM Guardium is a robust platform for enterprise database security, providing data backup, encryption, and threat detection. It provides both agent and agentless data connections, making it ideal for larger businesses. It comes with a 30-day free trial for Guardium Insights and a 90-day trial for Key Lifecycle Manager. IBM doesn’t list direct pricing details, but Guardium Insights provides a convenient cost calculator.
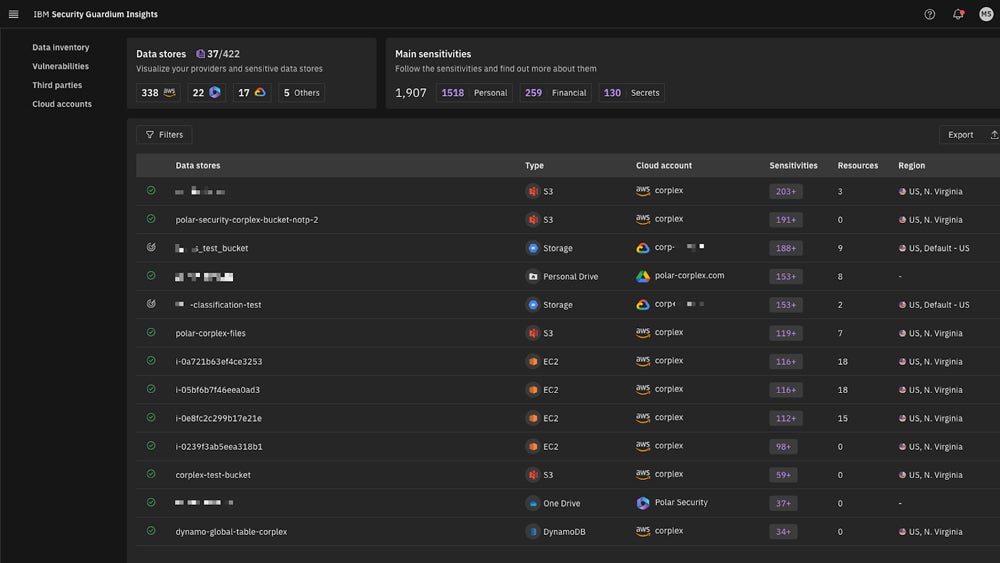

Imperva Cloud Data Security
Imperva Cloud Data Security offers a hybrid data security platform and cloud database protection as a service designed specifically for AWS DBaaS. They offer 24/7 phone and email support, making it suitable for smaller teams who require ongoing assistance. Imperva’s pay-as-you-go pricing on AWS includes a free tier of up to 5 million requests per month and a base plan of $10,000 per year for up to 50 million monthly events.
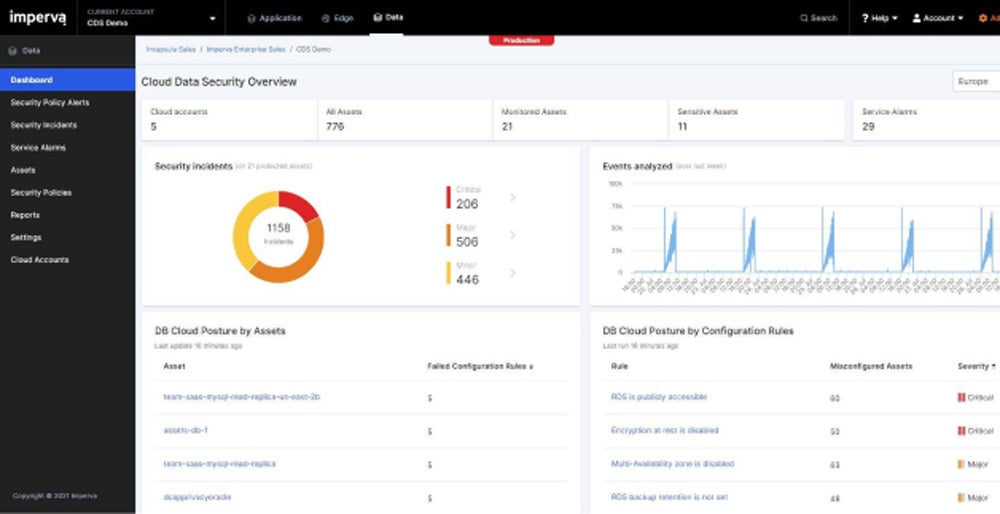
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Is Data Encrypted in the Cloud Database?
Data in cloud databases is encrypted using strong algorithms such as AES-256, which ensures data security during transmission and storage. Encryption occurs automatically upon data entry, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Network forensic tools improve security by checking encryption integrity, adding a layer of protection against potential breaches, and preserving data secrecy throughout its lifecycle.
What Are the Key Features of Cloud Database Security Solutions?
Top cloud database security solutions typically offer customer-managed keys, automated password management, comprehensive logging, and encrypted database access.
- Customer-managed keys: Gives you more control over access management by minimizing dependency on cloud providers.
- Automated password management: Grants temporary passwords and permissions to approved users, improving security in huge businesses.
- Comprehensive logging: Monitors and responds quickly to illegal access attempts, with consolidated records for convenient security event management.
- Encrypted database access: Protects sensitive data from illegal dissemination and ensures secure access without the need for decryption keys.
How Are Cloud Databases Deployed?
Cloud databases run on cloud virtual machines (VMs) that have database software installed. Alternatively, under platform-as-a-service (PaaS), cloud companies provide completely managed services. These models provide scalability and managerial flexibility, allowing them to accommodate a wide range of organizational needs and operational efficiencies.
Bottom Line: Secure Your Cloud Databases Now
While fundamental cloud database security practices provide essential protection, they’re just a part of a layered security defense. Integrate these practices with advanced security tools to improve threat detection and response skills. Human expertise further enhances these tools by interpreting alerts, researching issues, and applying additional security measures. This combined strategy increases overall defense and protects your sensitive cloud.
Integrate your cloud database security practices with security information and event management to automate your cloud security events analysis. Read our full review of the top SIEM tools, including their key features, pros, cons, and more.
The post What Is Cloud Database Security? Types, Best Practices & Tools appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post 6 Best Cloud Data Management Software in 2024 appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>Here are the six best cloud data management software and solutions:
- Informatica: Best overall cloud data management software
- Hevo Data: Best option for customer service and support
- NetApp BlueXP: Best for hybrid and multi-cloud environments
- Rubrik: Best for data security and industry standard compliance
- Snowflake: Best for third-party tools integration and support
- Airbyte Cloud: Best for ease of use and administration
Top Cloud Data Management Software Comparison
This table provides a summary of cloud data management solutions, including their essential features and the availability of free plans and trials.
| Big Data Management | Data Quality Management | Zero-ETL | Free Plan | Free Trial | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informatica |  |  |  |  | 30 days |
| Hevo Data |  |  |  |  | 14 days |
| NetApp BlueXP |  |  |  |  | 30 days |
| Rubrik |  |  |  |  | Contact sales |
| Snowflake |  |  |  |  | 30 days |
| Airbyte Cloud |  |  |  |  | 14 days |
 =Yes
=Yes  =No/Unclear
=No/Unclear
All of the solutions listed here excelled in specific categories, but Informatica emerged as our overall winner, with its wide range of core capabilities plus a free plan offering. Continue reading to learn about each solution’s features, pros and cons, and alternatives, or see how I evaluated each top solution below.
Informatica – Best Overall Cloud Data Management Software
Overall Rating: 4/5
- Core features: 4.8/5
- Pricing and transparency: 3.5/5
- Data security: 4/5
- Cloud data governance and compliance: 3.5/5
- Customer support: 3.8/5
- Ease of use and administration: 4.1/5
Informatica, an AI-powered cloud data management solution, tops our list with a broad product portfolio focusing on data integration, quality, cataloging, and governance. It combines data from multiple sources to enable seamless analysis and reporting. Informatica provides thorough extract, transform, and load (ETL) capabilities to ensure effective data warehousing. It’s most suitable for enterprises looking for a feature-rich and versatile data management solution.

Pros
Cons
Hevo Data – Best Option for Customer Service & Support
Overall Rating: 3.9/5
- Core features: 4.3/5
- Pricing and transparency: 3.4/5
- Data security: 3.5/5
- Cloud data governance and compliance: 4.2/5
- Customer support: 4.2/5
- Ease of use and administration: 4.3/5
Hevo Data, an automated zero-maintenance data platform, unifies data from over 150 sources in near real time via an easy-to-use no-code user interface. Its fault-tolerant architecture ensures 100% data correctness, 99.9% uptime, and fast system alarms — all backed by responsive 24/7 customer assistance and a five-minute response time via Live Chat support. Hevo uses models and workflows to quickly make data analytics-ready.

Pros
Cons
NetApp BlueXP – Best for Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Environments
Overall Rating: 3.8/5
- Core features: 4.1/5
- Pricing and transparency: 2.2/5
- Data security: 4.3/5
- Cloud data governance and compliance: 4.7/5
- Customer support: 3.5/5
- Ease of use and administration: 4.5/5
NetApp BlueXP, formerly NetApp Cloud Data Sense, uses AI-powered technologies to improve data governance in hybrid and multi-cloud systems. It provides a SaaS-based unified control plane to enhance your visibility and control. BlueXP unifies data services and provides a flexible, secure infrastructure with robust AIOps capabilities, making it best for navigating complicated hybrid and multi-cloud landscapes.

Pros
Cons
Rubrik – Best for Data Security & Industry Standard Compliance
Overall Rating: 3.8/5
- Core features: 4.3/5
- Pricing and transparency: 1.2/5
- Data security: 4.7/5
- Cloud data governance and compliance: 5/5
- Customer support: 3.9/5
- Ease of use and administration: 4.3/5
Rubrik, a key player in data security and compliance, largely focuses on cyberattack prevention through comprehensive backup, data protection, threat analytics, and cyber recovery solutions for different infrastructures and cloud environments. Its encryption capabilities ensure data integrity and regulatory compliance. These are backed up by secure coding methods and independent verification of compliance, security, and privacy requirements.

Pros
Cons
Snowflake – Best for Third-Party Tools Integration & Support
Overall Rating: 3.7/5
- Core features: 4.5/5
- Pricing and transparency: 3/5
- Data security: 4/5
- Cloud data governance and compliance: 3.4/5
- Customer support: 2.7/5
- Ease of use and administration: 4.3/5
Snowflake specializes in third-party tool integration and support, providing a scalable data cloud platform for application development, data warehousing, and lakes. It offers unified security, governance, and metadata management, which reduces ETL complexity. Snowflake also works with leading data management partners to ensure smooth integration and improve data consistency across analytics projects from various sources.

Pros
Cons
Airbyte Cloud – Best for Ease of Use & Administration
Overall Rating: 3.6/5
- Core features: 4.5/5
- Pricing and transparency: 2.7/5
- Data security: 3.2/5
- Cloud data governance and compliance: 4.5/5
- Customer support: 2.4/5
- Ease of use and administration: 4.5/5

Pros
Cons
Top 5 Features of Cloud Data Management Software
The best cloud data management software come with features such as zero-ETL capabilities, which allow for seamless data integration without the need for traditional ETL processes. They also feature powerful tools for handling massive amounts of data, incorporate AI for quick data extraction, enable disaster recovery to provide data resilience, and provide full data quality management to assure accuracy and reliability throughout the data lifecycle.
Zero ETL
Zero-ETL is a new approach in which data is integrated in real-time or near-real-time, minimizing the period between data collection and availability for analysis. Transformation occurs during querying, which eliminates the need for staging locations. This strategy allows enterprises to evaluate and query data straight from the source, increasing efficiency by avoiding traditional, time-consuming ETL operations.
Big Data Management
Big data management entails organizing, administering, and managing massive amounts of structured and unstructured data. It enables businesses and governments to manage terabytes to petabytes of data saved in multiple formats. It uses centralized interfaces to manage data resources, improve outcomes, ensure security, and increase analytics using efficient cycle procedures and visualization approaches while allowing multiple concurrent users.
AI Integration
Integrating AI into data management software means strategically deploying AI that enhances data quality and analytics. It includes techniques for efficiently collecting, organizing, storing, and utilizing data while assuring its integrity, accessibility, security, and compliance. It facilitates automation to improve data handling, easily support regulatory compliance, and accelerate processes to enable informed decision-making.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery services in data management ensure business continuity and resilience. They include developing backup systems, storing data off-site, and providing redundancy to reduce the impact of system failures. These safeguards protect against unforeseen disruptions and data loss, allowing activities to resume swiftly without extended downtime.
Data Quality Management
Data quality management ensures accuracy and reliability by integrating data collection, enhanced processing, and effective delivery. It takes administrative oversight to ensure data integrity, which is required for consistent and reliable data analysis. High-quality data is critical for generating actionable insights and assuring the precision of information utilized in your decision-making and strategic planning.
How I Evaluated the Best Cloud Data Management Software
I created a scoring rubric to evaluate the top cloud data management solutions based on six fundamental criteria. Each criterion has specific subcriteria or features listed under it. Then, I assessed if the product meets the specific features or services listed. Based on their scores per criterion, I determined each solution’s use case. Ranking their overall scoring, I identified the best six solutions, with the top scorer as our overall winner.
Evaluation Criteria
In my assessment, I prioritized the core characteristics necessary in evaluating cloud data management software. Next, I looked into their pricing and transparency and data security capabilities. I reviewed their cloud compliance and data governance to ensure regulatory compliance. Finally, I assessed customer assistance, ease of use, and administration to determine the user experience and operational efficiency.
- Core features (25%): Include zero ETL, big data management, data distribution, file sharing, disaster recovery, data quality control, unlimited storage for scalability, and AI integration for advanced analytics and automation.
- Criterion winner: Informatica
- Pricing and transparency (20%): Considers aspects like free trials, price structures, transparent pricing information, availability of free plans or tiers, free demos, and data egress fees.
- Criterion winner: Informatica
- Data security (20%): Covers additional security elements like cloud security policies, risk assessments, threat analysis, IAM integration, encryptions, endpoint security, and more.
- Criterion winner: Rubrik
- Cloud data governance and compliance (15%): Reviews the conduct of internal and external audits, resource and service governance, and adherence to key industry standards.
- Criterion winner: Rubrik
- Customer support (10%): Assesses the availability of support platforms like live chat, phone, and email assistance, manuals, demos, training, and user reviews to assess customer service quality.
- Criterion winner: Hevo Data
- Ease of use and administration (10%): Evaluates the UI, centralized management console, intuitive functionalities, workflow integrations, CSP maintenance, and user reviews for ease of use.
- Criterion winner: Airbyte Cloud
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Are the Common Challenges in Using Cloud Data Management Software?
Using cloud data management software might present issues, such as data egress prices imposed by providers when transferring or restoring data, which are designed to discourage data removal. Also, despite the cloud’s cost-effective brand, keeping huge amounts of data in cloud data lakes or databases can be expensive. This can affect your budgeting and data management techniques.
What’s the Difference Between Cloud Data Management & Traditional Data Management?
Traditional data management relies on on-premise hardware and IT infrastructure, which limits scalability and increases upfront expenses. Cloud data management makes use of cloud platforms to enable dynamic scalability, improved disaster recovery, and flexible data access without requiring large infrastructure expenditures to boost data agility.
What Are the Common Compliance Standards in Securing Cloud Data?
Here are some of the key data compliance regulations and standards for securing cloud data:
- SOC 1: Focuses on internal controls over financial reporting.
- SOC 2: Evaluates data security, availability, integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- HIPAA: Protects health information privacy and security.
- GDPR: Safeguards EU residents’ personal information.
- CCPA: Provides Californians with control over their personal information.
- PCI DSS: Ensures the secure handling of credit card information.
- ISO/IEC 27001: Governs information security.
- FedRAMP: Standardizes security for cloud services that interact with federal agencies.
Bottom Line: Securely Manage Your Cloud Data
Cloud data management makes data handling easier for both organizations and individuals. It maintains huge volumes of data on the cloud, adjusting to changing business needs with a diverse set of software and technologies available. When choosing the best solution, align your business needs with the software features, then take advantage of its free trials or plans to test its functionalities to make sure it seamlessly fits your business operations.
Employ a cloud security posture management (CSPM) tool to add another layer of security to your cloud data management solution.
The post 6 Best Cloud Data Management Software in 2024 appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post What Is Cloud Workload Security? Ultimate Guide appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>How Cloud Workload Security Works
Your organization can manage cloud workload security through coordination across multiple specialist teams. IT admins protect your consoles. Cloud security teams oversee virtual infrastructure and perform automated discovery. DevOps teams remove hard-coded secrets and manage consoles. Network security specialists monitor traffic insights, while the incident response teams monitor security events.
The following security processes performed by these teams should fully work together to ensure comprehensive protection:
- Securing cloud management consoles: IT administrators manage your consoles continuously and support all other security measures by managing permissions and configurations centrally.
- Protecting virtual infrastructure: Cloud security teams monitor virtual servers and combine this process with management panels and automated discovery to assure secure environments.
- Removing hard-coded secrets: DevOps teams prevent unauthorized access, eliminate hard-coded secrets, secure DevOps methods and integrate them into deployment frameworks.
- Overseeing and securing DevOps consoles: DevOps team track and defend DevOps consoles while enabling automatic discovery and integration into deployment frameworks.
- Conducting automated discovery: Security operations team evaluate and track workloads regularly to improve virtual infrastructure control and protection and security event management.
- Gaining insights into network traffic: Network security specialists manage and enhance the network data to assist in real-time threat identification and automated remediation.
- Integrating processes into deployment frameworks: Security and DevOps team automate security procedures during deployments to ensure coverage across all workloads and environments.
- Consolidating events: Security and incident response teams control and centralize security events to improve threat visibility and response while supporting all other security activities.
Incorporating these operations within your organization creates a strong, multilayered security structure for effective cloud workload protection. Examine the types, tools, and platform requirements for successful implementation. Then, through adhering to best practices, you can optimize the benefits of cloud workload security. This results in resilience against the common threats while protecting the reliability and integrity of your cloud environments.
Common Cloud Workload Protection Classifications
The different types of cloud workload protection can be grouped into three categories: cloud deployment models, cloud native technologies, and resource demands. These help you select proper security measures and deployment methodologies for your specific cloud workload requirements.
Deployment Model
There are three kinds of deployment models: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). Each cloud deployment model provides distinct benefits geared to specific organizational objectives and operational effectiveness in the cloud environment.
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): Controls virtualized resources such as virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking.
- Platform as a service (PaaS): Enables application creation and management without requiring infrastructure.
- Software as a service (SaaS): Provides entire software solutions through the internet via a subscription model.
Cloud Native Technology
Classifying cloud workloads via native technology allows you to optimize deployment methods and safety protocols. Understanding whether applications are better suited to containers, serverless environments, or virtual machines supports more efficient resource allocation, scalability planning, and security setting. Each provides distinct advantages in terms of flexibility, efficiency, and scalability.
- Containers: Are lightweight, portable components designed for application deployment in isolated settings.
- Container as a service (CaaS): Offers fully managed container environments that isolate infrastructure complexities.
- Serverless: Automatically scales computational resources for code execution without the need to manage infrastructure.
- Virtual machines (VMs): Simulate physical servers, and are often provided via cloud-based services.
Resource Demands
Categorizing cloud workloads types based on resource requirements helps optimize task resource allocation. It guarantees that computational resources such as CPU, GPU, memory, and storage are tailored for task demands to improve efficiency and performance in cloud settings. This classification enables enterprises to achieve affordability and scalability while meeting specific operational requirements.
- High central processing unit (CPU): Employ powerful central processing units to execute complex computations such as data analytics and scientific simulations.
- High graphics processing unit (GPU): Includes specialized graphics processing units to handle graphics-intensive applications like CAD and video rendering.
- High performance computing (HPC): Uses parallel computing to effectively execute complicated computations in large-scale contexts.
- Memory-intensive: Requires a large amount of memory to function properly and handle databases, analytics, and caching applications.
- Standard compute: Manages broad responsibilities like site hosting and software development effectively in cloud settings.
- Storage-optimized: Needs high input/output performance to conduct large data analytics and content management.
8 Benefits of Cloud Workload Security
Cloud workload security advantages, from protecting sensitive information to managing cloud complexity, maintaining data integrity, and guaranteeing operational continuity. They also help you in meeting regulatory standards and increasing efficiency across cloud settings. Each advantage contributes specifically to the organization’s overall resilience and security posture.
- Handles sensitive information: Minimizes illegal access and data breaches while maintaining trust and compliance.
- Maintains business continuity: Reduces disruptions and ensures continuous operations to improve organizational resilience and customer satisfaction.
- Supports compliance efforts: Adheres to regulatory rules and industry norms, avoiding legal concerns and reputational damage.
- Strengthens security posture: Improves overall cloud security posture by reducing risks and vulnerabilities to ensure long-term protection.
- Incorporates security measures: Enforces IAM and RBAC, which regulate access and reduce the risk of unauthorized exposure.
- Automates security processes: Increases efficiency in identifying and responding to threats, hence improving overall security effectiveness.
- Provides comprehensive asset visibility: Enables a unified picture of assets, allowing for proactive monitoring and speedier issue response.
- Centralizes workload management: Streamlines your workload control, reduces complexity, and improves operational efficiency.
8 Common Cloud Workload Risks & Threats
Cloud workloads are vulnerable to data breaches, malware, misconfiguration, and more. Regardless of cloud providers’ security measures, compromised credentials may harm entire systems, disclosing sensitive data to attackers. Hard-coded API keys, privileged access, and unpatched apps make them vulnerable to attacks, but you can reduce these risks by employing tools and secure practices. Here are the common threats and risks of cloud workload security:
- API vulnerabilities: Arise when insecure APIs in cloud apps allow unwanted access or compromise, usually due to poor design, weak authentication, or insufficient encryption mechanisms.
- Data breaches: Occur as a result of weak passwords, unpatched software, or weak access restrictions, which allow unauthorized parties to steal or change sensitive data housed in cloud environments.
- Distributed denial-of-service attacks: Flood cloud workloads with excessive traffic, disrupting services and causing downtime, frequently exploiting vulnerabilities in network infrastructure or application layers.
- Insider threats: Happen when internal users abuse privileges or credentials to access and exploit sensitive data or resources housed in cloud environments for personal gain or malevolent purpose.
- Malware and ransomware: Infect cloud workloads by exploiting vulnerabilities or misconfigurations, encrypting data or disrupting processes, and demanding ransom payments to restore access.
- Misconfiguration of security controls: Occur when credentials, firewalls, or access policies are incorrectly configured, resulting in vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to obtain unauthorized access or compromise cloud resources.
- Multi-tenancy risks: Result from sharing cloud infrastructure with multiple tenants, raising the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access if security measures are not properly segregated or monitored.
- Unauthorized access to workloads: Takes place after attackers use stolen or compromised credentials to circumvent inadequate access controls and get unauthorized access to cloud-hosted apps or data.
10 Cloud Workload Security Best Practices
The best practices for cloud workload security include established methods for risk mitigation and data protection. They ensure uniformity in the implementation of security measures across several cloud environments, hence reducing vulnerabilities. Evaluate your cloud infrastructure, workloads, and existing security measures first. Then, apply other best practices once you’ve identified which of the methods below best fit your business operations.
Examine Your Cloud Infrastructure
Begin by recording and analyzing the different types of cloud services (public, private, and hybrid) that your company employs. Identify the cloud providers you collaborate with and describe the types of workloads managed in each environment. This mapping aids in visualizing the complete cloud landscape and detecting potential security concerns linked with different types of services and providers.
Identify the Criticality of Your Cloud Workloads
This includes categorizing the data, applications, and infrastructure components that make up each workload in your cloud environment. It allows you to get insight into each workload’s sensitivity and criticality. Understanding these elements helps you prioritize security solutions, ensuring that the most critical workloads are adequately protected.
Evaluate Your Existing Security Measures
Assess the performance of your current security measures and practices throughout your cloud system. Conduct audits and assessments to discover any holes or flaws in your security posture. The assessment acts as a baseline for determining where improvements are needed, and it assists in developing your security goals and strategies.
Secure Individual Workloads
Apply appropriate security measures to each workload based on its classification and criticality. For example, sensitive data might need encryption at rest and in transit, whereas important applications may have stringent access controls and continual monitoring. To prevent potential hazards, address any vulnerabilities found during evaluations as soon as possible.
Automate Cloud Workload Management
Use automation tools and techniques, such as infrastructure-as-code (IaC), to handle and deliver workloads in hybrid or multi-cloud systems. Automation minimizes human errors associated with manual setups, assures consistency in security policy enforcement, and speeds up operations such as provisioning, monitoring, and patch management.
Restrict Access to Sensitive Workloads
To limit access to sensitive data and apps, use strong identity and access management (IAM) solutions such as role-based access control (RBAC) and zero-trust principles. By prohibiting over-privileged access and applying least privilege principles, you can reduce the attack surface and lower the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Deploy Monitoring & Logging Tools
Leverage cloud monitoring and logging tools to continuously manage the performance and health of your cloud applications and infrastructure. Monitoring aids in discovering odd activity or abnormalities that may signal a security breach. Logging provides audit trails for forensic investigation, as well as the ability to respond to and mitigate incidents quickly.
Apply Policy as Code
By incorporating security configurations directly into your code and deploying applications via containers, you ensure that security protections are reliably applied across several environments. The strategy improves security posture while reducing configuration drift and vulnerabilities.
Perform Security Analysis
Conduct regular security assessments, such as vulnerability scanning and penetration testing, to proactively discover and mitigate security flaws. Regular evaluations assist in understanding evolving risks, evaluating security procedures, and following regulatory compliance. Create and implement remediation plans based on the assessment results to improve your overall security posture.
Centralize Tracking for Visibility
Create consolidated monitoring and tracking capabilities across your cloud environments to acquire a comprehensive view of security events and activities. Integrate monitoring technologies that collect logs and metrics from many cloud providers and environments. This centralized method allows for proactive threat detection, rapid incident response, and effective security issue management.
Combine your workload-specific measures with general cloud security best practices and tips for deeper protection of your cloud systems.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform Requirements
Before choosing a CWPP solution, evaluate the support for hybrid and multi-cloud setups, ease of deployment, continuous monitoring, and runtime protection while maintaining performance. It should also provide visibility across all cloud types, security against misconfigurations, malware, and breaches, and automated risk management and compliance, among other things.
Consider the following factors:
- Deployment flexibility: Make sure the CWPP works flawlessly with your hybrid and multi-cloud settings.
- Ease of deployment: Select a system that integrates seamlessly without increasing operational overhead.
- Comprehensive security features: Verify that it has features like endpoint detection and response (EDR), vulnerability scanning, and compliance monitoring.
- Continuous monitoring: Consider a CWPP that provides real-time monitoring features to quickly discover threats and anomalies.
- Automation capabilities: Look for features that simplify risk management, compliance, and vulnerability prioritization.
- Runtime protection: Determine whether the platform offers full security for containers and cloud workloads during runtime, rather than merely at launch.
- Visibility: Ensure that the CWPP provides complete insight into workload events, including container activity, to enable effective threat detection and response.
- Performance: Assess the solution’s performance impact to ensure that it meets operational requirements without causing major delays.
- Integration with DevOps: Evaluate whether the CWPP works well with DevOps methods to facilitate agile development.
- Scalability: Check if the solution scales as your workload grows and if it adapts to your dynamic cloud environment.
Top CWPPs to Consider
CWPP solutions like Illumio Core, SentinelOne Singularity Cloud, and Sophos Cloud Workload Protection automate monitoring across servers. They provide unified visibility and administration for physical machines, VMs, containers, and serverless programs to boost cloud security. These solutions improve your overall cloud management, lower the likelihood of data breaches, and help strengthen your security posture.
Illumio Core
Illumio Core is a CWPP solution offering micro-segmentation capabilities, workload visibility, and real-time threat detection. It offers granular security control over network traffic and dynamically modifies security settings based on workload behavior. Illumio Core provides consistent protection through easy scaling in cloud environments. Pricing starts at $7,000 per year for 50 protected workloads and 25 ports.
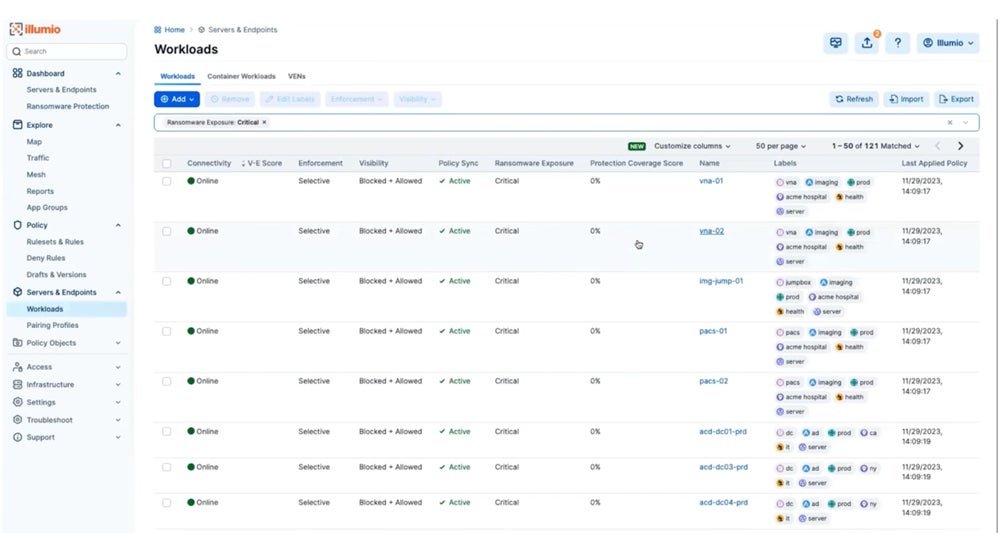

SentinelOne Singularity Cloud
SentinelOne’s Singularity Cloud specializes in advanced automation, with a focus on runtime detection and response for cloud virtual machines, containers, and Kubernetes clusters. It employs AI-powered algorithms and behavioral analytics to respond to advanced threats in real time. Singularity Cloud expands across many cloud environments and starts at $36 per VM or Kubernetes worker node, per month.
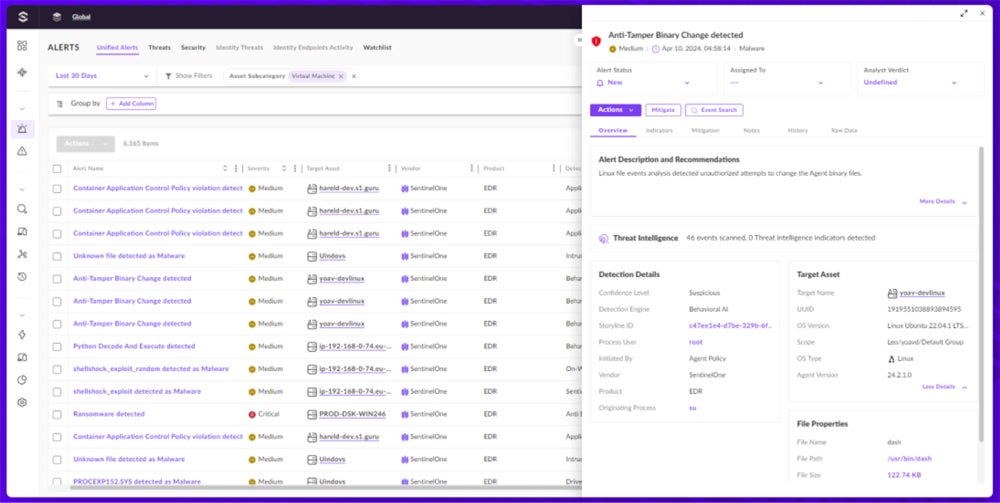

Sophos Cloud Workload Protection
Sophos Cloud Workload Protection provides effective cloud workload protection through a user-friendly interface, strong security features, and seamless integration possibilities. It offers extensive visibility and detects threats, including container escapes and kernel exploits. Sophos’ Integrated Live Response enables rapid incident response, hence improving total cloud workload protection. Custom quotations are available by contacting their sales team.
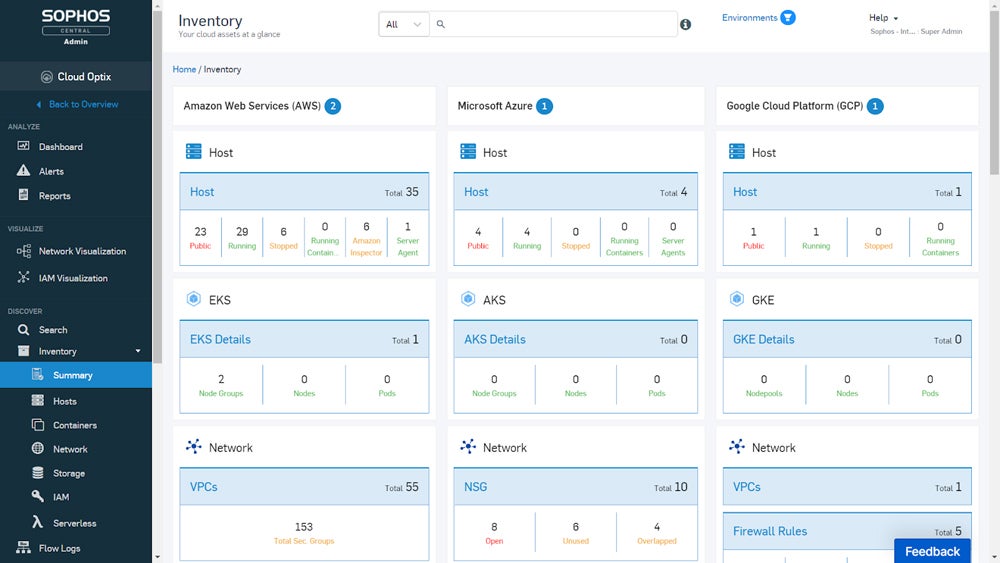
Discover more solutions in our full review of the top CWPP solutions covering their use cases, features, pros, cons, and more.
Bottom Line: Boost Your Cloud Workload Security Now
Implementing cloud workload security best practices and utilizing CWPP tools improve security, guarantee regulatory compliance, and sustain business continuity. Combining CWPPs with supplementary cloud solutions enhances your overall protection through the integration of multiple security layers specific to different aspects of cloud security. Utilize CWPPs’ integrative capabilities to strengthen the security and resilience of your cloud workloads.
To further enhance your cloud security posture, explore other solutions by reading our comprehensive guide covering CSPM, CWPP, CIEM, CNAPP, and CASB, plus their distinct features and practical applications.
The post What Is Cloud Workload Security? Ultimate Guide appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post What Is Cloud Data Security? Definition, Benefits & Best Practices appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>Why Should Organizations Prioritize Cloud Data Security?
Organizations switching to cloud-based storage and services must prioritize cloud data security in order to properly protect critical information. With data spread across numerous cloud environments and accessed from a variety of devices, a cloud-native security solution guarantees strong protection while promoting flexible innovation and compliance with regulations.
Gartner anticipates a major shift in IT investment to the public cloud by 2025, up from 41% in 2022, highlighting the scalability and agility of cloud solutions to protect businesses against the rising data loss threats. The data-intensive and dynamic corporate setups make cloud data security essential for protecting against both new and existing cyberthreats while also maintaining trust, operational integrity, and regulatory compliance.
Consider cloud data security if your company is:
- Dealing with increasing data volume and complexity: As you manage enormous amounts of data across multiple platforms and cloud settings, it becomes more important to protect sensitive information effectively.
- Migrating to cloud or hybrid environments: Make sure your security keeps up with the nature of cloud-based services, applications, and rapid business processes as you move to cloud or hybrid adoption.
- Supporting remote and hybrid workforces: Cloud data security practices allow safe data access from multiple locations and devices while retaining accessibility for remote and hybrid workforce models.
How Cloud Data Security Works
Cloud data security protects sensitive information stored and processed in cloud environments by combining encryption, authentication, access controls, data masking, monitoring, and incident response measures. These precautions protect data security, integrity, and availability while limiting the risks of unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks.
Security teams work together to develop and maintain effective cloud data security through six general but critical steps: encryption, authentication, access control, data masking, monitoring, and incident response. The effectiveness of cloud data security is heavily dependent on the skills and efforts of these security teams.
Here’s how you and your team can accomplish cloud data security:
- Encryption: The initial step requires the IT security teams to use encryption tools to encode data at rest and in transit using powerful algorithms so that only authorized individuals with decryption keys have access to sensitive information.
- Authentication: Next, the IT security teams are in charge of implementing authentication mechanisms such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) using identity and access management (IAM) systems.
- Access control: IT security teams then use role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) to design and implement access control policies based on organizational requirements and regulatory standards.
- Data masking and obfuscation: Data privacy officers and information technology security specialists use strategies to conceal sensitive data pieces by substituting identifiable information with pseudonyms or proxy characters.
- Monitoring and auditing: IT security teams regularly examine logs and audit trails to spot suspicious activity, anomalies, or potential security breaches as soon as possible. This ensures that risks to cloud-stored data are detected and addressed early on.
- Incident response and recovery: Finally, the incident response teams and the IT operations team define protocols for containing security incidents, researching root causes, and quickly restoring data integrity and system functionality.
Understanding the roles played by different security teams in protecting your cloud data is fulfilled through the shared responsibility approach. The model clarifies the fundamental cloud security responsibilities of cloud service providers (CSPs) and consumers. CSPs protect infrastructure and services, while consumers control data, apps, and access. This methodology provides full protection, reduces security gaps, and encourages accountability.
The teams’ expertise, along with proper implementation of best practices, ensures that cloud-based data remains protected against cloud security challenges while leveraging the advantages of secure cloud computing.
Benefits of Securing Cloud Data
Implementing strong cloud data security measures protects sensitive information while simultaneously offering several operational advantages. The security measures ensure that businesses can confidently gain the benefits of cloud computing while adhering to regulations, optimizing resources, and improving overall efficiency.
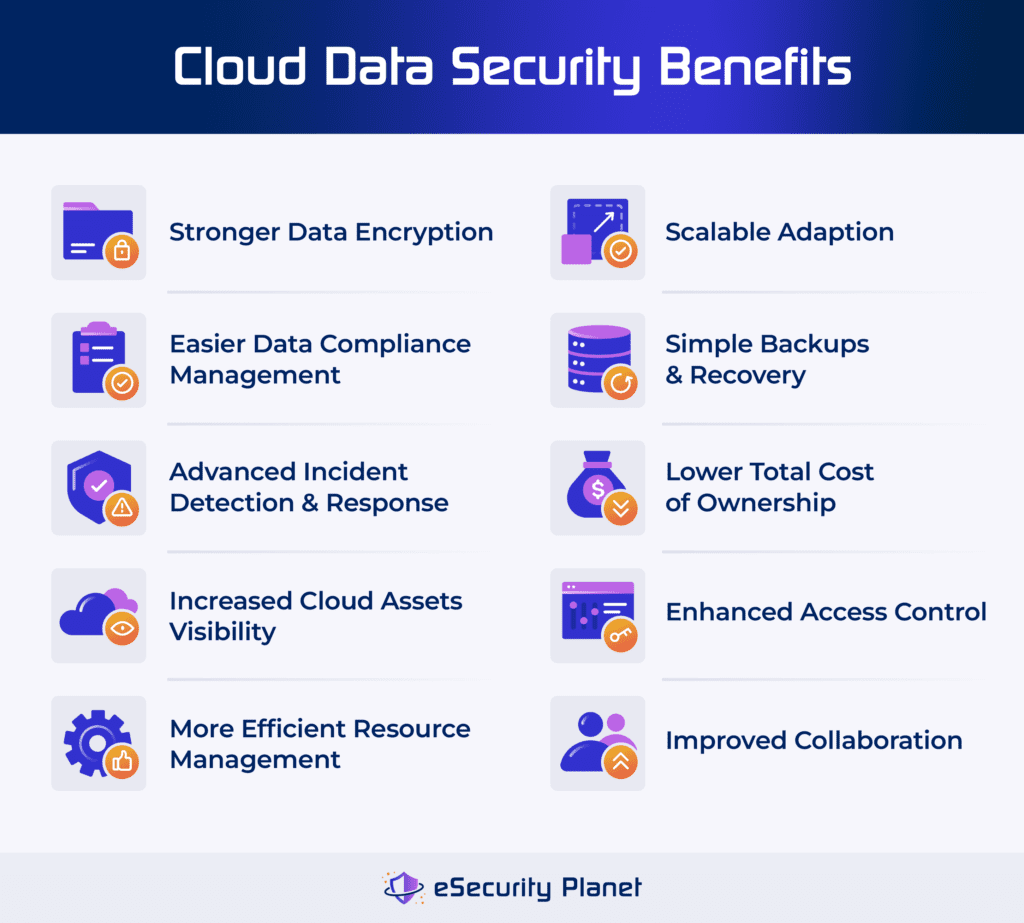
Here are the 10 major benefits of cloud data security:
- Stronger data encryption: Uses modern encryption technologies to protect sensitive data during transit and storage. You can use encryption tools to strengthen confidentiality and security from unauthorized access.
- Easier management of data compliance: Complies with regulations by tracking data storage, access, processing, and protection. Apply data loss prevention tools to lower the likelihood of compliance infractions.
- Advanced incident detection and response: Quickly identifies and responds to security incidents with AI-driven security analytics and automated scanning for suspicious activities, reducing potential damage.
- Increased cloud assets visibility: Monitors and gains insights about your cloud assets, user activity, and data access patterns to ensure transparency and improved control over your data environment.
- More efficient resource management: Assigns infrastructure maintenance to the CSP to save money on IT and free up workers to focus on essential business areas such as customer care and modernization.
- Scalable adaption: Quickly adjusts your cloud resources to match your company demands as they increase. Cloud data security tools enable efficient activity management and cost-effective scaling.
- Simple backups and recovery: Automates backup solutions and standardizes recovery procedures to reduce manual oversight and allow for quick data and application restoration, hence improving business continuity.
- Lower costs: Reduces the total cost of ownership (TCO) by eliminating the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure and employing your cloud providers’ latest security features and capabilities.
- Enhanced access control: Ensures that authorized users may access cloud-hosted databases from any device and place with an internet connection, meeting the needs of today’s digital workforce.
- Improved collaboration: Offers a secure, centralized platform for data exchange and communication so team members can work together seamlessly to increase productivity and collaboration.
Common Challenges of Cloud Data Security
As enterprises adopt cloud and hybrid environments, they experience various data protection challenges. Ensuring strong cloud data security necessitates navigating a complex environment filled with possible risks and compliance challenges. Here are the common issues that businesses encounter when safeguarding data in the cloud:
- Inconsistent coverage: Different levels of coverage and capabilities across several clouds and hybrid environments lead to inconsistency in protection.
- Rising cybersecurity threats: Cloud databases and storage are popular targets for threat actors, especially when businesses adopt new data management techniques.
- Stringent requirements: Implementing security policies across various settings to meet severe data protection regulations can be complex.
- Dispersed data storage: International data storage not only reduces latency and increases flexibility but also creates data sovereignty concerns.
- Increased attack surface: Flexible and scalable cloud infrastructures frequently result in misconfigurations and assets placed outside of security policies.
9 Best Practices for Cloud Data Security
Effective cloud data security practices consist of identifying and categorizing data, applying unified visibility, regulating resource access, encrypting data, deploying DLP, enhancing data posture, monitoring risks, and using a single platform for documentation. By adhering to these best practices, you can build a strong cloud data security architecture that secures sensitive information. They enhance the dependability and integrity of your cloud infrastructure.
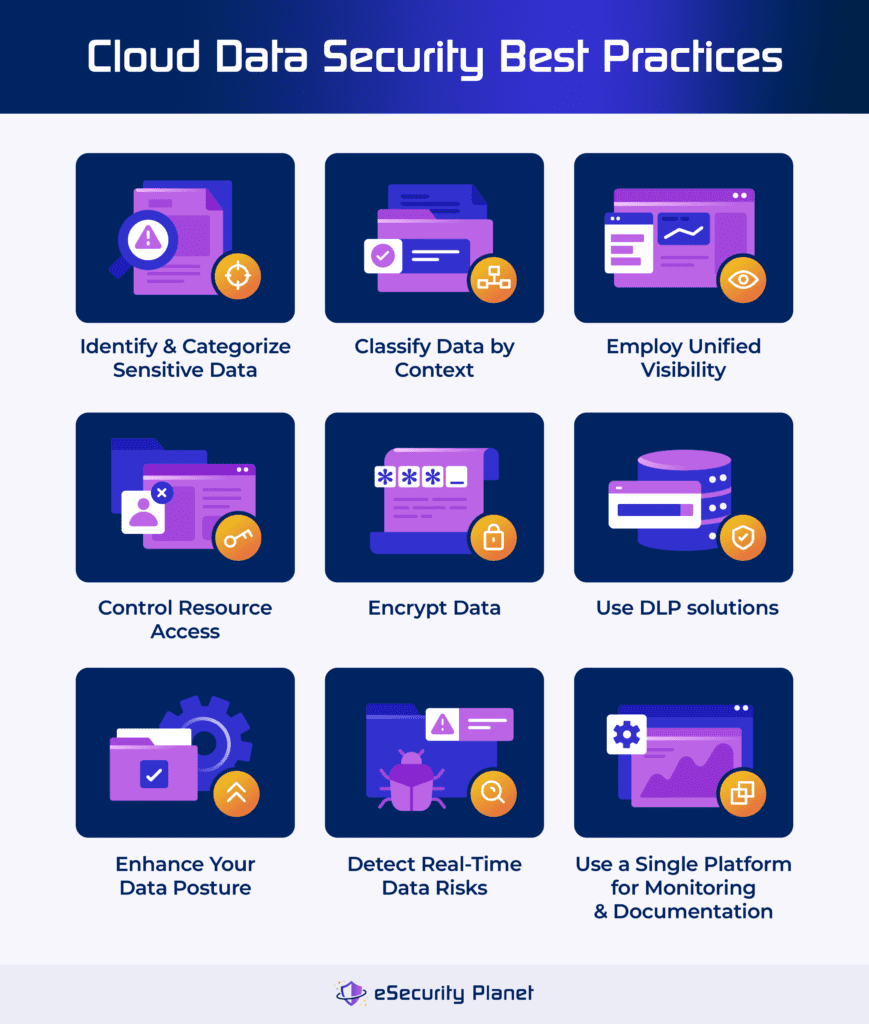
Determine Sensitive Data
Identify and categorize sensitive data from public cloud platforms, virtualization environments, data analytics platforms, and databases. This includes finding “shadow data.” Use automated discovery technologies to examine your whole environment, making sure no data is missed. Regular audits can help keep data inventories up to date.
Categorize Data by Context
Classify data by kind, sensitivity, and control rules. Consider how data goes across the company and how it’s used. Implement data classification policies and tools for labeling and tracking data. Review data classifications on a regular basis to verify they’re up to date and meet compliance standards.
Provide Unified Visibility
Use unified discovery and visibility to detect misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and threats in private, hybrid, and multi-cloud systems. Employ centralized dashboards and monitoring technologies to acquire complete visibility. Ensure constant monitoring in order to recognize and respond to concerns as they arise.
Regulate Resource Access
Apply role-based access controls (RBAC) and attribute-based access controls (ABAC) to give users the least amount of access required for their position’s responsibilities. Regularly check and update access permissions. Use identity and access management (IAM) technologies to provide strict access constraints.
Encrypt Data in Transit & Data at Rest
To prevent unauthorized access, encrypt sensitive data during transmission and storage. Use strong encryption techniques like TLS for data in transit and AES-256 for data at rest. To maintain security, ensure that encryption keys and protocols are regularly updated.
Deploy Data Loss Prevention Tools
DLP solutions can detect and prevent data leakage or loss during cooperation, compromised systems, or malevolent insiders. Implement DLP tools to monitor data transfer and enforce policies. To reduce inadvertent data leaks, educate personnel about proper data handling methods.
Enhance Your Data Posture
You can utilize data security posture management (DSPM) tools to detect static threats including misconfigurations, deactivated encryption, versioning issues, and unauthorized access. Perform regular scans and assessments of your cloud infrastructure. Use automated methods to discover and close security weaknesses while also ensuring policy compliance.
Monitor Data Risks in Real-Time
The real-time surveillance of dynamic cloud systems can detect new data assets, developing threats, and novel attack tactics. Use modern threat detection and response tools, like SIEM solutions, to assess and manage risks. To keep up with new threats, update threat intelligence on a regular basis.
Implement a Single Platform for Monitoring & Documentation
Combine monitoring, remediation, and documentation into a single platform to provide complete visibility and automatic responses to cloud security issues. Use a unified security management system to consolidate all security activities. Maintain extensive logging and reporting for auditing and compliance purposes.
In addition to the cloud data security–specific measures listed above, read our comprehensive guide and checklist for cloud security best practices.
What Solutions Help Secure Cloud Data?
CWPP, CSPM, CNAPP, IAM, and DLP solutions improve cloud data security by addressing vulnerabilities, enforcing access rules, and securing applications. They protect sensitive data across cloud infrastructures. Integrating these solutions into your cloud data security frameworks allows you to limit risks while also strengthening the security of your cloud data.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
CWPPs are used to secure cloud-native apps and workloads. They provide visibility into cloud systems by detecting vulnerabilities and managing risks across a variety of platforms, including Kubernetes, serverless architectures, and classic virtual machines. CWPPs reduce the risks associated with cloud-based application deployment by continuously monitoring for threats and guaranteeing compliance with security regulations.
Our recommended solution: Orca Security is a CWPP tool suited for businesses that value comprehensive cloud workload protection and compliance monitoring. It specializes in complex cloud configuration security, with strong vulnerability management and broad visibility across different cloud platforms. You can contact Orca Security sales for custom quotes and free demo requests.
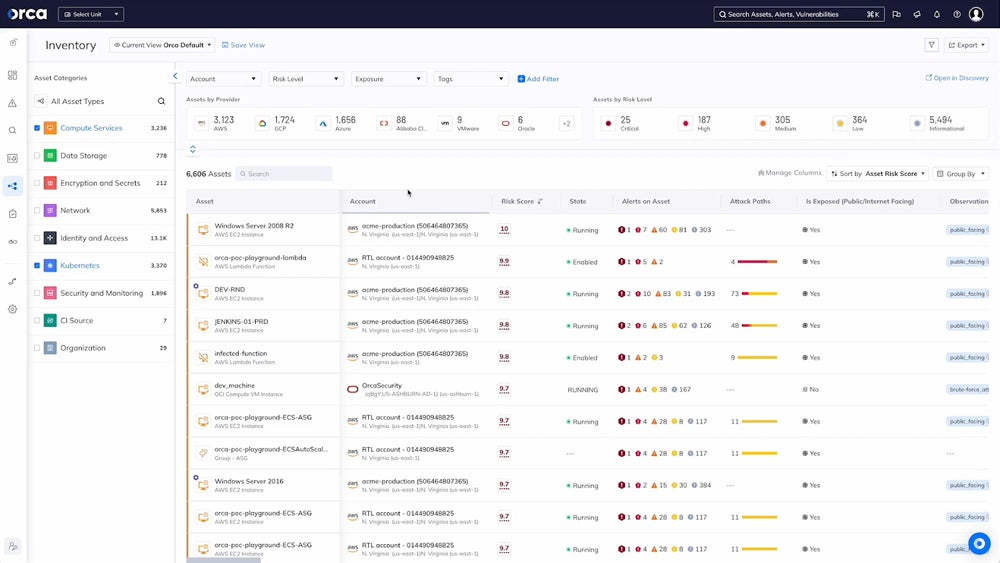
Explore the top CWPP solutions, highlighting each solution’s top features, strengths, pricing information, and more.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tool
CSPM solutions offer security and compliance across all cloud infrastructures. They automate the examination of cloud setups, detecting errors that could expose sensitive data or introduce security flaws. CSPMs enforce security policies, audit trails, and compliance standards so that cloud resources are properly set up and maintained in accordance with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
Our recommended solution: Palo Alto Prisma Cloud stands out for its flexible deployment choices, robust third-party security and compliance integrations, machine-learning-driven threat detection, and complete code scanning capabilities. It streamlines customization and automation, making it more user-friendly. The Enterprise Edition costs $18,000 for 100 credits and a 12-month membership through AWS Marketplace.
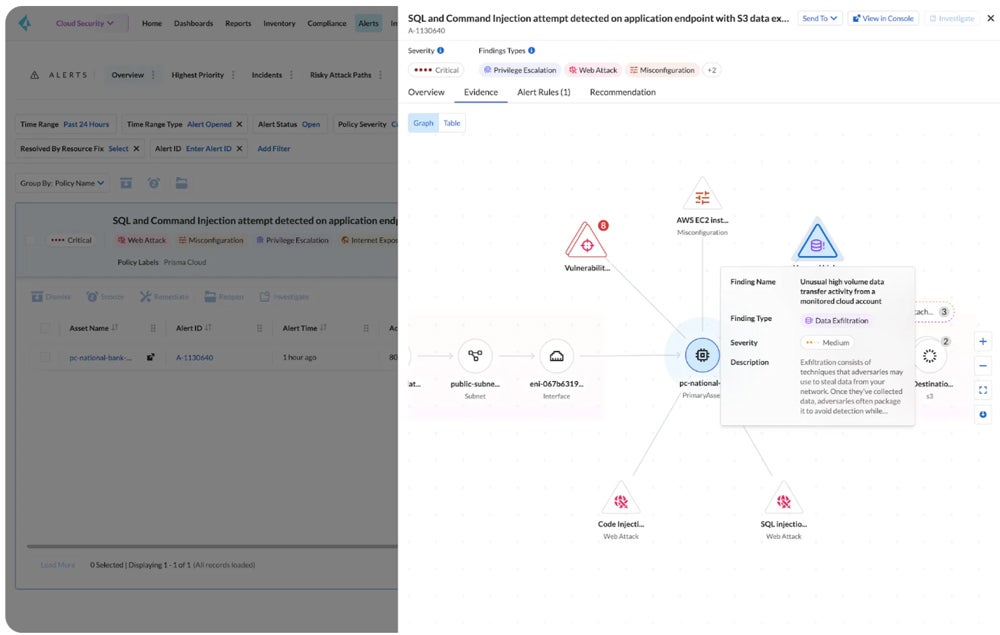
Discover the top CSPM tools, their strengths, use cases, and features in our detailed review.
Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP)
CNAPPs secure cloud-native apps throughout their lifecycle. They offer security features like runtime protection, API security, and threat intelligence tailored to cloud environments. CNAPPs enable enterprises to secure applications from development to production. They provide safeguards against developing threats and vulnerabilities specific to cloud-native architectures.
Our recommended solution: Check Point CloudGuard excels at container security and runtime protection by combining CWPP and CSPM. It’s designed for companies that require powerful security for cloud-native apps, with a unified dashboard, policy rules, and both agent and agentless monitoring. It also provides full security across cloud platforms through unified visibility and auto-remediation. CloudGuard costs $625 per month for 25 assets on AWS Marketplace.
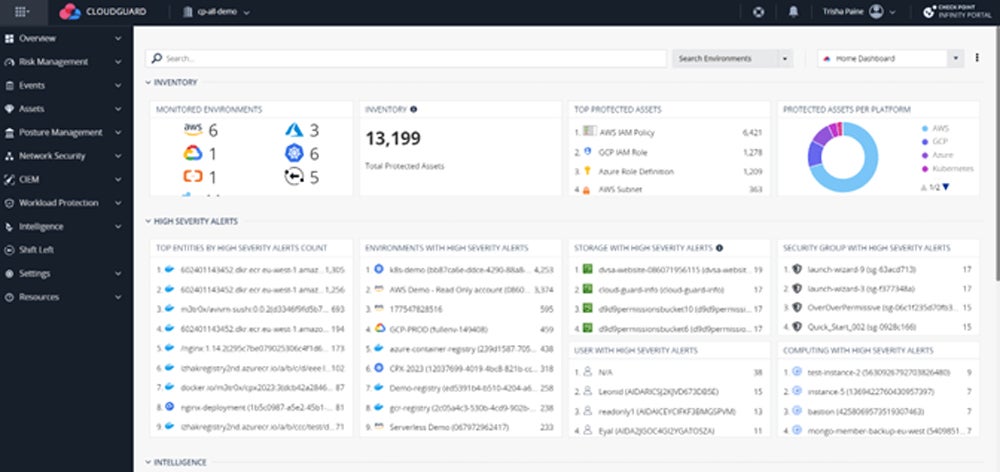
Learn more about the top CNAPP tools available in the market in our comprehensive guide covering their key features, pros, cons, and more.
Identity & Access Management (IAM) Solution
IAM systems manage user identities, permissions, and access rights across several cloud services. They consolidate user authentication processes, impose RBAC controls, and interface with single sign-on (SSO) solutions to improve access management efficiency. IAM enables companies to execute the least privilege principle so that users only access the data required for their tasks. This prohibits unwanted access.
Our recommended solution: JumpCloud is a comprehensive identity, access, and device management tool designed for cloud environments. It offers zero-trust policies, Cloud LDAP for user administration, and Cloud RADIUS for device authentication using certificates. Its Cloud Directory solution centralizes identity control and lifecycle management, making it suitable for both small and large corporations. JumpCloud’s full platform costs $15 per user per month.
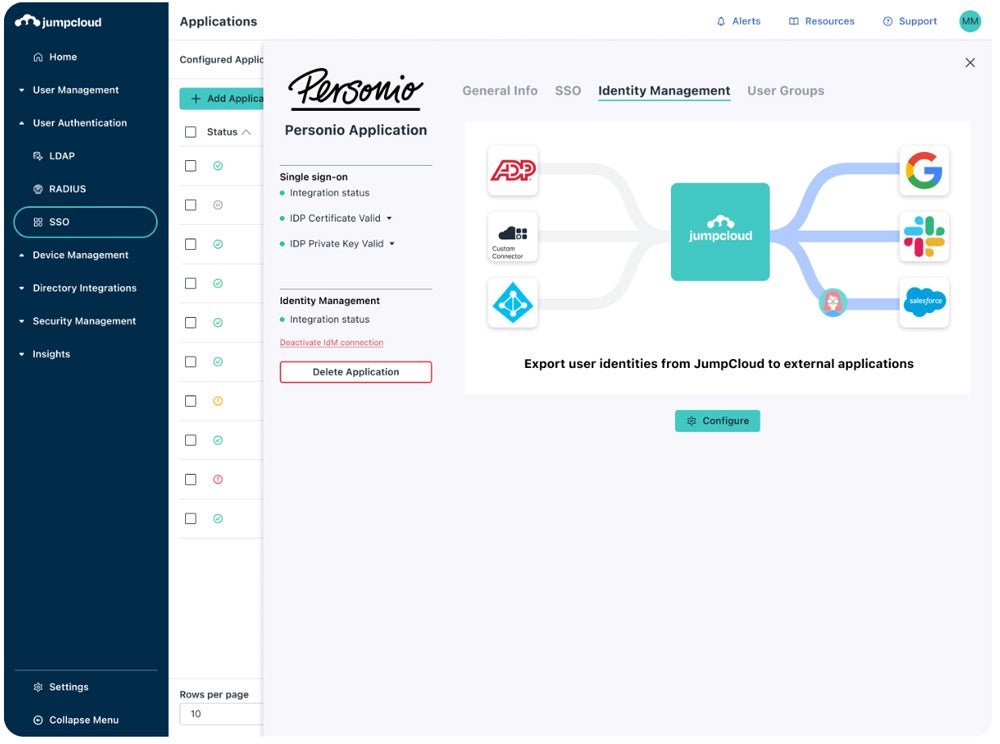
Check out our thorough review of the best IAM solutions, plus their advantages, key features, cost, and ideal use cases.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tool
DLP systems are crucial for preventing data leaks and maintaining data security in cloud environments. They track and analyze data both in transit and at rest, identifying sensitive information and enforcing regulations to prevent unwanted access, sharing, or loss. DLP solutions provide visibility into data usage patterns, detect abnormalities indicating potential breaches, and allow for quick response measures to manage risks and ensure data integrity.
Our recommended solution: Forcepoint DLP is well-known for its full global policy management across key channels such as endpoint, network, cloud, online, and email. It offers over 1,500 predefined templates and rules to help businesses comply with requirements from 83 countries, making it perfect for large firms. Pricing information is available by contacting Forcepoint’s sales team. They also offer a 30-day free trial for evaluation.
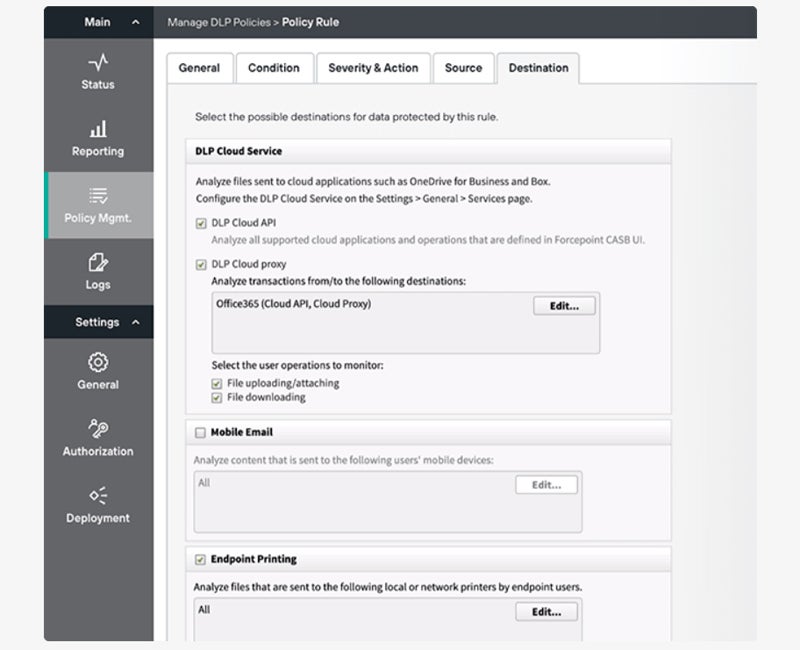
Compare the top DLP solutions in our in-depth guide including their pricing details, key features, strengths, and more.
Bottom Line: Enhance Data Protection with Cloud Data Security
Cloud data security is necessary for enterprises that use cloud-based storage and services. It protects sensitive information in the face of rising data quantities, complicated contexts, and rapid digital transformation. Cloud data security offers plenty of data protection benefits — obtained by applying best practices to properly manage risks. Enhance your protection by implementing these practices along with other cloud security management techniques.
Learn more about the different types of cloud security management in our detailed guide, covering the protection strategies, benefits, challenges, and tools you can use.
The post What Is Cloud Data Security? Definition, Benefits & Best Practices appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post What Is Cloud Security? Definition, Best Practices & Types appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>Software Spotlight: Lookout SPONSORED
Lookout Secure Cloud Access is a unified cloud-native security platform that safeguards data across devices, apps, networks, and clouds.
- Offers a seamlessly integrated security approach for end-to-end zero trust.
- Identifies and prevents advanced zero-day threats via Cloud Sandbox.
- Simplifies compliance management and security governance on all cloud and SaaS apps.
Featured Partners: Cloud Backup & Storage Software
Why Cloud Security Is Important
Cloud security safeguards sensitive cloud information and enables secure access for authorized users. It addresses stringent compliance requirements, offering a structured framework for regulation adherence and thorough audits. As remote collaboration becomes more prevalent globally, cloud security secures access to information from anywhere in the world.
Here are a few reasons why prioritizing cloud security is crucial:
- Data security: Protects your data from unwanted access, securing the confidentiality of personal and commercial information. It defends you against any breaches that might damage sensitive information by employing strong security procedures.
- Assurance of privacy: Serves as a defender, guaranteeing that your personal and sensitive information is treated with the highest care. This increases the user and service provider’s peace of mind and trust.
- Continuity of operations: Maintains continuity for firms that use cloud services. Cloud security measures limit risks associated with data loss or service outages, allowing operations to continue smoothly even during unexpected problems.
- Compliance requirements adherence: Facilitates compliance with governing data handling and privacy requirements in various industries and jurisdictions. Establishes a systematic framework for overseeing and auditing data access and usage.
- Cyber threat mitigation: Shields you from cyber threats that can compromise millions of data, ranging from hacking and phishing to malware attacks. Functions as a protective barrier against malicious activities by identifying and neutralizing potential threats.
- Enhanced collaboration and remote access: Ensures the security of cloud-based platforms is imperative. Enables safe and protected access to data and applications globally by fostering collaborative environments without compromising safety.
- Scalability and flexibility: Assures that measures are designed to be scalable and adaptable, and that it provides a flexible and secure environment capable of adjusting to the changing requirements of an organization.
- Trust and reputation: Establishes practices so cloud service providers entrusted with user and client data can maximize its defense against a breach in security and reduce the potential to damage businesses’ reputation.
How Cloud Security Works
When securing data in the cloud, you integrate key cloud components with your organization’s policies and your cloud solutions. These form the foundation of an effective cloud security that provides you with data security and access control benefits. Although storing your data in the cloud still poses different challenges and risks, you can still address these issues through proper deployment of cloud tools and best practices.
Cloud security starts when the user and the cloud service provider (CSP) define their shared responsibilities. It requires a coordinated effort from both the CSP and the customer. Each party’s duties vary based on the cloud service paradigm (IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS). Customers are typically responsible for protecting their data, apps, and user access, but CSPs handle the underlying infrastructure, such as computing resources, storage, and physical network security.
Here’s a quick overview of how you and your CSP share these cloud security functions:
| Cloud computing service model | Your responsibility | CSP responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure as a service (IAAS) | Secure your: • Data • Virtual network controls • Applications • Operating system • Authorized user access | Secure the: • Computational resources • Storage • Physical network including patching and configuration management. |
| Platform as a service (PAAS) | Secure your: • Data • User access • Applications | Secure the: • Computational resources • Storage • Physical network • Virtual network controls • Operating system. |
| Software as a service (SAAS) | Secure the authorized user. | Secure the: • Computational resources • Storage • Physical network • Virtual network controls • Operating systems • Applications • Middleware |
This division of responsibility guarantees that both parties contribute to a safe cloud infrastructure. Continuous monitoring further aids in the early discovery of suspicious behaviors and potential threats, so you can perform a timely response to limit potential risks. Together, these practices ensure that cloud environments are secure, compliant, and resilient to cyber threats.
4 Key Components of Cloud Security
Cloud security components are standard security elements that operate together to provide a strong cybersecurity posture for cloud settings. To secure sensitive information and maintain the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of cloud-based systems, consider a comprehensive solution that tackles identity access management (IAM), network defense, data protection, and application security.
Identity & Access Management (IAM)
To secure and regulate access, IAM verifies identities, defines permissions, and manages the lifespan of user accounts. It provides authentication methods like multi-factor authentication, regulates authorization by defining permissions, and manages account provisioning and deprovisioning to reduce unauthorized access and insider threats.
Here’s how its security aspects work:
- Authentication: Makes sure that only authorized individuals or systems can access resources in the cloud. Proper authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, help verify the identity of users.
- Authorization: Defines and manages permissions, specifying what actions users or systems are allowed to perform. Enforce the principle of least privilege to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Account provisioning and deprovisioning: Controls the creation, modification, and removal of user accounts. Timely de-provisioning is crucial to revoke access for employees who no longer need it, minimizing the risk of insider threats.
Network Security
Network security entails protecting cloud infrastructure by deploying perimeter defenses (firewalls, IDPS, VPNs), guaranteeing isolation through network segmentation (VLANs), and constantly monitoring traffic for anomalies. These methods prevent unwanted access, contain breaches, and allow for rapid threat detection and response, assuring data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
These factors form an integrated network security approach for protecting cloud infrastructure:
- Perimeter security: Establishes and maintains the perimeter defenses of the cloud infrastructure. Firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs) help prevent unauthorized access and protect against external threats.
- Isolation: Checks that if one part of the network is compromised, the rest remains secure. Limit the potential impact of a security breach through containment strategies like network segmentation and using virtual LANs (VLANs).
- Traffic monitoring and analysis: Helps detect anomalies and potential security incidents through continuous monitoring of network traffic. It allows for rapid response to mitigate threats before they escalate.
Data Security
Data security in the cloud entails protecting information throughout transmission, storage, and processing. Among the measures taken are encryption (in transit and at rest), access controls (IAM, MFA), data masking, and frequent compliance audits. Encryption prevents illegal access; DLP tools monitor and safeguard sensitive data; and backup and recovery methods reduce downtime and potential loss in the event of an incident.
Below are the common measures applied in data security:
- Encryption: Ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access to data, they cannot understand or use it without the proper decryption keys. Protect sensitive information both in transit and at rest with data encryption tools.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): Helps identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access, sharing, or accidental exposure via DLP tools. Utilize tools for compliance with data protection regulations.
- Backup and recovery: Takes additional security measures so you can restore their data from backups in the event of a security incident or data loss. It minimizes downtime and potential data loss.
Application Security
Application security in the cloud entails protecting cloud-based applications against threats and vulnerabilities. Its goal is to secure code, APIs, and configurations against unwanted access and data breaches. Code scanning, API security, and regular audits offer long-term protection. Web application firewalls protect against XSS and SQL injection attacks by blocking HTTP traffic.
Here’s how the various elements of application security function:
- Code security: Helps identify and fix vulnerabilities in applications with secure coding practices and regular code reviews. It reduces the risk of exploitation by attackers seeking to compromise the integrity of the application.
- API security: Many cloud-based applications rely on application programming interfaces (APIs). Ensuring the security of these APIs prevents unauthorized access or manipulation of data and services.
- Web application firewalls (WAF): WAFs protect web applications from various security threats, such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection attacks. They help filter and monitor HTTP traffic between a web application and the internet.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Security?
Implementing robust cloud security measures can help you improve your overall security posture by providing you with greater visibility, expediting backups and recovery procedures, assisting you with compliance adherence and more. To successfully minimize risks while meeting your organization’s goals, check if your cloud security procedures are aligned with your specific business objectives and regulatory needs.
Greater Visibility
In a cloud environment, you obtain a better understanding of your IT architecture. Cloud platforms provide powerful monitoring and logging features, allowing you to watch activities, discover anomalies, and assess your system’s security posture. The increased visibility improves your capacity to implement proactive security measures and respond quickly to possible attacks or vulnerabilities.
Seamless Backups & Recovery
You can benefit from automatic backups and recovery with cloud services. Simply back up your data and applications for prompt recovery in the event of data loss, system failures, or interruptions. This dependability supports company continuity while reducing downtime, improving overall operational efficiency and resilience.
Reliable Cloud Data Compliance
Many providers follow strong security and industry requirements for reliable cloud data compliance. Organizations that use cloud services can better meet industry-specific criteria by using these strategies. It maintains data integrity and confidentiality that reduce the risks associated with noncompliance and increase confidence among customers and stakeholders.
Robust Data Encryption
Cloud providers often provide encryption techniques to safeguard data both in transit and at rest. It protects critical information from unwanted access and improves the organization’s overall security posture.
Reduced Costs
Instead of investing in and maintaining on-premises infrastructure, your business may take advantage of cloud providers’ economies of scale. Additionally, cloud services are frequently offered on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing enterprises to expand resources based on their need and potentially lower total IT expenses.
Advanced Incident Detection & Response
Cloud security systems frequently incorporate enhanced incident detection and response capabilities, which use machine learning algorithms to identify and neutralize security threats in real time, thereby minimizing possible damage. It helps you discover and neutralize possible dangers before they cause major damage.
5 Top Challenges & Risks of Cloud Security
Even though cloud security solutions are widely accessible in the market, there are still some challenges that companies face when it comes to protecting their data in the cloud. Some of the most common issues in cloud security include misconfiguration, unauthorized access, account hijacking, external data sharing, and unsecured third-party resources.
Misconfiguration
Misconfigurations occur when cloud resources aren’t correctly configured, resulting in security risks. Some examples are poorly set up access restrictions, improperly configured storage buckets, or incorrect network settings. Attackers may take advantage of these errors to obtain unauthorized access to or modify cloud resources.
Unauthorized Access
Malicious actors can obtain unauthorized access to sensitive data or resources if suitable access controls and authentication procedures are not in place. Unauthorized access might include exploiting weak passwords, hacked credentials, or other authentication flaws.
Hijacking of Accounts
Unauthorized persons obtain control of user accounts through account hijacking. It occurs as a result of phishing campaigns, compromised credentials, or other malicious activity. Once an account is compromised, attackers may get access to critical data and resources, creating a significant security risk.
External Sharing of Data
Cloud services frequently entail user and company cooperation and data exchange. It’s important to manage and govern external data exchange in order to avoid unintended disclosure of sensitive information. To prevent this risk, organizations must adopt appropriate access restrictions and encryption.
Unsecured Third-Party Resources
Many businesses employ cloud-based third-party services and apps. If these external resources’ security is not sufficiently examined and managed, they might cause a vulnerability. Third-party integrations and dependencies should be thoroughly vetted and managed for security.
Understand how the top cloud security threats, risks, and challenges occur and read our guide on how to solve these issues.
Best Practices for Securing Each Cloud Environment
Cloud environments are commonly classified into five types: public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, multi-cloud, and multi-tenant cloud. Despite their distinct characteristics, these clouds have a common strategy for maintaining each environment’s security.
Public Cloud
Public cloud is a cloud computing service available to the general public over the internet. The shared responsibility model governs security duties in public cloud systems. The provider secures the infrastructure, while the consumer handles access, application connections, and data storage.
Apply these best practices:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA): Strengthen user logins by providing an additional degree of safety beyond passwords. Reduce the risk of unwanted access by demanding various types of verification.
- Conduct regular updates and patching: Keep software and applications up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities. Regular updates guarantee that security patches are applied quickly, lowering the risk of exploitation.
- Maintain continuous monitoring and alerts: Monitor cloud resources in real time for suspicious activity and configure alerts for potential security breaches. Enable timely detection and response to attacks to improve your overall cloud security posture.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment that is dedicated to a single organization. It’s typically hosted on-premises and managed by the organization’s IT department. Private clouds, which are tailored to specific enterprises, provide greater security control, making them appropriate for sensitive data and applications, despite the fact that they require knowledge and cost.
Practice the following recommended methods:
- Isolate networks: Segment networks with VLANs to reduce attack surface and enforce security regulations. Customize the rules and access limits to increase isolation.
- Control user access: Use authentication and RBAC to control data access. See to it that only authorized users can access vital resources.
- Manage patches: Apply updates on a regular basis to resolve vulnerabilities and keep your system secure. Patching in a timely manner decreases the danger of exploitation.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud security safeguards data and applications across private and public clouds, combining on-premises and cloud-based resources for a wide range of computing requirements with strong security. This method blends the scalability and flexibility of public clouds with data control on private infrastructure, combining on-premises controls with cloud-specific technologies to provide comprehensive protection.
Employ these techniques to secure your hybrid cloud:
- Secure your connection: Establish secure connections, such as VPNs or specialized network links, between on-premises and cloud settings. Encrypt data in transit to prevent interception or tampering.
- Create uniform security policies: Enforce consistent security policies for both on-premises and cloud components. Verify consistent protection to lower the likelihood of weaknesses or gaps.
- Deploy data management: Implement measures such as encryption, access controls, and data classification to ensure that data is transferred seamlessly and securely between environments.
Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud is a type of cloud environment that uses services from several public providers or combines public and private clouds to provide flexibility to its users. Running programs across several cloud platforms requires consistent security measures. Businesses benefit from its scalability, but they must handle challenges with data protection across several cloud infrastructures.
Here are some standard security practices for a multi-cloud environment:
- Centralize your policy configuration: Consolidate policy configuration into a single console to maintain consistency in security policies across numerous cloud platforms. Simplify access controls, firewall rules, and compliance settings administration.
- Integrate DevSecOps practices: Incorporate security practices throughout the software development life cycle. Automate security testing, code scanning, and vulnerability assessments as part of the continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD).
- Implement data security using SaaS: Use Security as a Service (SaaS) solutions to protect data on several cloud platforms. Access encryption, data loss prevention (DLP), and firewalls through a unified interface for consistent protection and accessibility.
Multi-Tenant Cloud
Multi-tenancy in cloud computing enables many entities to share resources while keeping data separate. Because multiple entities use the same infrastructure, vulnerabilities or breaches impacting one tenant can potentially affect others. Because of its structure, you need careful adherence to its best practices.
These additional actions can help to improve multi-tenant security:
- Employ virtualization security measures: Use techniques like hypervisor-based segmentation and virtual firewalls to isolate resources and secure multi-tenancy in the virtualized architecture.
- Apply tenant isolation: Apply network segmentation, access controls, and encryption to ensure strong tenant separation and prevent unwanted access to critical data or resources.
- Utilize cloud security solutions: Implement comprehensive security solutions such as cloud-based firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption services to protect sensitive data in the cloud.
Explore the general cloud security best practices and tips to further enhance your cloud environment’s security measures.
4 Common Types of Cloud Security Solutions
Different cloud security solutions like CASB, SASE, CSPM, and CWPP work together to provide a complete and tiered approach to cloud security. Depending on an organization’s individual goals and difficulties, it may use a mix of these solutions to address various areas of cloud security, such as data protection, access control, threat detection, and compliance management.
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB)
CASBs are security technologies that lie between an organization’s on-premises infrastructure and the infrastructure of the cloud provider. They provide you visibility and control over the data transmitted to and from cloud apps. CASBs aid in the enforcement of security policies, the monitoring of user behavior, and the prevention of data breaches, addressing issues about shadow IT, illegal access, and data leaking.
These are our top picks for CASB solutions:
- Broadcom: Symantec CloudSOC CASB delivers comprehensive insight into cloud application security, which is critical for meeting regulatory requirements. It provides sophisticated content inspection and context analysis to monitor the movement of sensitive data. For pricing and demo information, contact Broadcom’s sales team.
- Netskope: A leading CASB provider, Netskope provides ongoing security assessments and compliance, as well as a comprehensive SASE solution. Notable features include Cloud Exchange for smooth tech interfaces and virus protection for email and storage services. Netskope’s sales team can provide price information through a demo or executive briefing.
- Proofpoint: Proofpoint’s CASB is focused on user and DLP protection, exposing shadow IT, and managing third-party SaaS usage. It provides numerous security integrations and identifies high-risk personnel, making it ideal for firms that prioritize employee safety. For pricing and a free trial, contact Proofpoint’s sales team.
Explore our comprehensive guide on the top CASB solutions, detailing key features, pros, cons, and more.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
SASE is a security architecture that integrates network security functions with WAN capabilities to serve enterprises’ dynamic, secure access requirements. Software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) is combined with security services such as secure web gateways, firewall-as-a-service, and zero-trust network access. SASE is especially important in the context of remote work and the growing usage of cloud services. Some of our top picks are:
- Cloudflare: Cloudflare One distinguishes itself as the best entry-level SASE solution by providing transparent pricing, simple deployment, and robust IoT compatibility. With a free tier for up to 50 users, it’s ideal for small organizations. The Cloudflare One Pay-as-you-go Tier costs $7 per user each month.
- Cato: Cato SASE Cloud offers a streamlined deployment process with only two hardware configurations and automated connection setup. Its full-service offerings include end-to-end SASE administration, threat detection, and ISP management, making it the leading provider of comprehensive SASE solutions. For price information, contact Cato Sales.
- VMware: VMware’s SASE product thrives in a wide range of technical scenarios with its extensive virtual network function (VNF) compatibility. Its functionalities enable seamless integration with a wide range of third-party security technologies. To accommodate 12 bandwidth levels, VMware offers 26 Edge hardware options ranging from $550 to $10,000.
Read our extensive reviews of the top SASE products and their best offerings to find the right solution for your business.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM solutions are designed to guarantee that a company’s cloud infrastructure is set in accordance with cloud security best practices and compliance standards. These tools continually monitor cloud setups, detect misconfigurations, and make remedial recommendations. CSPM aids in the prevention of security problems caused by incorrectly configured cloud resources. These are some of our recommended solutions:
- Palo Alto: Palo Alto Networks’ Prisma Cloud is the best overall CNAPP solution, providing top-tier cloud security posture monitoring across many environments. Pricing for complete capabilities across major public clouds varies; for example, the Enterprise Edition costs $18,000 for 100 credits via AWS Marketplace.
- Check Point: Check Point CloudGuard CSPM is a part of the CloudGuard Cloud Native Security Platform. It provides automated solutions that prioritize compliance. It caters to major cloud providers and Kubernetes users. Pricing varies depending on the feature set. Access to CNAPP Compliance & Network Security for one month and 25 assets costs $625 on AWS Marketplace.
- Lacework: Lacework unifies CSPM, vulnerability management, IaC security, and other features for major cloud providers and Kubernetes. It uses smart behavioral analysis to automate risk management and anomaly identification, assisted by machine learning. Lacework costs $1,500 per month, with a usage fee of $0.01 for every item purchased via Google Cloud Marketplace.
Compare other alternatives in our comprehensive guide on the top CSPM tools, covering their key strengths and features.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
CWPP solutions are intended to protect workloads (applications, processes, and services running in the cloud. They provide cloud workloads with capabilities such as threat detection, vulnerability management, and runtime protection. CWPP assists enterprises in protecting their cloud-hosted apps and data against a variety of cyber threats. Here are our chosen CWPP tools:
- AWS GuardDuty: AWS GuardDuty, designed specifically for AWS users, uses machine learning to detect vulnerabilities in AWS services. It continuously monitors accounts and workloads through anomaly detection and network monitoring. Their default level of service coverage costs $1.00+ per gigabyte per month.
- Microsoft Defender: Microsoft Defender for Cloud is suitable for Azure, providing powerful threat detection and adaptive security protections that are targeted to Azure workloads. With native integration, real-time threat information, and adaptive rules, it offers strong protection within the Azure environment. Prices start at $14.60 per server per month.
- Orca Security: Orca Security excels at cloud configuration security by providing comprehensive visibility and continuous monitoring across different platforms. Its agentless design and comprehensive features make it an appropriate choice for effective cloud workload protection. For a customized estimate, contact Orca Security Sales.
Discover more tools, their key features, pricing, and more in our detailed review of the top CWPP solutions available in the market today.
Future Trends in Cloud Security
Cloud security has progressed from an IT-specific concern to a critical consideration for all business leaders in the cloud age. As the cloud security workforce path intersects with future trends, investing in workforce training or collaborating with CSPs become ever more crucial. Confidential computing, incorporating DevSecOps into cloud pipelines, and utilizing LLMs in cloud services are among the emerging trends of cloud security today.
Confidential Computing
One of the emerging trends in cloud security, confidential computing encrypts data as it’s being processed rather than just at rest or in transit. Cloud providers accomplish this by utilizing trusted execution environments (TEEs), which create segregated enclaves in the CPU where sensitive activities can be carried out safely. This solution improves overall cloud security by protecting critical data from potential breaches and illegal access.
Integrating DevSecOps into the Cloud
DevSecOps integration transforms cloud app development by incorporating security measures across the entire development process. Bringing together developers, IT operations, and security teams improve application security while maintaining deployment speed. Integrating DevSecOps into the cloud pipeline includes shift-left security, automated testing, team collaboration, and other measures to smoothly integrate security into the development process.
Reliance to Large Language Models (LLMs)
Advanced natural language processing methods enable the integration of LLMs into cloud services. These models assess user queries and deliver contextually relevant responses, allowing for more natural interactions with cloud interfaces. Cloud solutions using LLMs provide intelligent support for troubleshooting, optimization, and configuration management, improving user experience and optimizing cloud operations with minimal human participation.
Bottom Line: Implement Enhanced Cloud Security Measures Now
Cloud security is a critical practice for securing sensitive data, maintaining regulatory compliance, and defending against a wide range of cyber attacks. Businesses today are increasingly adopting the cloud environment, so strong security measures are required to limit risks, ensure the integrity and confidentiality of organizational assets. Reinforce your strong cloud security posture with best practices and reliable cloud solutions.
Find the most suitable cloud provider by exploring our comprehensive guide on the best cloud security companies and vendors.
Kaye Timonera contributed to this article.
The post What Is Cloud Security? Definition, Best Practices & Types appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post What Is Cloud Security Management? Types & Strategies appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>How Cloud Security Management Works
Led by the cloud security manager and the IT team, cloud security management starts with the assessment and identification of security requirements and tools. Next, the IT team sets up access controls and data encryption methods, followed by network security configuration and cloud activities monitoring. Then, the IT team develops and applies incident response plans, while the manager maintains compliance.
An effective cloud security management fully works through a combination of the technical controls, rules, and procedures that specify how to use and safeguard your cloud resources. This is a shared responsibility between the user, the security team, and the provider. Cloud security management covers the following key processes meant to protect your organization’s cloud environment:
- Risk assessment: Begin by identifying the cloud services you use and assessing security and potential risks.
- Access control: Set user rights to restrict access to sensitive information and update them as needed.
- Data encryption: Ensure that your data is safe in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Network security: Manage and protect connections to allow genuine traffic while restricting suspicious activity.
- Security monitoring: Constantly monitor cloud activity to detect and respond to any threats in real time.
- Incident response: Create and enforce plans to respond rapidly to any security breaches, limit any damage, and restore normal operations.
- Compliance: Verify that you satisfy every regulatory and legal standard for cloud security.
Your cloud security team must evaluate and update native security settings within each application. Manage all users and devices to make sure that only authorized devices and individuals have access to data and services. Then, get an overview of cloud activity through reporting and monitoring for improved risk management and operational control.
Cloud security management covers three types, each focusing on securing different cloud functions. To maximize the benefits of cloud security management and counteract its challenges, apply effective strategies and tailored cloud security tools.
3 Types of Cloud Security Management
There are three categories of cloud security management: cloud database security, cloud migration security, and cloud database management. Cloud database security focuses on protecting data stored in cloud databases. Cloud migration security protects data and applications as they transfer to cloud environments. Finally, cloud database administration entails supervising the storage, organization, and accessibility of data in cloud databases for maximized performance.
Cloud Database Security
Cloud database security protects data from breaches, DDoS assaults, viruses, and unauthorized access in cloud environments. To protect data, it uses encryption, access controls, monitoring, and audits. Access controls restrict user access, encryption protects confidentiality, and monitoring detects unusual activities. To improve security and resilience, additional approaches include data masking, patch management, disaster recovery, and backup.
Cloud database security mainly focuses on these cloud security functions:
- Encryption: Maintains confidentiality and protection of data stored in cloud databases.
- Access control: Regulates cloud data access to minimize unauthorized users’ entry.
- Audits and monitoring: Detects suspicious database activities for timely intervention.
To properly apply cloud database security best practices, learn the shared responsibility model. Understand the scope of you and your provider’s security responsibilities. Then, ask your cloud provider about their security procedures and practices to check that they meet your needs. Write policies outlining cloud service usage and security procedures, and use automated enforcement methods when possible.
Cloud Migration Security
Cloud migration security is the process of moving traditional programs, IT resources, and digital assets to the cloud, either completely or partially. This can include transitioning from one cloud to another or implementing a multi-cloud architecture. Cloud migration security protects data and applications during the move, protecting their confidentiality and integrity.
It targets the secure handling of these cloud operations:
- Data migration: Develops solid outlines of the migration process, timelines, roles, and responsibilities.
- Data transfer: Checks and uses secure protocols to validate that all data in transit and at rest are encrypted.
- Identity and access management (IAM): Establishes policies to control data access and authenticate user identities.
As a best practice, consider applying additional security measures to prevent data corruption and unwanted access. Configure the control plane to manage baselines and maintain constant synchronization with the data plane. You may also take advantage of the cloud’s pay-as-you-go model to reduce costs as you migrate your on-premises data to the cloud.
Cloud Data Management
Cloud data management entails storing company data in remote data centers maintained by cloud providers such as AWS or Microsoft Azure. This technique provides automated backups, professional support, and remote access from anywhere. Benefits include automated backups, expert assistance, and remote access, all of which streamline data administration and improve corporate accessibility and reliability.
The goal of cloud data management focuses on the following aspects:
- Data backup and recovery: Assists in creating a copy of your data and recovery plans in case of data corruption or loss.
- Data integration: Manages the synchronization of data across different cloud and on-premises systems.
- Data governance: Supports the enforcement of data governance policies and cloud-specific regulatory requirements.
To ensure effective cloud data management, develop a plan first. Include defining the scope and deployment model, establishing access restrictions, and comparing different approaches to data processing. Monitor data by validating, cleansing, and ensuring its quality for accurate analytics and decision-making. Make it a habit to save copies of your data on a regular basis to prevent loss, ensure availability, and verify automated copies of data.
Benefits of Cloud Security Management
Cloud security management includes more effective monitoring, user and device management, improved data protection, easier policy enforcement, and dynamic scalability. These enable you to effectively monitor your infrastructure, securely manage people, protect data thoroughly, strictly enforce policies, and seamlessly change security measures as your organization evolves.
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities
With extensive monitoring capabilities, your IT staff may remotely access a dashboard to assess the security of your entire cloud infrastructure. This lets them monitor potential threats and weaknesses in real time from any location. Increased accessibility allows for rapid responses to security incidents, improving overall security posture and reducing the chance of data breaches or system compromises.
Convenient User & Device Management
The proper application of cloud security management safely manages devices and users from any location. This resolves concerns about malware on user-owned devices in remote work environments. By efficiently managing access and security policies, you reduce the risks associated with illegal access or compromised devices, delivering a strong and secure cloud environment.
Enhanced Data Protection
Increased data protection secures your data from threats by installing strong measures like access restriction and threat detection. These safeguards guarantee that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data while actively monitoring for potential breaches. Cloud security management reduces the risk of data breaches while ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of your organization’s digital assets.
Improved Enforcement of Internal & External Security Policies
By improving the implementation of internal and external security policies and standards, you also improve your capacity to detect and resolve policy infractions quickly. This proactive approach to cloud security management protects your organization by identifying and fixing security vulnerabilities before they become more serious. With this, you maintain strong security standards and ensure compliance with industry requirements.
Dynamic Scalability & Flexibility
Cloud security management allows you to readily modify your security measures as your business develops. This lets you respond to emerging threats and changing requirements without the need for major infrastructure changes. By smoothly expanding your security processes, you ensure that your organization stays resilient and adaptable in dealing with threats, and promotes ongoing growth and innovation.
Challenges of Cloud Security Management
Complex data tracking, multi-tenant security concerns, access restriction complications, and potential asset misconfigurations all pose challenges that cloud security management must address. To effectively protect data integrity and prevent threats, these challenges need regular monitoring, strong security measures, and proactive management.
Complex Data Tracking
An intricate data tracking presents issues since third-party providers host cloud services, complicating monitoring and mandating audit trail log retrieval. This has an influence on data governance and compliance initiatives, increasing the risk of data breaches and regulatory noncompliance. To counteract this, develop clear data tracking processes, check audit logs on a regular basis, and maintain vendor engagement in delivering critical data usage insights.
Security Risks in Multi-Tenant Environments
Multi-tenant setups pose security threats from potential malicious attacks, endangering data integrity and system stability. Collateral damage is an issue since an attack on one tenant can affect others. To avoid wide consequences, install strong security measures such as encryption and access controls, as well as routinely monitor for unusual activity.
Access Restriction Complexity
Access restriction complexity issues emerge when managing access between on-premises and cloud environments, requiring seamless transitions and BYOD policy compliance. This intricacy might result in unwanted access and security breaches. To prevent this, develop clear access protocols, strictly enforce BYOD policies, and employ identity and access management solutions to achieve unified access control across many environments.
Potential for Asset Misconfiguration
Without paying close attention to management and swift remediation by dedicated teams, asset misconfigurations might lead to exploitable vulnerabilities. To ensure network security, employ strict configuration management processes, conduct frequent audits, and resolve any flaws as soon as possible.
5 Strategies for Cloud Security Management
With cloud security management strategies like performing audits, setting protection, managing and monitoring users, and using cloud security tools, you can maximize the benefits of cloud technology while minimizing risks. Implementing these procedures will allow you to protect sensitive data, ensure compliance, and keep your operations running smoothly. Consider some of these basic strategies for managing cloud security effectively.
Perform Security Audits
Security audits protect the integrity of your cloud infrastructure. It entails regularly scanning your cloud-based products and services for potential security flaws. By following these actions on a regular basis, you can discover and remedy any security vulnerabilities:
- Define objectives: Determine the audit scope and objectives in accordance with regulatory standards and business goals.
- Assess controls: Examine your organization’s current security controls and configurations for cloud assets.
- Scan for vulnerabilities: Use scanning software to find potential security flaws and vulnerabilities.
- Examine logs: Analyze access records for illegal access attempts and identify questionable activities.
- Monitor changes and fixes: Create a remediation strategy, implement security measures, and constantly monitor for changes and vulnerabilities.
Here’s an overview of performing security audits using SolarWinds’ auditing tool:
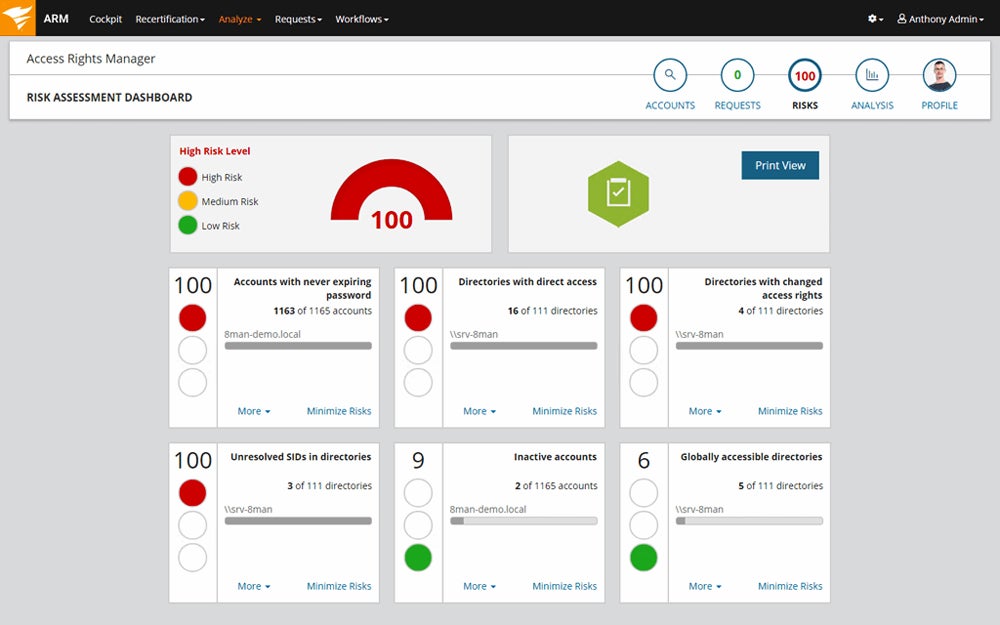
Set Proper Levels of Protection
Implementing appropriate levels of protection entails giving your IT security staff complete control over the security settings for cloud-based applications and configuring them to the highest security level. This provides protection against cyber attacks, unlawful access, and data breaches. Deploy these security measures to protect sensitive data, ensure regulatory compliance, and strengthen your overall cloud cybersecurity resilience:
- Define security policies: Create comprehensive security rules that specify the required security levels and requirements for cloud-based applications.
- Assign access controls: Grant suitable access permissions to users and roles while limiting access to necessary resources according to the concept of least privilege.
- Implement encryption: Secure sensitive data in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access or interception.
- Implement threat detection tools: Use threat detection and monitoring technologies to discover and respond to potential security risks in real time.
- Conduct regular security check-ups: Evaluate the efficacy of security measures, discover vulnerabilities, and ensure adherence to security rules and regulations.
Use tools to easily configure your security settings. Take a look at this example from CrowdStrike:
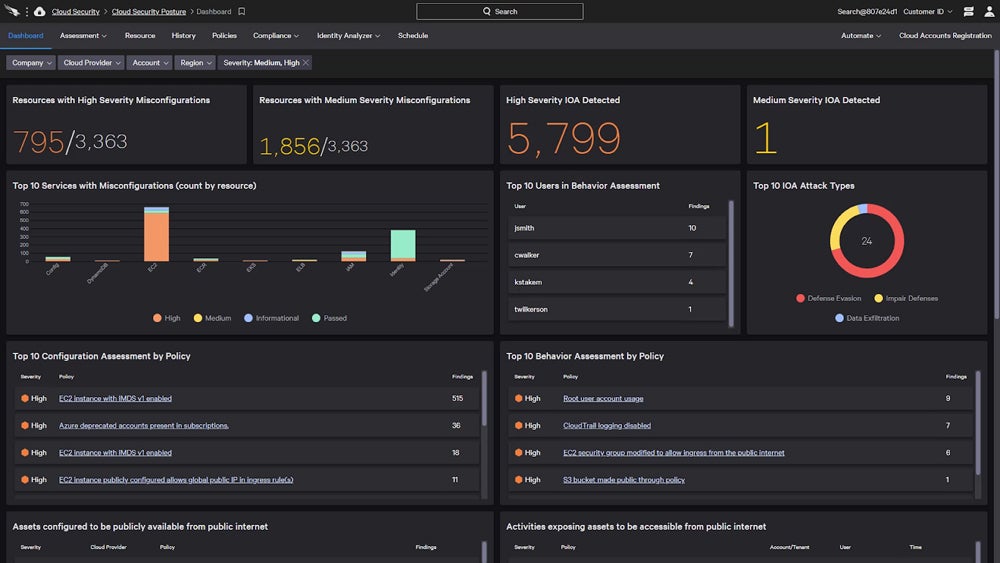
Manage Users & Devices
Ensure only authorized devices access your network and data, setting user-level controls to limit data access appropriately. By aligning access permissions with role requirements, you optimize operational efficiency while safeguarding data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance in your cloud environment. Here are a few ways to manage users and end-user devices:
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC): Assign access permissions based on users’ roles and responsibilities to ensure they only access data necessary for their tasks.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA): Require additional authentication factors, such as passwords and biometrics, to enhance security and prevent unauthorized user access.
- Utilize mobile device management (MDM) solutions: Employ MDM solutions to manage and secure mobile devices accessing cloud resources. Enforce security policies and encryption.
- Regularly update access controls: Review and update access controls periodically to reflect changes in user roles. This ensures continued alignment with security requirements.
- Track device activities using tools: Use monitoring tools to track user and device activity in real-time. Detect and respond to any suspicious behavior or security incidents promptly.
Here’s what user and device management looks like using a monitoring tool from ManageEngine:
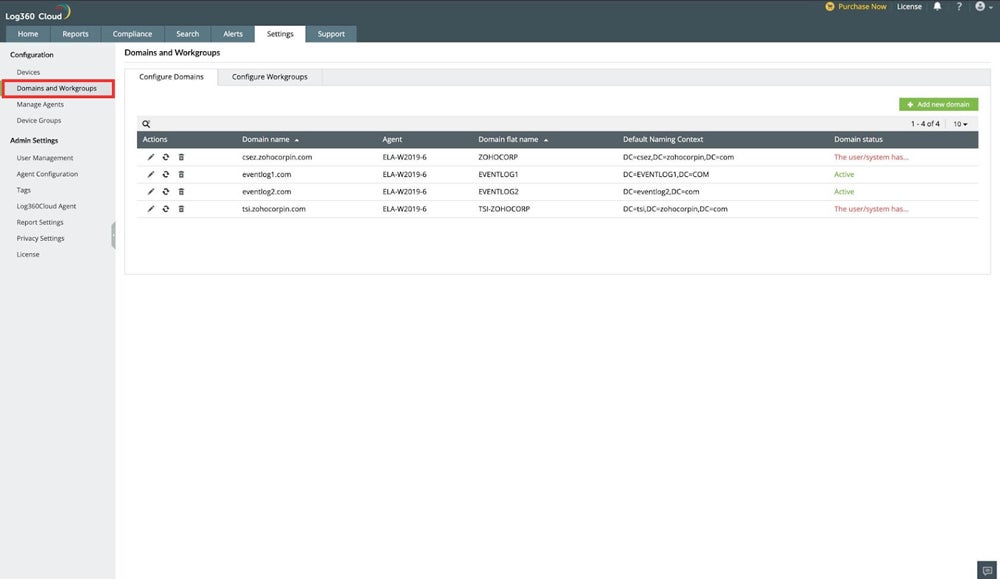
Monitor User Activities
This strategy involves going through reports to track user interactions in your cloud environment, which can provide insights into security concerns and compliance violations. By getting visibility into user activity, companies may detect and mitigate possible security threats in real time, improving overall security posture. Follow these steps to perform immediate responses to security incidents while assuring data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance:
- Define monitoring objectives: Determine the precise user actions and behaviors to monitor in accordance with security and compliance standards.
- Select monitoring tools: Choose tools and software that can track user actions and generate detailed results.
- Configure monitoring parameters: Set monitoring parameters and thresholds to record relevant user logs and detect odd patterns that may indicate a security threat.
- Analyze monitored data: Review and analyze monitoring reports on a regular basis to detect patterns, abnormalities, and potential security threats in user activity.
- Take preventive security measures: Address identified security concerns, such as modifying access controls or initiating incident response procedures when necessary.
This is the typical activity monitoring scenario using Microsoft Azure:
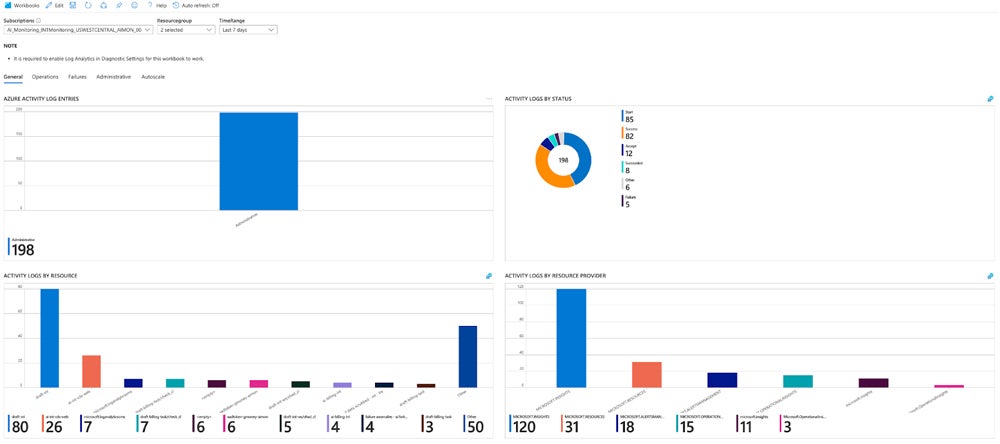
Use Cloud Security Tools
Use cloud security solutions to strengthen your cloud security management strategy. These tools include threat detection and encryption solutions, as well as identity and access management systems. Integrating these solutions into your cloud environment allows you to improve threat detection, impose access rules, and protect data confidentiality. Assess the cloud security solutions by employing these steps:
- Assess security needs: Evaluate your organization’s security needs and identify areas where cloud security products can help address weaknesses and threats.
- Research available options: Look for cloud security solutions that meet your security requirements, taking into account features, compatibility, and reputation.
- Implement selected tools: Deploy and configure your cloud security products in accordance with manufacturer specifications and best practices.
- Integrate with current systems: Combine new cloud security technologies with existing security infrastructure and processes to ensure smooth operation.
- Monitor and optimize tools: Continuously monitor the performance and efficacy of cloud security tools, modifying configurations and processes as needed.
Most cloud security tools commonly open to their dashboard view, like this one from Prisma Cloud:
Check out our guide on the fundamentals of cloud security to understand and develop more robust cloud security management strategies.
3 Top Tools for Cloud Security Management
Choosing the right cloud security management provider is essential for complete protection, cost effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. When selecting a cloud service provider, carefully review their security policies and processes to verify that your sensitive data is adequately protected. For easier management, use common cloud security tools like CWPP, CSPM, or CNAPP. Check out our recommended provider for each solution below.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
CWPP defends against a variety of threats, including malware and data breaches. It provides unified visibility and administration of physical computers, virtual machines (VMs), containers, and serverless applications, hence improving cloud security. CWPP adoption improves security posture by limiting risks and reducing the impact of security incidents.
Our recommended solution: Illumio Core excels in advanced micro-segmentation by providing granular cloud security control and real-time threat detection. It offers significant workload visibility and adapts to fluctuating workloads, making it suitable for organizations looking to improve cloud workload safety. Illumio Core starts at $7,080 per year for 50 protected workloads and 25 ports.
Explore other alternative cloud workload protection platforms and compare each solution’s advantages, key features, pricing, and more.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM tools monitor, evaluate, and resolve security and compliance issues in cloud systems in real time. These tools, along with CWPP and CIEM, are essential components of comprehensive CNAPPs. The ability to quickly detect and correct cloud misconfigurations makes standalone CSPM solutions useful tools for enterprises of all sizes.
Our recommended solution: Cyscale specializes in cloud security mapping, with support for AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and Alibaba setups. Cyscale’s mapping features let firms visualize and manage security and compliance risks more efficiently. The Pro plan costs $10,000 for a 12-month subscription that includes up to 1,000 assets via Azure Marketplace.
Read our comprehensive review on the different cloud security posture management tools to assess their features, benefits, and cost.
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP)
CNAPP is an all-in-one solution for protecting cloud applications and workloads from various security threats. Combining various cloud security functionalities such as CWPP, CSPM, and CIEM, CNAPP ensures protection across several levels. This includes workloads, applications, identity management, and development environments, handling a wide range of threats and vulnerabilities in cloud-native environments.
Our recommended solution: Prisma Cloud by Palo Alto Networks offers full cloud-native application security features. Its CNAPP solution provides full-stack protection for cloud settings and encourages collaboration between security and DevOps teams. Prisma Cloud CNAPP is suited for businesses requiring proactive cloud-native application security. Prices begin at $9,000 per year for 100 Business Edition credits.
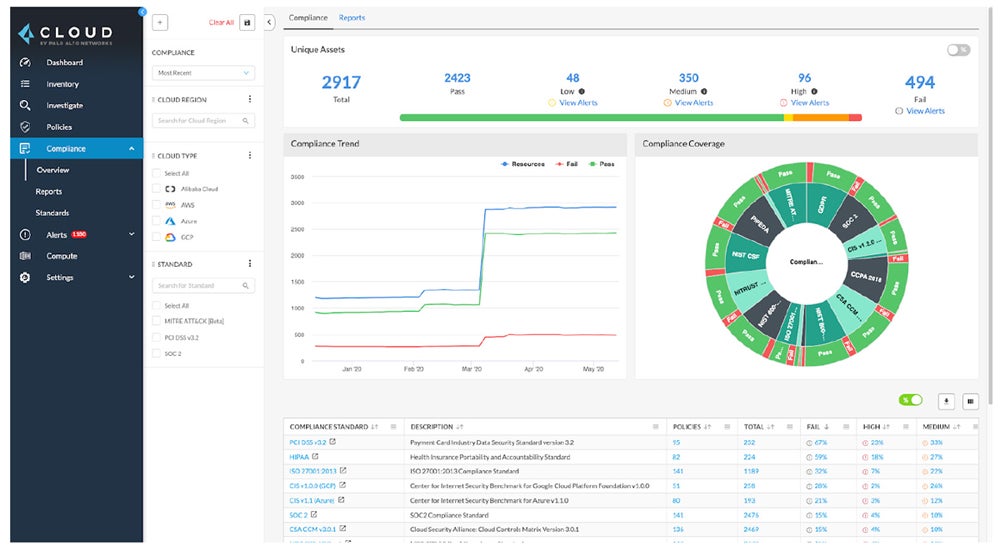
Compare the top cloud native application protection platforms available in the market by checking out our full buyer’s guide covering their distinct features, cost, pros, and cons.
Bottom Line: Enhance Your Strategies with Cloud Security Management
In-house cloud security management guided by a dedicated manager gives firms complete control over their cloud security strategies. You may protect sensitive data and assure continuous cloud operations by leveraging the appropriate knowledge, techniques, and technologies. Combine these strategies with the general cloud security best practices to create a safer, more secure cloud ecosystem.
Take a look at our guide for the cloud security best practices and tips to further improve your cloud security management strategies.
The post What Is Cloud Security Management? Types & Strategies appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>The post Top Cloud Security Issues: Threats, Risks, Challenges & Solutions appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>Featured Partners: Cloud Backup & Storage Software
4 Top Cloud Security Threats
Cloud security threats are any possible harm that can be done to your cloud systems. When you actively defend cloud assets, you’re protecting them from unintentional or intentional threats that use weaknesses to destroy or steal data. The focus of threat management is mitigating these dangers in order to protect cloud assets effectively. Some of the biggest threats in cloud security are DDoS attacks, cloud storage buckets malware, insider threats, and APT attacks.
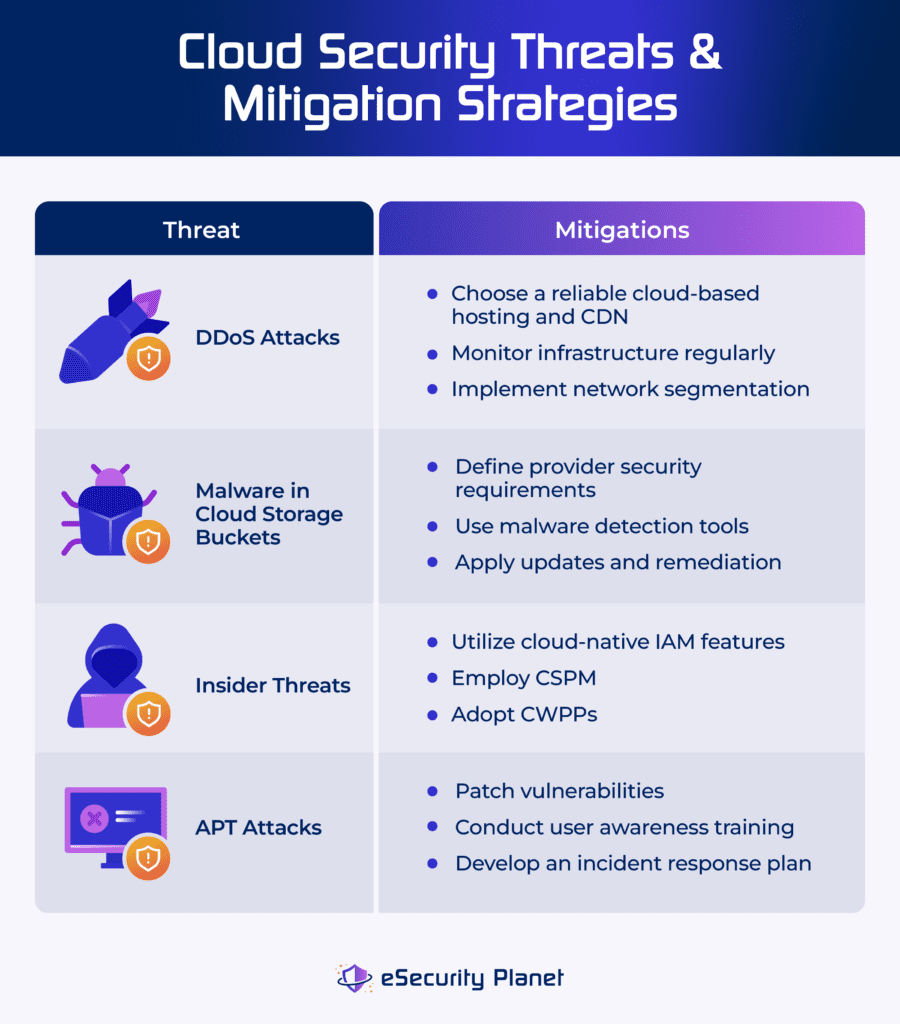
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks flood cloud services with excessive traffic, rendering them inaccessible to users. They overwhelm networks or applications with more connections than they can handle, resulting in major disruptions and financial losses. DDoS attacks use several infected devices across multiple networks to establish a botnet. This botnet is a collection of malware-infected machines that coordinate the attack.
Apply the following strategies to mitigate DDoS attacks:
- Select a good cloud-based hosting: Choose a provider with large bandwidth and content delivery networks (CDN). Hide the origin web server’s IP and restrict access with a firewall.
- Monitor infrastructure continuously: Check system capacity, traffic, and essential infrastructure, such as firewalls, on a regular basis to discover irregularities.
- Apply network segmentation: Separate internal and external networks and isolate essential systems to mitigate the impact of assaults.
To help you decide a solution that reduces the impact of DDoS attacks in your organization, explore our buyer’s guide on the best DDoS protection service providers.
Malware in Cloud Storage Buckets
Malware threatens cloud storage buckets due to misconfigurations, infected data, and phishing. It spreads via insecure settings, which enable malicious uploads, unpatched software, susceptible apps, and supply chain assaults involving third-party dependencies kept in these buckets.
Here’s how you can reduce the impact of cloud storage buckets malware:
- Implement malware detection tools: Employ heuristic scanning and signature-based detection for known and unknown malware.
- Set provider security requirements: Only allow access to trusted third-party providers who have a demonstrated track record of security and proper certifications.
- Apply updates and prioritize remediation: Keep your software and dependencies up to date. Prioritize remediation actions according to the sensitivity of the data.
Read our guide on the most secure cloud storage solutions, and discover each solution’s key features, pricing, and benefits.
Insider Threats
Insider threats in the cloud occur when people with authorized access to a company’s cloud services, such as employees, contractors, or partners, abuse their privileges to actively harm the business. This can happen through data sharing or intentional sabotage, such as deleting data or installing malicious software. The cloud’s remote access complicates detection and protection, increasing the potential attack surface.
Lower the risk of insider threats by employing these methods:
- Utilize cloud-native IAM features: Use enhanced identity and access management (IAM) to enforce least privilege access and prevent insider threat vectors.
- Implement CSPM: Employ cloud security posture management (CSPM) systems to recognize threats, misconfigurations, and unwanted access attempts.
- Adopt CWPPs: Apply workload protection platforms (CWPPs) to detect and prevent suspicious activity across all cloud workloads.
Explore our list of the best cloud security companies and vendors to compare the solutions that could help you mitigate insider threats.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) Attacks
An advanced persistent threat (APT) is an extended and focused cyber attack in which an intruder gains access to a network while remaining unnoticed. APTs seek to steal critical information and retain long-term access. They’re painstakingly planned and frequently carried out by well-funded groups, who use methods such as spear phishing, zero-day exploits, watering hole attacks, and credential theft to breach high-profile targets.
Try these to prevent APT attacks:
- Patch vulnerabilities immediately: Keep the software up to date by applying patches as soon as possible and executing regular vulnerability scans to identify and fix vulnerabilities before they’re exploited.
- Conduct user awareness training: Incorporate a focused training program into onboarding and workflow process so employees can learn about social engineering strategies, phishing risks, and cloud security best practices.
- Monitor and develop an incident response plan: Employ continuous monitoring to spot suspicious behaviors early on and create a strong incident response strategy to resolve security breaches quickly.
4 Top Cloud Security Risks
A cloud security risk is a combination of the possibility of a threat arising and the system’s vulnerability. Cloud risks include insecure APIs, misconfigurations, cloud concentration, and unmanaged attack surface. Though completely eliminating risks is almost impossible, they can be controlled to remain within a company’s tolerance level through assessments, regulations, and developing plans for the consequences of a threat.
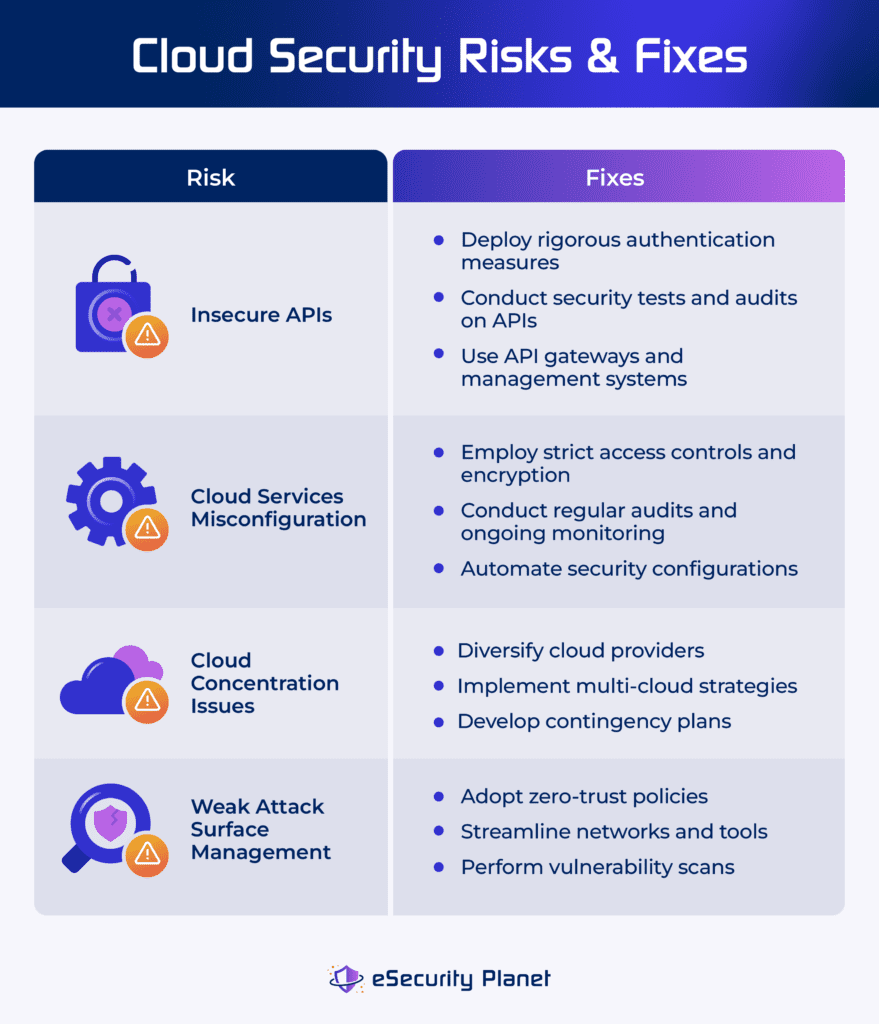
Insecure APIs
Insecure application programming interface (API) in cloud services allows unauthorized access and data breaches. APIs offer seamless integration between cloud services, but if not properly secured, they become points of access for attackers. API security risks may cause weak authentication, input validation, encryption, permissions, error handling, and rate limit issues.
Address insecure APIs through these practices:
- Implement comprehensive security measures: Deploy rigorous authentication, authorization, input validation, and API security testing and monitoring on a continual basis.
- Perform regular security tests and audits on APIs: Quickly detect and address problems using techniques like penetration testing, code reviews, and vulnerability assessments.
- Use API gateways and management systems: Reduce the risk of vulnerabilities in individual APIs by centralizing security features such as authentication, rate limitation, and encryption.
Explore our guide on how to strengthen your API security with the top API security solutions and tools, including their features, advantages, and more.
Cloud Services Misconfiguration
Misconfiguration of cloud services happens when cloud configurations are incorrect, resulting in security breaches and unauthorized access to critical data. It’s a common source of data breaches, which are frequently caused by configuration problems. This exposes sensitive information to the public internet, resulting in reputational damage and financial loss.
To lessen your cloud services misconfiguration risks, implement the following:
- Apply strict access controls and encryption: Employ stringent access control and encryption mechanisms to protect sensitive data from unwanted access.
- Conduct regular audits and ongoing monitoring: Discover and correct misconfigurations using auditing and monitoring solutions.
- Automate security setups: Use automation tools to provide consistent and safe setups across cloud services and lower the risk of human error and misconfiguration.
Delve into our complete guide on cloud configuration management to better understand how it can address misconfiguration in the cloud.
Cloud Concentration Risks
Cloud concentration risk occurs when a company relies excessively on a few key cloud suppliers. This dependence raises the possible disruptions caused by a single provider’s failure. With few options, enterprises confront difficulties in reducing this risk while reaping cloud benefits. Potential effects include widespread event impact, high vendor dependence, which limits technological options, and regulatory compliance failures due to varying restrictions.
These strategies can address your cloud concentration risks:
- Diversify cloud providers: Reduce dependency by distributing risk among several cloud providers and minimize the impact of any single provider’s failure.
- Implement multi-cloud strategies: Distribute workloads and services over multiple cloud platforms to ensure redundancy and resilience to disruptions.
- Develop contingency plans: Create carefully planned continuity plans to quickly address large cloud service outages.
Weak Attack Surface Management
Weak attack surface management occurs when vulnerabilities in a system aren’t detected and mitigated properly. It results from a failure to identify, test, and monitor potential access points, such as devices, users, and software flaws. Impacts include increased risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks as a result of undetected vulnerabilities, which endanger system integrity, privacy, and the overall security posture.
Resolve weak attack surface management through these tips:
- Adopt zero-trust policies: Limit illegal access by adopting zero-trust security, which ensures that only authorized users can access networks. This lowers entry sites, strengthening the infrastructure against cyber assaults.
- Streamline networks and tools: Remove unnecessary software, program, and equipment, minimize errors, and reduce the attack surface to prevent unauthorized access to your organization’s data.
- Conduct vulnerability scans: Run regular network scans to detect and repair any vulnerabilities, ensuring visibility of the attack surface and protecting both cloud and on-premises networks from exploitation.
Take a look at our in-depth review on the best attack surface management software, their benefits, key features, and pricing.
4 Top Cloud Security Challenges
Cloud security challenges refer to the difficulties that a business faces when protecting its cloud systems against attackers and intrusions. These challenges develop as a result of weaknesses and complexities in the cloud architecture, thus putting your assets at risk. Managing cloud challenges focuses on discovering and fixing issues, particularly during system migration, to ensure robust security measures are in place.
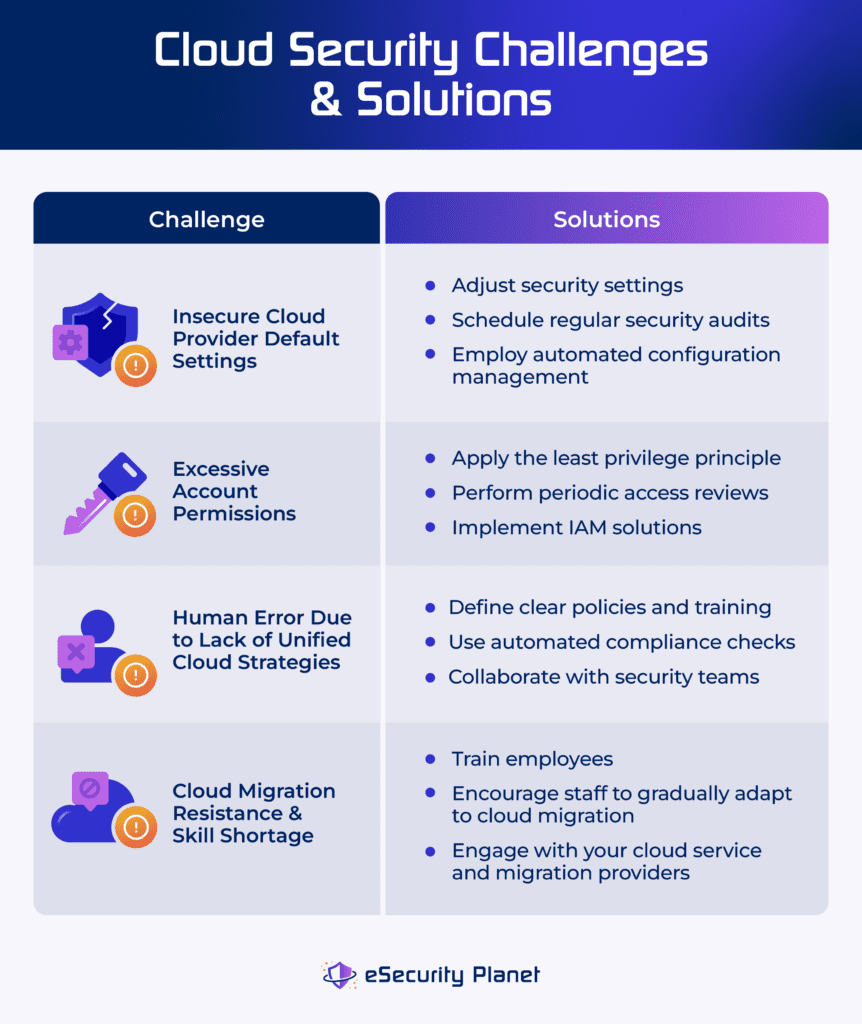
Insecure Cloud Provider Default Settings
Insecure cloud provider default settings occur when an organization’s security rules fail to satisfy its requirements. Crowdstrike’s 2023 cloud risk report discovered that 36% of reported misconfigurations are due to insecure default settings. It may result in public snapshots, open databases, and neglected cloud infrastructure, exposing sensitive data to malicious actors and risking data theft, destruction, or tampering.
Here are the ways to fix insecure cloud provider settings:
- Customize security settings: Adjust the cloud provider’s default settings to meet the organization’s security needs and ensure effective protection against potential vulnerabilities and illegal access.
- Conduct regular security audits: Schedule consistent audits to identify and fix unsafe default settings. Make sure configurations remain in line with security best practices and company rules.
- Employ automated configuration management: Use automated technologies to manage and enforce security configurations. Ensure that security settings are consistent across cloud environments.
Excessive Account Permissions
Excessive account permissions occur when organizations allow user accounts more rights than necessary, thus increasing the risk of security breaches. Attackers who use these privileges can cause significant damage, including data exfiltration, destruction, code modification, lateral movement, persistence, and privilege escalation. This increases the likelihood of security events and jeopardizes system integrity and confidentiality.
Consider these methods to address excessive account permissions issues:
- Implement the least privilege principle: Restrict user accounts to only the permissions required for their duties and roles.
- Conduct regular access reviews: Perform periodic reviews of user permissions to detect and eliminate unnecessary rights.
- Use identity and access management solutions: Implement IAM solutions to consolidate and automate user access management and enforce granular permissions.
See which identity and access management solution offers the most ideal features and strengths for your organization.
Human Error Due to Lack of Unified Cloud Strategies
The lack of unified cloud strategy and human error are interconnected cloud challenges. Human error, such as misconfigurations or inability to adhere to security regulations, is frequently the result of a lack of clear instructions and unified cloud resource management techniques. A fragmented approach to cloud management increases the possibility of human error, as staff may unintentionally miss security measures in the absence of uniform advice and control.
Reduce human error due to lack of unified cloud strategies by performing these practices:
- Provide clear policies and training: Define thorough security policies and provide regular training to staff on cloud security best practices. Lower the chance of human error by monitoring the execution of your cloud policies.
- Implement automated compliance checks: Use automated tools to constantly monitor cloud environments for compliance with security standards. Reducing the impact of human error by adhering to unified tactics.
- Promote cross-functional collaboration: Encourage collaboration among IT, security, and DevOps teams to create unified cloud strategies that prioritize both speed and security. Align goals and lower the chance of fragmented approaches.
Cloud Migration Resistance & Skill Shortage
Resistance to cloud migration is frequently motivated by concerns about unfamiliarity with new technology. Skills gap relates to a scarcity of competent individuals with knowledge in cloud migration. The skills shortage worsens resistance by limiting access to critical cloud skills and impedes the successful adoption and implementation of cloud solutions. This impacts the timeframe and quality of cloud migration, as well as organizational agility and competitiveness.
Apply these approaches to lessen cloud migration resistance and skills shortage in your organization:
- Invest in employee training: Educate your current IT personnel in cloud migration strategies and technology. Provide constant training to ensure that employees are up to date on the newest developments in cloud computing.
- Cultivate internal talent: Allow staff to gradually acquire cloud migration capabilities. Encourage cross-functional collaboration and knowledge sharing to increase departmental expertise.
- Engage in strategic vendor partnerships: Work with cloud service providers and migration suppliers to have access to external knowledge and resources. Utilize vendor support for training, consultation, and guidance throughout the migration process.
How to Build a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
A strong cloud security strategy includes complete measures to address threats, risks, and challenges thoroughly. A solid strategy relies on comprehensive enterprise resources planning, assessment of risks, threat response, and container security methods. Finally, it should address cultural and technical challenges by deploying solutions and training programs that raise security awareness and streamline security operations.
Develop a Comprehensive Enterprise Cloud Strategy Resources
Before shifting to the cloud, develop a comprehensive enterprise cloud strategy and resources to mitigate hazards associated with unauthorized or unreported public cloud use. This strategy offers a secure and regulated transition that aligns with company goals, reducing the risks associated with unapproved cloud practices. Here’s how to start:
- Assess your company’s current cloud security state: Evaluate current cloud usage. Detect any unauthorized or unrecognized deployments, and assess associated risks.
- Define strategic objectives: Set explicit goals and objectives for cloud adoption that are consistent with company priorities and regulatory constraints.
- Develop a management framework: Create policies and procedures to regulate cloud usage, such as provisioning, access control, and compliance.
Implement a Risk Treatment Model
Apply a risk treatment model that includes agility, availability, security, supplier, and compliance domains to assess cloud risks transparently. This model facilitates informed decision-making by thoroughly examining risks and establishing clear security expectations. Addressing vulnerabilities across these areas allows firms to successfully manage cloud risks while also ensuring alignment with overall security objectives. Take the following steps:
- Define risk domains: Tailor each domain to represent specific security concerns and goals for the organization’s cloud environment.
- Assess cloud risks: Use risk assessment tools and procedures to measure and prioritize risks based on their severity and potential consequences.
- Develop mitigation strategies: Implement preventive measures to mitigate high-priority risks, such as improving security processes, creating access controls, and compliance.
Utilize Cloud Security Tools & Solutions
Implement cloud security solutions like cloud workload protection platform (CWPP), Cloud Security Policy Management (CSPM), and Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM). These solutions continuously monitor, detect, prevent, and manage sophisticated threats, misconfigurations, identity breaches, and malicious behavior in hybrid and multi-cloud settings. Follow the practices below in order:
- Select proper solutions: Research and select cloud security solutions, such as CWPP, CSPM, and CIEM, that satisfy your specific security requirements.
- Deploy chosen solutions: Implement the recommended security solutions across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Update and maintain tools on a regular basis: Keep your tools up to date to efficiently address new security threats and vulnerabilities.
Compare the differences between CSPM vs CWPP vs CIEM vs CNAPP to assess which cloud security solution is the most suitable for your needs.
Implement Container Security Measures
Container security measures need the deployment of robust tools and mechanisms to detect, evaluate, and respond to threats within containerized environments. This provides the continuous security of containers by recognizing and mitigating threats throughout their lifecycle, from creation to decommissioning. It protects against any breaches or vulnerabilities in the cloud architecture. Apply these security measures:
- Deploy container security tools: Monitor and protect against attacks using specialized security solutions developed for containerized settings.
- Implement container scanning: Run regular scans of container images and deployments to discover vulnerabilities and maintain security compliance.
- Utilize runtime protection: Use runtime security measures to monitor container operations in real time and detect suspicious activities.
Enhance your container security with the best container and kubernetes security solutions and tools.
Maintain Employees’ Cloud Security Awareness
Organizations may empower their employees to make educated decisions and actively contribute to the maintenance of a safe cloud environment by keeping them up to date on cloud security best practices, emerging risks, and new technology. This continuing education ensures that personnel remain aware, adaptable, and prepared to properly address new security problems. Employ these strategies in your organization:
- Include training programs in your security strategy: Create and implement training programs that address practices like data protection, access control, encryption, and threat detection.
- Offer regular workshops: Provide monthly training, webinars, and seminars on cloud security. Keep personnel informed of the newest trends, dangers, and technology.
- Encourage certification and skill development: Urge staff to obtain certifications and engage in skill development programs to improve their cloud security knowledge.
For easier implementation of your cybersecurity training programs, read our review on the best cybersecurity training for employees.
Bottom Line: Prevent Cloud Security Issues with a Solid Strategy
To effectively manage cloud issues, you must carefully assess prevention and remediation methods while keeping budget and risk tolerance in mind. This strategic decision-making should be incorporated into your overall cloud security plan to guarantee a balanced approach to cybersecurity. Cloud issues are inevitable, but you can reduce the harmful impact associated with these risks, threats, and challenges by implementing a solid cloud strategy.
To bridge the gaps in cloud security, DevSecOps tools integrate security for all levels of the workflow, from development to deployment processes. Check out our extensive review on the best DevSecOps tools, covering their use cases, key features, and more.
The post Top Cloud Security Issues: Threats, Risks, Challenges & Solutions appeared first on eSecurity Planet.
]]>